PVC VS PVDC: Which Is Right For Your Pharmaceutical?
In this article we are going to closely study about two plastics, with a common mission of protecting your pills but only one does it better. PVC and PVDC are the most commonly used packaging material in the pharmaceutical. It is safe to say that this competition between PVC and PVDC is not really about the plastic but it’s a matter of protection, precision and above all pharmaceutical performance.
As we know very well, only the right packaging can keep a drug safe in its original form. The main attribute of the PVC that makes it use wider is its cost effectiveness with comparatively less barrier properties than the PVDC. These two materials are also very commonly used as a combination of PVC/PVDC to achieve the best of both worlds.
Let’s find out more about the environmental impacts, regulatory trends and performance of these two materials in the following FAQs.
1.What is PVC?

Irregular PVC formation
PVC stands for “Poly Vinyl Chloride”. It is the most widely used thermoplastic polymer. It is best known for its cost effectiveness with versatility. PVC comes in various forms, ranging from flexible to rigid that makes it useful in various manufacturing environments including pharmaceutical, chemical, food industry, construction and many more.
It is a made from polymerization of the vinyl chloride monomer. PVC itself is chemically non-reactive which made it suitable for food and pharmaceutical packaging. It is durable and resistance to weathering and chemical wear off. The strength of PVC can be increased by the use of additives as per the requirement of manufacturing.
2.What is PVDC?
Colorfull PVDC rolls
PVDC stands for “Polyvinylidene Chloride”. Its excellent barrier properties especially against oxygen, water vapor and other gases make it make versatile and a best choice for coating in packaging and lamination. PVDC is a thermoplastic polymer which allows it to be melted and reshaped into for various processing techniques.
The molecular structure of PVDC has degree of crystallinity which is a major aspect of good barrier properties. PVDC offers better chemical resistance against alkalis, acids and impermeable to molds, bacteria and insects, all these characteristics make it suitable for protecting products from dehydration or spoilage. These properties made PVDC a pharmaceutical favorite in packaging and blistering.
3.PVC vs PVDC which is right for your pharmaceutical packaging?
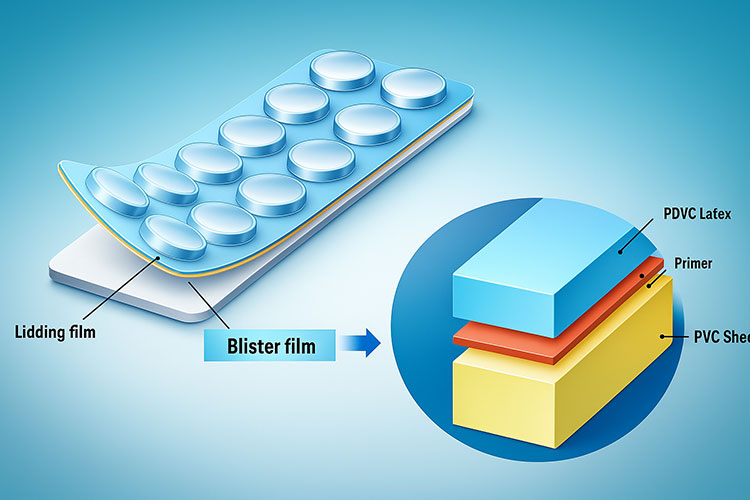
Structure of PVC and PVDC combine in a blister
Let’s imagine your blister pack as a layered cake, the sponge at the bottom is made up of PVC which is sturdy and provides a firm shape to the blister. The PVDC on the other hand is icing on the top! This is a protective layer, thin and essential to keep everything fresh. The packaging industries make them work together to make the packaging beautiful and functional.
But if you have to choose one from both, it can have a major impact on your pharmaceutical packaging. You cannot get a “one size fits all” answer while choosing a pharmaceutical packaging. The better packaging is always related to the type of drug and its requirements. Here is a quick comparison of PVC and PVDC in pharmaceutical packaging:
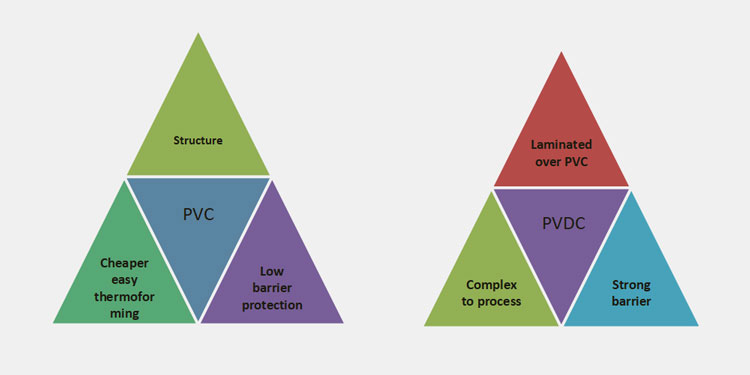
Both PVC and PVDC has their pros and cons when it comes to pharmaceutical packaging. PVC can be a go to option for plastic packaging due to its cost effectiveness and easy to mold properties but it cannot provide a good barrier and protection to the drug from humidity.
For that purpose when the drugs are sensitive and prone to environmental humidity and oxygen PVDC is applied as a coating over PVC and it act as a perfect protective partner that block all the humidity, light and air from reaching the product.
PVC can do a good job for regular medicines like vitamins, antacids or painkillers. High maintenance medicines like antibiotics, effervescent tablet, drugs with sensitive APIs, sterilize preparations and drugs made for use in tropical climates definitely require a PVDC packaging.
Hence, it is recommended to choose the pharmaceutical packaging not by habit but consider what the requirement of your drug is.
In a nutshell,
PVC: when the drug has to be cost effective and is a low risk drug.
PVDC + PVC: when there are potential risk factors like humidity, heat, oxygen and long term use.
4.What are the key structural and chemical differences between PVC and PVDC packaging?
Chemical formulae of PVC and PVDC
Polyvinyl chloride and Polyvinylidene chloride both are thermoplastic polymers of plastic and are widely used in the pharmaceutical packaging, not to forget the main blister packaging above all. But where they have many similarities they have much more distinct chemical and physical properties which make them suitable for different applications.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
| Properties | PVC | PVDC |
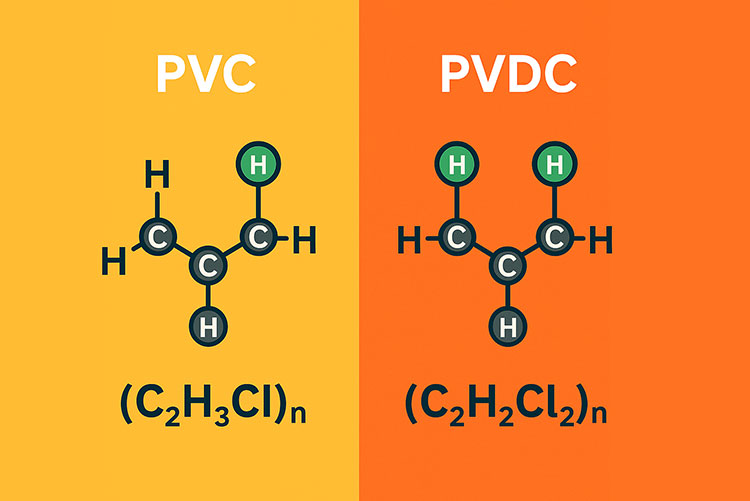
| Chemical formulae | 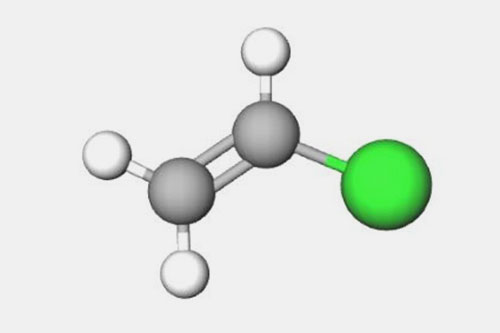
Green color showing one chlorine atom (C2H3CL)n |
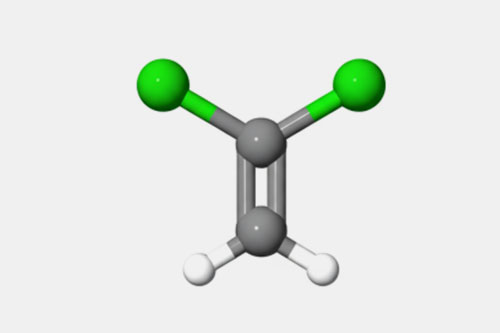
Green color showing two chlorine atoms (C2H2CL2)n |
| Structure | It has repeating units of vinyl chloride in the structure. | It has repeating units of vinylidene chloride in structure. |
| Chlorine content | It has approximately 56.8% of chlorine by weight. | It has approximately 73.1% of chlorine by weight. |
| Polymer backbone | It has only one chlorine atom per monomer. | It has two chlorine atoms per monomer. |
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Properties | PVC | PVDC |
| Transparency
|
It is clear and transparent with high clarity. | It has a slightly hazy or yellowish appearance with less clarity. |
| Flexibility
|
It is rigid but can be plasticized upon heating. | It is more brittle and less flexible but it can be made flexible with the use of additives. |
| Thermal sensitivity
|
It is stable at higher temperatures. | It is sensitive to processing at high temperature and can degrade easily. |
| Chemical resistance
|
It has a moderate chemical resistance. | It has a higher resistance to acids, base and solvents. |
| Water vapor transmission
|
It has approximately 0.5-1.0 g/m²/day | It is less than 0.1g/m²/day. |
| Barrier
|
It has a moderate barrier to oxygen and moisture. | It has excellent barrier to moisture, oxygen and even environmental aromas. |
5.What are the applications of PVC and PVDC?
PVC and PVDC are widely used in packaging and lamination in various industries and you might have been using them in your daily life without even knowing. So let’s take a look that PVC and PVDC are not just fancy names, in fact they have got some real jobs at your home, in your medicine cabinet and not to forget even in your lunch box.
Let’s find out in the following tables:
Applications of PVC:
| Applications | Features |
| Packaging industry
PVC container for donuts-picture courtesy: blister packaging |
PVC has a wide use in our food packages made of rigid plastic is PVC.
The cosmetics and personal care blister packs are made from PVC, which gives them a rigid and firm shape. The shrink wraps and cling films are PVC actually. There are widely produced bottles of oil and non-food products which are made up of PVC plastic. |
| Pharmaceutical industry
Capsule blister pack made of PVC-picture courtesy: hySum |
The blister packaging of tablets and capsule comprises of PVC plastic.
When the barrier requirements are low, monolayer of PVC film is used as primary blister pack. It also offers flexible tubing for the medical devices. |
|
Electronics industry PVC packaging for electronic mouse |
PVC packaging has been very convenient and economical in electronic industry.
It is versatile and offers protection with different types of shapes. The cables jackets and insulation requires PVC. The switch boxes comprises of PVC. |
| Construction industry
Construction pipes made of PVC-picture courtesy: plastic technologies |
PVC has made innovations in the construction industry somewhat economical.
The vinyl flooring and wall coverings made from PVC are elegant and cost effective. PVC is being used in window frames. The use of PVC in pipes and fittings is the most common use in construction industry. |
| Medical industry
Syringe and PVC tubing in PVC packing-picture courtesy: Klockner pentaplast |
The PVC covers a major part of medical devices.
The tubing and IV bags are mainly made of PVC. The disposable gloves are made cost effective due to PVC. Catheters and connectors also made up of PVC. |
Applications of PVDC
| Applications | Features |
| Pharmaceutical packaging
Liquid solution for injections in PVDC packaging |
The moisture and oxygen sensitive drugs are packed with PVDC packaging as it provides better barrier properties.
Unit doses for tablets are made. PVDC is also combining with PVC for better properties in pharmaceutical packaging. |
| Food packaging
Food wrapped with pvdc cling film-picture courtesy: aosen |
Apart from moisture and oxygen PVDC provides aroma barrier.
Therefore it’s suitable for food packaging and lamination. Cling films like Saran wrap were used to be made of PVDC. |
| Cosmetic & personal care
Cosmetic tubes made of PVDC-picture courtesy: smile kaun |
The shelf life of cosmetics products is protected by PVDC packaging.
Creams and lotions have PVDC containers that provide excellent protection and keep the product stable. It is best suited for volatile formulations. |
| Industrial applications
A chemical container made of PVDC |
It provides barrier layers in fuel tanks and containers.
The chemical packaging requires multilayer lamination which is provided through PVDC. It is used in corrosion resistant coatings. |
6.How do you compare PVC and PVDC in pharmaceutical packaging?
PVC and PVDC are usually combined together to provide the best barrier and protective properties to the product in pharmaceutical packaging, but let’s go through a few examples to have an insight about the use of PVC and PVDC separately:
Barrier and protection:
Layers of barrier-picture courtesy: versa perm
PVC works as the base or skeleton of the packaging structure, while the PVDC is added as a protective shield to the packaging. The barrier protection of PVC is comparatively lower than the PVDC as PVC can prevent the dust particles from entering but it cannot prevent humidity or air. For that PVDC is added which prevents the humidity and air like a pro.
Shelf life support:
Effect of shelf life on fruits-picture courtesy: medallion labs
PVC provides a very limited support to shelf life of the product. It is usually short lived. If you’re dealing with the drugs which are not really high maintenance and doesn’t mind a little humidity then PVC is a go to option.
But that’s not very common in pharmaceutical packaging. Most of the drugs freak out even with a little of humidity therefore PVDC is better suited especially in the case of hygroscopic drugs.
Cost and economical value:
Value for money-picture courtesy: dailyindustry news
PVC is more economical as it provides a standard base material for the most of the pharmaceutical blisters. PVC is easier to thermoform and is suitable for more stable drugs. So it alone becomes a cost effective option for less sensitive options.
PVDC comparatively more expensive than PVC is preferred for oxygen and moisture sensitive drugs like antibiotics or effervescent tablets. The reason of increased cost in PVDC packaging is that PVDC is not used alone; it is coated over PVC to enhance the barrier properties. The cost and thickness of the coating are directly proportional to each other. The raw material cost of PVDC is also high due to its complex chemical structure.
Processing and manufacturability:
The processing of PVC is easier as compared to PVDC. PVC is relatively stable at higher temperatures while PVDC is heat sensitive and tends to degrade during processing alone. Therefore, PVDC requires very precise processing to avoid any kind of discoloration and degradation.
You can use PVC as mono layer or multi-layer depending upon the requirement but PVDC can only be used as a thin coating layer.
Regulatory Acceptance:
Picture courtesy: ocallaghanmoran
PVC and PVDC are both universally accepted and listed in pharmacopeia (USP, EU, and JP). But PVDC has a closer scrutiny due to environmental and stability concerns. It is important to keep up with the regulatory and market requirements some markets prefer only PVC and ecofriendly multilayer films.
Storage and handling conditions:
PVC-PVDC packed blisters
PVC is better option for bulk handling and storage. The PVDC coated films are suitable for the controlled conditions with labels like store away from light and heat and in dry conditions. PVC packaging is room temperature friendly and easier to handle. It requires 15-30̊C and humidity requirement is below 60% which are normal industry conditions. Although PVC is self-stable, but at prolonged heat or UV exposures can cause the added plasticizers to degrade.
PVDC is recommended to store at 15-20̊C and humidity conditions are recommended below 50%. Even while converting film rolls to blister during packaging, the extended exposure to air or humidity can reduce the effectiveness.
Why the storage conditions matter in pharmaceutical packaging?
Pharmaceutical packaging is a critical procedure which has a great impact on the efficacy and stability of the drug. Therefore the effectiveness of the packaging material has an equal importance in the pharmaceutical environment.
The changes in the barrier property of PVC and PVDC due to poor storage conditions can have a major impact causing drug degradation and regulatory noncompliance. Ultimately, such mishandling just outsmarts their purpose for use.
7.What are the machines that can process PVC and PVDC pharmaceutical packaging?
We can see that PVC and PVDC are extensively used in pharmaceutical packaging. The important point to consider is that they also require use of precise machines to avoid any kind of mishandling and as PVDC require careful handling due to its thermal sensitive characteristic.
Study the tables below to find out about the machines that are involved in processing of PVC and PVDC during pharmaceutical packaging:
| Type of machine | Role in processing of PVC & PVDC |
| Thermoforming blister machine
AIPAK PVC PVDC blister thermoforming machine |
They have a primary role in processing of PVC and PVDC into blister and formation of different shaped cavities.
These machines heat the plastic films and use pressure or vacuum to form the cavity. PVC is easily molded but molding of PVDC requires precise temperature control because PVDC is heat sensitive. |
| Vacuum packaging machine
Vacuum PVC PVDC blister forming machine |
They are more commonly used for the flexible multi layered PVDC films.
These machines use vacuum pressure to form and seal the PVC and PVDC blisters. PVC provides the structure to the blister structure and PVDC is applied as a coating layer for barrier. |
| Pouch or sachet packaging machine
AIPAK sachet forming machine |
These machines process PVC and PVDC to make three or four sided seal pouches.
They fill them and seal the pouches. These machines do not process rigid PVC but only flexible PVC. PVDC is only used as a layer of protection and not alone. |
8.How do PVC and PVDC perform under thermoforming conditions of blister packaging?
Thermo former molding the films-picture courtesy: ULMA packaging
PVC –Ideal for thermoforming:
- PVC behaves best with thermoforming.
- It is rigid originally but it becomes flexible with heating.
- The softening of PVC is predictable.
- It doesn’t degrade even at 100-120̊C, which enables formation of deep and details cavities for capsules, tablets and other products.
- PVC even main its clarity and shape after thermoforming.
PVDC-cannot be thermoformed alone:
- PVDC is heat sensitive and it cannot undergo thermoforming alone.
- The thermoforming temperature of the machine is controlled under 150̊C otherwise it can damage the PVDC layer and its barriers properties can be destroyed.
- PVDC is only used as a thin layer of coating on thermoformable base like PVC.
- Whenever PVDC is employed in thermoforming a very controlled dwell time and gentle heating is ensured.
9.How would you compare PVC and PVDC in terms of compatibility with cold forming?
PVC raw material –picture courtesy: plastics today
Cold forming is a process which mechanically deforms metallic films like aluminum, at room temperature to form blister packs.
PVC and PVDC are not compatible with the cold forming method because PVC is too brittle and stiff at room temperature while PVDC is a thin coating layer and cannot be formed alone.
PVC has low barrier properties and is not suitable for cold forming packs.
PVDC, although have high barrier properties but it cannot be formed alone it always require a base over which it is coated.
The bottom line is PVC or PVDC can be used as a part of layers in multilayered laminated film but cannot be used as a forming material themselves.
10.How does the water vapor transmission rate differ between PVC and PVDC?
Picture courtesy: world energy org
Water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) tells us how much water vapor can pass through a material over period of time. It is important in pharmaceutical packaging because it has a direct effect on the stability and shelf life of the product. PVDC has a better water vapor barrier than the PVC due to its chlorine content. PVDC has higher chlorine content than PVC which makes it less permeable to the water vapor transmission.
Here is a detail view of how this happens:
- The WVTR for PVC is 0.5-1.0g/m²/day at a temperature of 30C̊.
- The WVTR for PVDC is as low as 0.06-0.1g/m²/day.
- PVDC is among the best moisture barriers in pharmaceutical packaging.
- The moisture barrier of PVC is only low to moderate.
- The moisture barrier of PVC is only slightly increased even upon increasing the thickness of the film.
- In case of PVDC, there is a significant improve in the barrier properties of the film upon increasing the thickness.
- This property of PVDC makes it ideal for pharmaceutical products with sensitive APIs.
11.What is the behavior of PVC and PVDC under accelerated stability conditions?
Accelerated stability chamber in pharmaceutical industry-picture courtesy: aralab
There are storage units in the pharmaceutical industry with artificial humidity and temperature conditions to check for the stability of the product under accelerated and normal conditions. These artificial storage units simulate the long term aging in shorter time in the accelerated chamber. This is done to check for the stability of drug and packaging in harsh humid conditions.
The ICH guideline for accelerated chamber for pharmaceuticals is mainly for 6 months with:
Temperature: 40̊C ± 2
Relative Humidity: 75% ± 5%
Following table gives us a comparison of behavior of PVC and PVDC under accelerated conditions:
| Property | PVC | PVDC (coated on PVC) |
| Drug protection | Stable drugs are better protected with PVC in accelerated conditions. | Even the oxygen and moisture sensitive drugs remain stable with PVDC coated packaging. |
| Moisture barrier and WVTR | The moisture barrier is weakened over time and moisture influx is increased into the drug. | The moisture barrier remains intact at accelerated condition and even at high humidity rate WVTR remains very low. |
| Shelf life | The shelf is immediately affected and decreased as there is visible degradation of the drug | The shelf life is not affected even at harsh conditions with PVDC, but if there is any kind of mishandling of the product than there could be drug degradation. |
| Film discoloration | PVC generally does not lose its clarity even after heating. | PVDC becomes yellow if overheated and can also degrade. |
12.What is the environmental impact of PVC and PVDC in terms of toxicity and recyclability?
Picture courtesy: RMIS
Environmental impact of PVC:
- PVC is generally recyclable but in the pharmaceutical packaging recycling is not possible mainly due to the contamination and somehow it’s multilayered structure.
- When the PVC is burnt it releases harmful toxins for health and environment.
- The almost 57% chlorine content of the PVC make it a problem for the environment.
- It is a major non bio degradable which means it doesn’t break down in the environment and add to plastic waste.
- It needs to burn down at high temperatures with closed gas system.
- Even after causing such environmental impacts, PVC is widely used due to its cost effective and easy processing method.
Environmental impact of PVDC:
- PVDC is not recyclable when coated over PVC.
- PVDC is even more toxic when burnt, it release hazardous gases upon burning.
- The chlorine content of PVDC is 73% which makes it a bigger problem than PVC.
- It also has a long term effect on the environment by creating plastic pollution and non-bio degradable characteristic.
- PVDC is the main target to be replaced in eco sustainability efforts.
Conclusion:
PVC and PVDC may not be very fancy materials in the world of pharmaceutical packaging but they have a major role to play for the protection of the drug and outcome of the patients. On one hand PVC provides strength and structure to the packaging while on the other hand PVDC is a silent warrior, providing a high barrier protective layer over the PVC. This combination keeps the medicine protected from moisture and environmental oxygen especially when the drugs are sensitive to harsh conditions. But we cannot totally rule out the environmental impacts of PVC and PVDC. So if you are designing a blister packaging or you are evaluating its regulatory compliance, it is important to fully understand the strengths and trade-offs of PVC and PVDC. For more information visit our AIPAK website for our team.
Don't forget to share this post!
Blister Packaging Machine Related Posts
Blister Packaging Machine Related Products
Blister Packaging Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 156 0710 8630

Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine