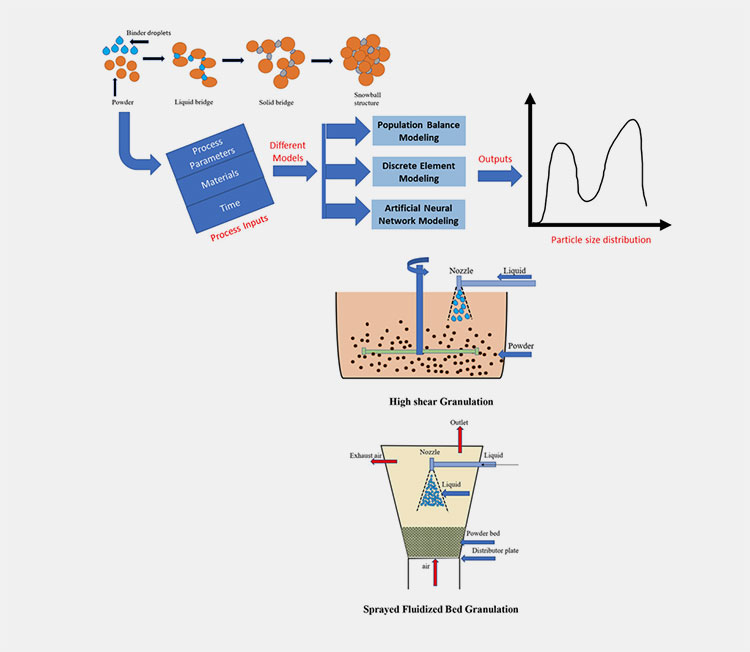
High Shear Granulation Vs Fluid Bed Granulation
Pharmaceuticals are heavily based on granulation. The small particles merge into the large mass, possessing identifiable properties, which are basically known as granulation. Within granulation, there are other major components, such as high shear, fluid bed granulation techniques.
In this article, you’re going to explore the important manufacturing aspect of high shear granulation VS fluid bed granulation. Studying comparative analysis would help the manufacturer to pick the right and accurate method for reliable and smooth formulation processing.
1.What Is Granulation in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and Why Is It Important?
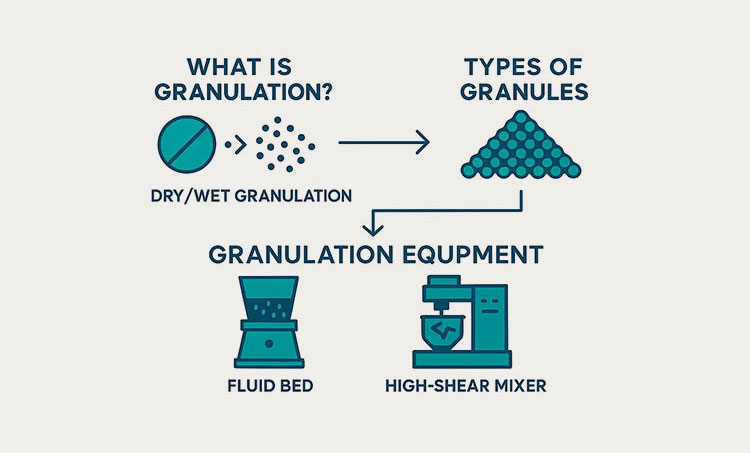
Granulation
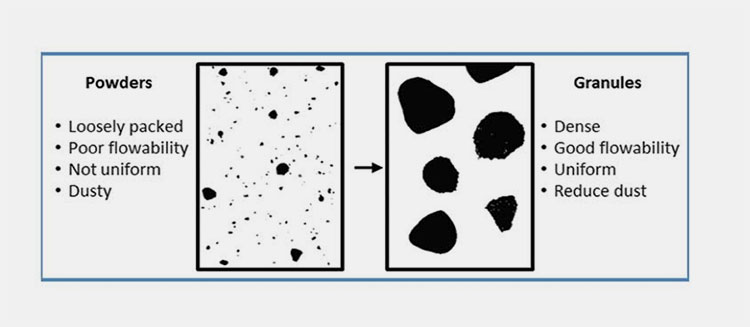
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, granulation is defined as any process where small particles accumulate to form a permanent mass with identifiable properties. The primary reason for granulation is to improve the characteristics of powder, its flowability, uniformity, and compressibility.
There are two ways granulation is done: wet granulation and dry granulation. Wet granulation uses a liquid binder, while dry granulation does not require any solvent, ideal for heat and moisture-sensitive materials. However, the common granulation equipment is known as the fluid bed and high shear granulator.
Granulation is important in pharmaceutical manufacturing as it:
Ensures consistency and Uniform dosing
Granulation converts APIs and excipients and aligns them together to prevent segregation, to achieve better flow, and to achieve accurate tablet weight.
Improves Flowability
The granulation process enhances powder flowability as fine powders have poor flow consistency. Granules have a proper flow characteristic, which prevents the risk of weight variation.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory bodies like the FDA highlight the importance of content uniformity and consistent powder in their Compliance Policy Guide, which can be achieved through proper granulation.
Role in Market Growth
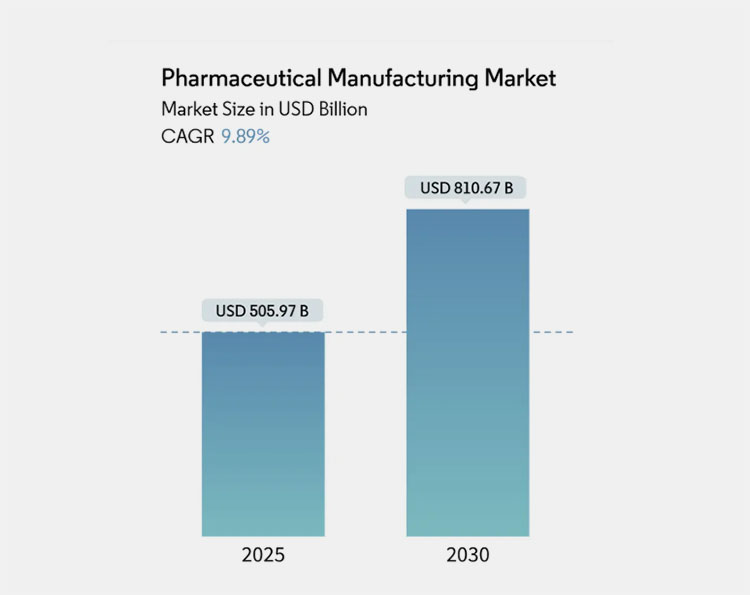
Granulation is a highly important aspect of the oral dosage form market, according to Fact.MR, the global dosage pharmaceutical market is predicted to reach USD 1,211 billion by 2035.
| Market Overview | |
| Study Period | 2019-2030 |
| Market Size (2025) | USD 505.97 Billion |
| Market Size (2035) | USD 810.67 Billion |
| Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) | 9.89% |
| Fastest Growing Market | Asia Pacific Region |
| Largest Market | North America |
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Market Size Chart in USD Billion. Chart Source: Mordor Intelligence
The chart illustrates how the pharmaceutical manufacturing market is rapidly expanding, implying an increase in accurate and precise granulation to accelerate tablet manufacturing while complying with regulatory requirements.
Reduces Dust Formation
The agglomerates form reduces the risk of dust generation, preventing contamination and material loss while enhancing workplace safety.
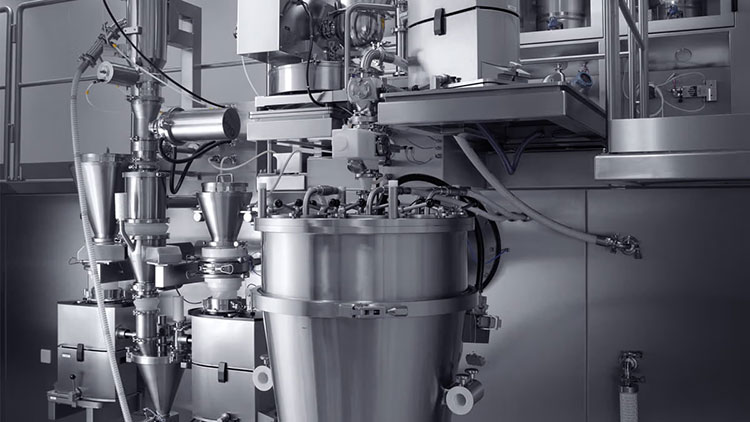
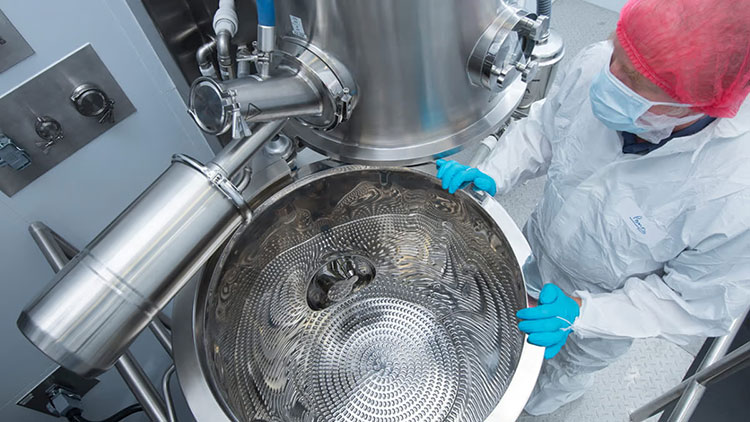
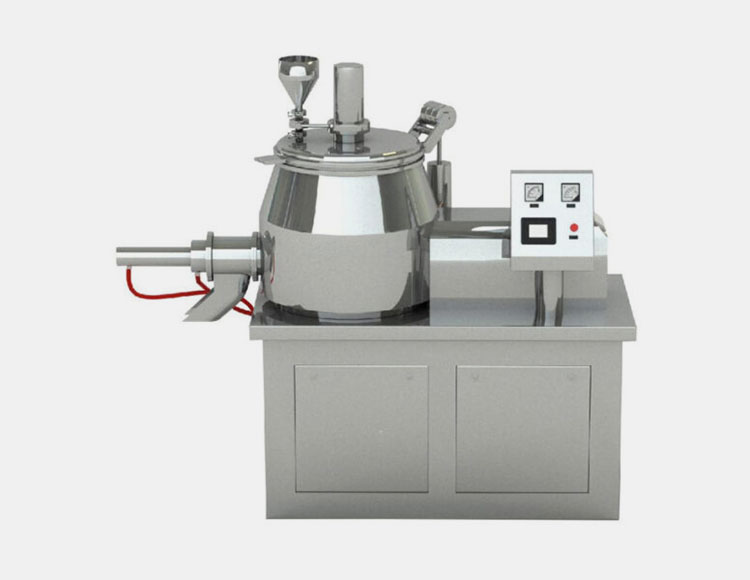
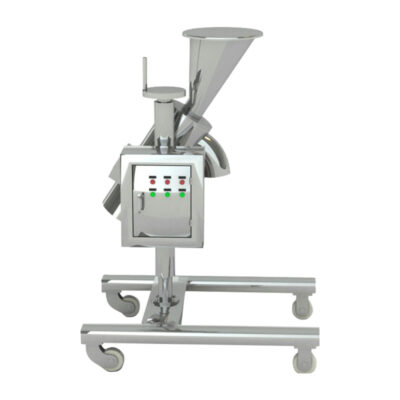
2.What Is High Shear Granulation and How Does It Work?
High Shear Granulator-Picture Courtesy: S3 process and Contract Pharma
High shear granulation is a wet granulation process that converts powder into thick and dense granules with the help of a high-speed impeller and chopper that applies intense mechanical force to obtain fine particle agglomeration.
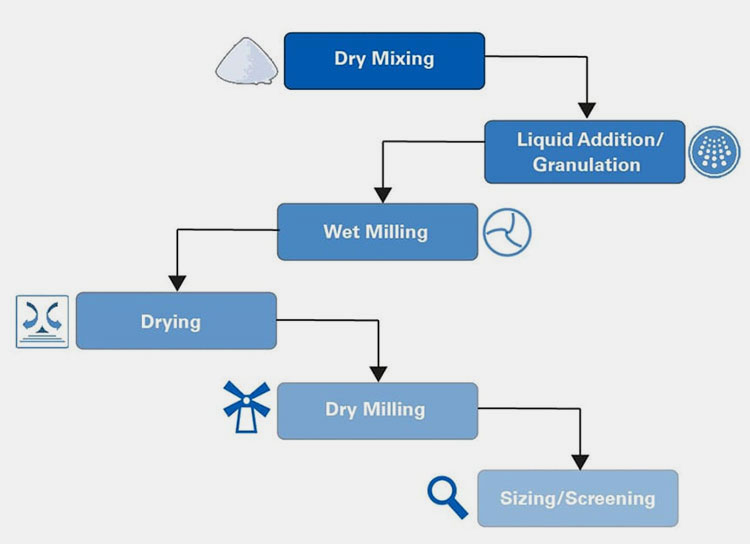
The following is a step-by-step guide on how high shear granulation works.
Step-by-Step Working of High Shear Granulation
Step 1: Dry Mixing
During dry mixing, the impeller rotates at a controlled speed to obtain uniform powder components. This step is crucial as it prevents the risk of segregation and content variability, enhancing effective granule formation.
Step 2: Liquid Addition
A wet binder solution is then introduced, typically sprayed through a nozzle. Through mechanical force, the impeller distributes the binder rapidly, and the chopper prevents the formation of oversized lumps.
Step 3: Wet Milling
After binder addition, liquid bridges start to develop between particles. Finally, the particles start mixing together and start forming initial clusters called nuclei.
Step 4: Drying
Following wet granulation, the wet agglomerates are dried using controlled heated air flow, which removes the excess moisture content from the granules.
Step 5: Dry Milling
After the granules are dried, they may be an inaccurate size; dry milling is the process that breaks down these agglomerates into smaller particles to achieve the desired size.
Step 6: Screening
After the desired size is achieved, the granules are screened. For this process, the granules are passed through a sieve to separate accurately sized granules from oversized granules for further processing.
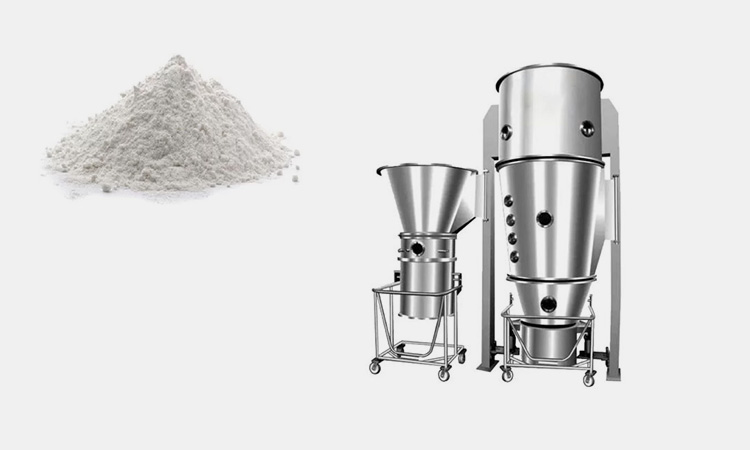
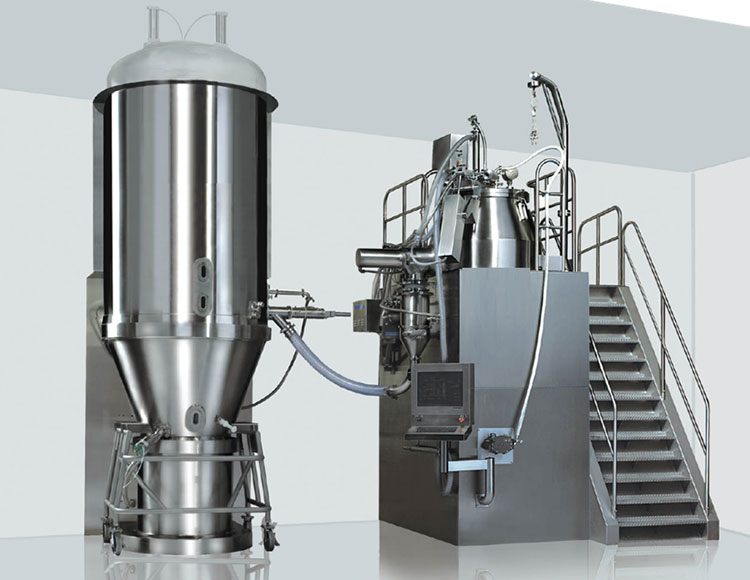
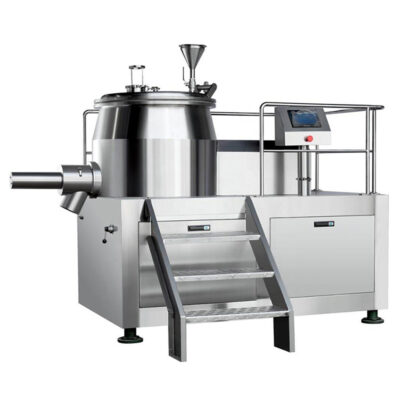
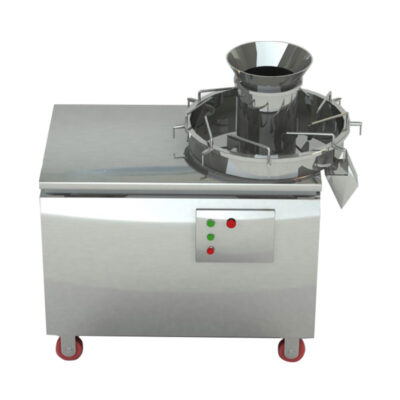
3.What Is Fluid Bed Granulation and What Happens Inside the System?
AIPAK Fluid Bed Granulator
Fluid bed granulation is a wet granulation process that uses aerodynamic force to fluidize powder, while a liquid binder is sprayed. The equipment can be classified as a single-unit process because it combines mixing, granulating, and drying all in one unit, facilitating product transfer while preventing the risk of material loss and contamination.
According to EMA’s pharmaceutical quality guidelines, the aerodynamic force of the fluid bed granulation system is considered a critical quality attribute, as it directly impacts granule size and quality. The following section outlines the internal system of fluid bed granulation.
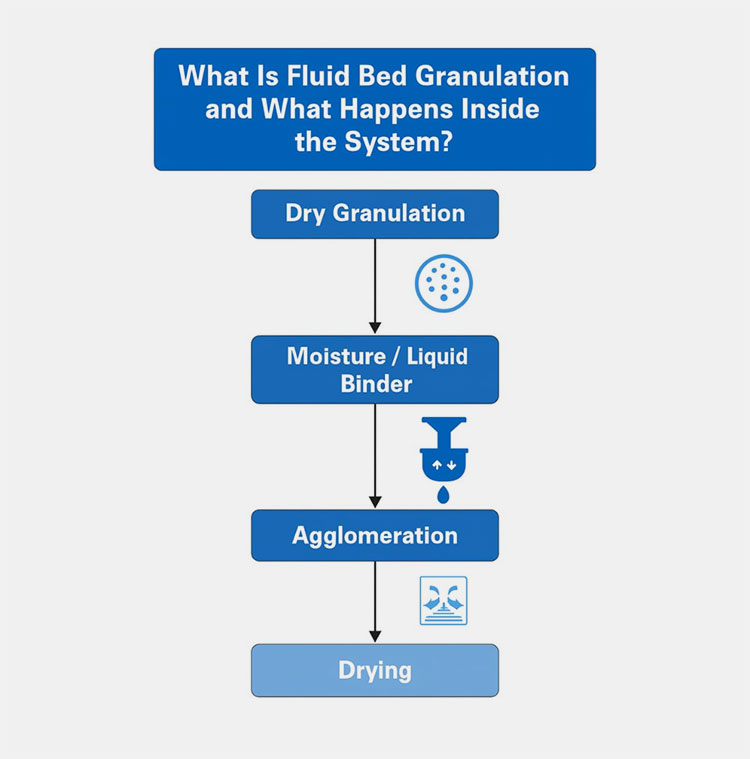
Step-By-Step Working Of Fluid Bed Granulation
Step 1: Dry Granulation
The dry powder particles are suspended in a controlled system of heated air, which creates a fluid-like state. This process ensures consistent exposure of powder particles to the binder.
Step 2: Liquid Binder
Following fluidization, a liquid binder is sprayed onto the fluidized powder particles, sticking them together and forming small nuclei.
Step 3: Agglomeration
Under gentle mixing, the nuclei collide and form large agglomerates; the controlled hot air stream prevents these agglomerates from clumping together.
Step 4: Drying
After achieving the desired granule size, the binder spraying is stopped. The heated air flow is continued, which acts as a drying medium. The agglomerates are dried until they reach the desired low moisture content. The dried granules are then cooled and discharged for further processing.
4.What Are the Key Differences Between High Shear and Fluid Bed Granulation?

High Shear Granulator |
Fluid Bed Granulator- Picture Courtesy: ENCP North America |
Granulation is a complex procedure in pharmaceutical manufacturing as it directly impacts the quality of dosage formulations. According to the FDA’s guide on Oral Solid Dosage Forms, inconsistent granulation causes dosage deviations and inconsistency.
Understanding key differences between high shear granulation (HSG) and fluid bed granulation (FBG) is essential for GMP compliance and product efficacy.
| Critical Parameters | High Shear Granulation | Fluid Bed Granulation |
| Speed | This is a fast process due to its mechanical mixing, which uses a high-speed impeller and chopper. | Fluid bed granulation is a slow process as it depends on controlled air suspension. |
| Particle size | HSG produces thicker, denser, and less porous granules. | FGB produces more porous, lighter, and consistent granules. |
| Energy Consumption | It consumes mechanical energy because its agglomeration process relies on the impeller and chopper. | The system consumes more thermal energy because the integrated system uses heated and controlled pressurized air. |
| Thermal sensitivity | HSG is not ideal for thermally sensitive active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) because of heat generation. | FGB is suitable for heat-sensitive APIs because of the controlled airflow system. |
| Investment cost | This is less cost-intensive with a simple unit. | The investment cost of FBD is high, with a single pot unit composed of in-built drying, spraying, and fluidization systems. |
5.Which Process Produces More Uniform Granules?
Uniform Granules- Picture Courtesy: Clavela
The process that produces more uniform granules is fluid bed granulation, where powder particles are continuously flowed in upward air using aerodynamic force, ensuring consistent binder spray and precise exposure of powder particles into the granulation process.
The reasons behind fluid bed granulation producing more uniform granules are:
Consistent Binder Exposure: In FBG, each powder particle is evenly exposed to the binder, which prevents under-wetting or over-wetting of granules.
Equal Drying: The heated air for drying particles prevents the generation of large clumps, ensuring even size distribution.
Less mechanical Stress: Fluid bed granulation uses lower mechanical stress, unlike high shear granulation, ensuring less breakage and large lumps.
Stable inner environment: Consistent pressure, airflow, and temperature create a stable environment, which supports standard granule density.
6.Which Method Is More Suitable for Heat-Sensitive Materials?
High Shear Granulation VS Fluid Bed Granulation
Fluid bed granulation is generally more suitable for heat-sensitive materials as it employs controlled air and aerodynamic force to balance heat generation and extraction simultaneously. Whereas high shear granulation uses mechanical energy which generates internal heat without effective heat extraction.
Why fluid bed granulation is the preferred method for heat-sensitive materials?
Temperature Comparison
Heat-sensitive materials if exposed to prolonged drying time can degrade and loose integrity. According to above data, fluid bed granulation is ideal for heat-sensitive materials with 0.66 hours drying time.
Minimal Heat Generation: Fluid bed granulation depends on controlled air suspension where heat is evenly distributed across the system which reduces the risk of heat generation.
Temperature Control: Fluid bed granulation allows the operator to control airflow rate, inlet temperature and outlet temperature ensuring safe range of temperature for thermal sensitive materials.
Low-stress Granulation Environment: Fluid bed granulation uses fluidization to flow particles carefully in air, reducing mechanical stress while preventing the risk of material degradation.
Sustained Thermal Extraction: The air stream in fluid bed granulation continuously extracts the heat generated during granulation process. This develops a self-cooling effect within the system, which protects heat generation and damage.
7.Which Equipment Has a Lower Operating Cost in Real Production?
Operating Cost in Real Production- High Shear Granulation VS Fluid Bed Granulation- Picture Courtesy: ScienceDirect
In a real-time scenario, the fluid bed granulation is an outstanding technique with low operating cost for manufacturers in many real case studies. For example, when you need to subject material with FBD, three main functions such as granulation, drying, and coating take place simultaneously. Additionally, the entire processes are done in the same vessel. This means that you’re saving your labor, time, and the transfer of material, etc.
High shear granulation is also commercially considered with lower operating costs. This is because the machine is associated with offering short-term working, though it needs few operating hands. In various market research analyses, this is also shown that high shear granulation yields throughput in a few minutes. However, its operating cost is higher than FBD. The generation of intense mechanical forces is also known as involving energy consumption; therefore, it is high.
8.In What Real-World Scenarios Do Companies Prefer High Shear Granulation?
The real real-world scenarios related to high shear granulation are discussed below:
CASE STUDY 1: The Rise of Continuous Manufacturing
Case Study High Shear Granulation by GEA- Picture Courtesy: GEA
A renown pharmaceutical company GEA transformed conventional process into continuous manufacturing called CM to deliver high quality products. The modern strategy was implemented when industry was under pressure to bring products in a short time and in health care budget.
Improvement
The plan was resolved with an integrated system of high shear granulation, fluid bed dryer and a tablet press. The set of machines comes up with a single unit.
Outcome
The study was carried out with positive results such as:
- Uniformity of granules sizes and dealt with large production batches under friendly budget.
- Material loss, time and energy was reduced with cost efficiency.
- The industry was achieved with faster and continuous scaling up from initial till commercial preparations.
CASE STUDY 2: High Shear Scaling Up
Foam Granulation- Picture Courtesy: PharmTech
A pharmaceutical company, Perrigo implemented a foam binder in high shear granulation instead of conventional binder. This study was conducted on lab trial, pilot, then on a commercial scale.
Improvement
It was noticed that foam binder was capable of producing an even and uniform wetting instead over wetting or clumping.
Outcome
- Evenly distributed binding properties were observed in all cases.
- The foaming agent requires low drying time as well as energy consumption.
- Without hectic procedures and major changes, the high shear granulation was proved as reliable option for granule formation.
9.Do High Shear and Fluid Bed Granulators Meet GMP And FDA Requirements?
Yes, high shear and fluid bed granulators are absolutely compliant with GMP and FDA requirements if in case they are adjusted, installed, and well-documented as per GMP/21 CFR/industry guidance.
The machine alone doesn’t based on compliance rather it holds complete validated properties, processing, and main qualification such as IQ, PQ, OQ papers. However, it shows that machine is suitable enough for intended processing safely. For instance:
High Shear and Fluid Bed Granulators Meet GMP And FDA Requirements
Machine Design & Material
The respective design and material of both machines are main made up with high grade stainless steel where no dear corners are featured. The subjected formulation mostly operated with hygiene and less contact fully ensures GMP and FDA specifications.
Process Validation Documentation
High shear and fluid bed granulator must be offered with process validation documentation to meet GMP and FDA requirements for consistent work. For instance, establishment of installation qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ) Performance Qualification (PQ) that is collectively as an elemental approach to biologicals or human products as a validated manufacturing.
Cleaning and Cleaning Validation
The cleaning and cleaning validation for respective machines are also validated in the term of pre-determined procedures that ensuring scientifically justified protocols. The GMP and FDA (21 CFR 211.67) entails regulation in order to prevent contamination and prevail safety, and quality beyond official established protocols. This is included with necessary wash cycles, that results in no visible particles and contaminants are considered as acceptable.
International GMP/Industry Best Practices
The GMP also supports the best possible practices related to high shear granulation and fluid bed granulation to yield best expected outcomes. this is involved with installation of sterile construction, working, installation of HVAC in order prevent dust and maintaining controlled workplace. However, the documentation and side by side monitoring must be scheduled for healthcare establishment.
10.How Do You Decide Whether to Use High Shear or Fluid Bed Granulation for Your Product?
For the development of tablets, capsules, or related pharmaceutical preparations, which method of granulation is right for you is critical decision. Just like your different blood groups, the pharmaceutical powders also behave differently with different characteristics.
High Shear Granulation VS Fluid Bed Granulation- Picture Courtesy: PTK & GEA
The high shear granulation or fluid bed granulation both are meant to improve flow and above related properties, though they work differently. This is deeply linked to properties of your material. Therefore, choose the method if you have below mention conditions:
| State | High Shear Granulation | Fluid Bed Granulation | Description |
| Material is sticky or difficult to mix | ★ | For quick mixing high shear is good option. | |
| Less dense and flowable material | ★ | Fluid bed granulation is ideal for lightweight materials. | |
| Heat Sensitive substances | ★ | It dries material utilizing a gentle temperature. | |
| For normal temperature | ★ | If heat is not an issue, fluid bed is fine. | |
| For strong granules | ★ | If you want strong and dense granules, high shear granulation is used. | |
| Granulation and Drying Simultaneously | ★ | For one machine and same time procedure, fluid bed granulation is preferred. Although for separate processes, high shear is used. | |
| Rapid and Large Batch Production | ★ | Fluid bed granulation is gentle and controlled process. high shear is associated with fast processing. |
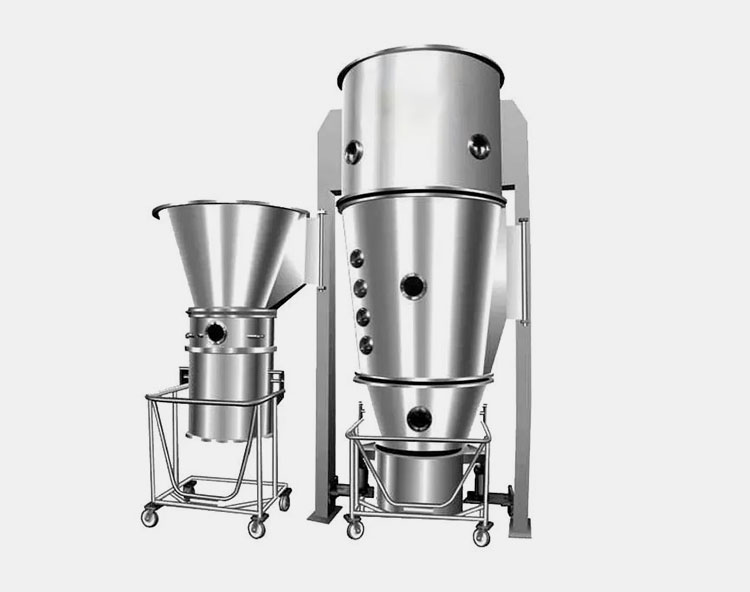
11.When Is Fluid Bed Granulation the Better Choice?
Fluid Bed Granulation- Picture Courtesy: GEA
The fluid bed granulation is the better choice for formulation drying under precise controlled conditions. The process is meant to suspend the stream of particles in a fluidized state for evenly drying and thoroughly coating of solution. This in results gives a high-quality spherical shape and porous particles with remarkable flow ratio.
This method is way more beneficial for substances with greater thermal stability. Therefore, a streamline of warm environment makes the evaporation process sufficient. Moreover, it is based on single vessel unit which is easy to maintain, clean, and carries low risks for contamination.
According to research studies, the fluid bed granulation is good choice for uniformity and consistency in granule shapes. Especially when it is integrated under humidity control monitoring parameters and NIR humidity analysis.
12.Can These Two Processes Be Combined in One Production Line?
Integrated Production Line- Picture Courtesy: FREUND
Yes, processes of high shear and fluid bed granulation can be combined in one production line. The hybrid production line is mainly implemented to boost up the manufacturers’ goal to strength the workflow. Generally, the high shear granulation provides fast wet massing. On the other hand, fluid bed granulation gives a consistent way to eliminate moisture levels. Combination techniques support and optimize the transformation than an alone procedure. The combination of these two methods is used for:
Fast Wet Massing and Uniform Drying
This is suggested in PubMed study that high shear granulation allows a quick and create dense granules. The integration with FBD permits the rapid moisture elimination without subjecting the content to intense heat. In a result, a robust granule formation is achieved for pharmaceutical preparations.
Better Control Over Granulation Parameters
The integration systems are used to have better control on over granulation, wetting or aggregation, and variability in drying factors.
Favorable Quality
If you see commercially successful examples, the production is scaled up with combine uses of HSG and FBD. This is for the reason to have improved moisture, drying uniformity and professional established protocols.
Easy Handling with Combined Processing
The modern systems from companies like GEA, AIPAK, Romaco, and others offering HSG and FBD in a combination process. They enable easy transferring, automatic handling, limits risk of contamination, fast cleaning etc.
13.Which Method Offers Better ROI for Manufacturers?
High Shear Granulation VS Fluid Bed Granulation- Better ROI Methods
The ROI or return on investment is mainly based on three factors. First type of product, capacity, and manufacturing planning. Nevertheless, both equipment is associated with offering better ROI, although, it is based on specific scenario.
However, when it comes to consider fluid bed granulation; its various working steps are involved a single vessel. This directly impacts on low production expenditure, no cross-contamination and lesser changeover.
On other side, high shear granulation is suitable for dealing with large production batches and formulation with high density. the production time is shorter with high outcomes.
In comparison analysis of both, the FBG is offering with improved cost expectation and are offering lesser failure of production. Whereas the HSG gives shorter production timeline that gives better ROI for business.
14.What Are the Common Problems Encountered in Each Process and How to Solve Them?
The common problem encountered with high shear granulation and fluid bed granulation are described in the table below:
High Shear Granulation
Problems and Solution related to High Shear Granulation
| Common Problem | Cause & Solution |
| Lump Formation | When you add excessive binder, long wetting time or slow granulation speed, this problem occurs. For solution, well controlled and optimized binding spray and wetting time is recommended. Chopper and impeller operation must be well-regulated to maintain uniformity. |
| Need for Separate Drying & Risk of Contamination | The HSG yields materials that require separate drying time. This can occur on either tray dryers or fluid bed dryers that increase complexities and high risk of contamination.
In certain situations, the integrated equipment is a possible solution to keep process well-controlled and easy. |
Fluidize Bed Granulation
Problems and Solution related to Fluid Bed Granulation
| Common Problem | Cause & Solution |
| Failure in fluidization of particles | This is common problem that occurs with powder cohesive in nature or high density. Therefore, it is recommended to pour or use flow aiding materials such as glidants to improve texture of powders. |
| Material Agglomeration | The powder lumpiness becomes profound during drying. The problem can be solved when you’re using control moisture level to maintain steady work. |
| Inconsistency in drying of materials. | There could be possible reasons aiding inconsistency in material drying such as, failure in proper air distribution, particle segregation, no proper detectors. Therefore, this is suggested to use NIR moisture sensors that help maintaining controlled humidity. Use of optimize mixing and drying would help in uniform granules formation. |
| Excessive Dust formation | When it comes to dealing too much fine powder, it results in dust formation. This can be managed with an adjustment of fluidize air velocity. |
Conclusion
In this article on High Shear Granulation VS Fluid Bed Granulation, you’ve taken a brief exposure of major technology, working, case studies, and relevant discussion. Nevertheless, when it comes to attaining uniformity of the granules with even size distribution, HSG and FBG are major techniques. Both processes give stability and strength to finished products. Using the reference of this article, it can be concluded that these methods are substantial for good quality manufacturing of medicines with safety and potency. For further help and equipment information. Discover AIPAK for granulation equipment. Message us now, our expert will respond to you shortly.
Granulator Machine Related Products
Granulator Machine Related Posts
Granulator Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586

Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box? Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter, we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machin