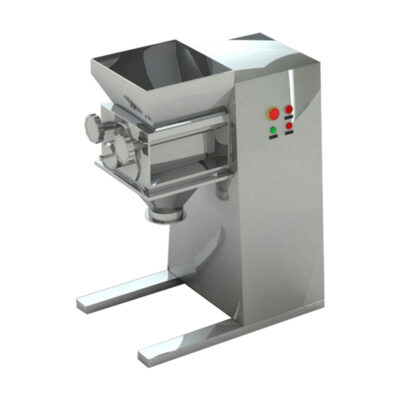
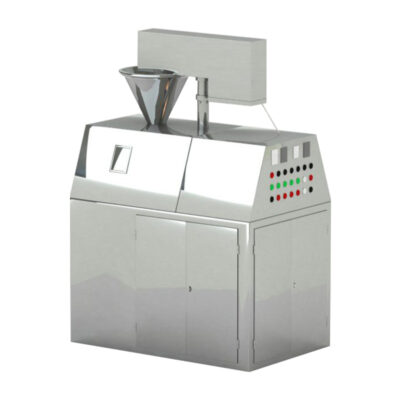
What do You Know About Fluid Bed Granulation Process?
You must have been familiar with the use of powders in the manufacturing industries of food, chemicals, agriculture, pharmaceutical and many more. But it might surprise you that powders are not always reliable and ideal. In fact, powders come with more challenges than benefits. There are challenges like poor flow ability of powders, dustiness or difficulty in down streaming procedures.

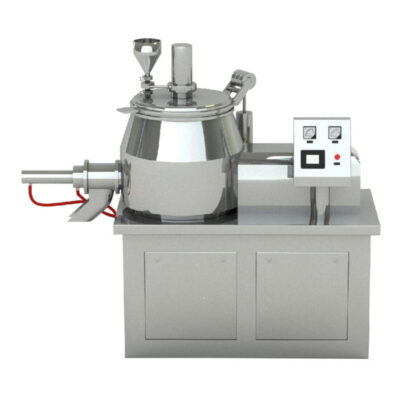
This is where granulation comes to rescue. Among many granulation procedures, fluid bed granulation stands tall for its efficiency, intelligence and hygienic control qualities. This fluid bed granulation process combines complex and multiple steps of mixing, blending, granulating and drying into one system. It is advanced and most widely used method lately.
Let’s find out more technicalities of fluid bed granulation process in the following editorial!
1.What is fluid bed granulation?
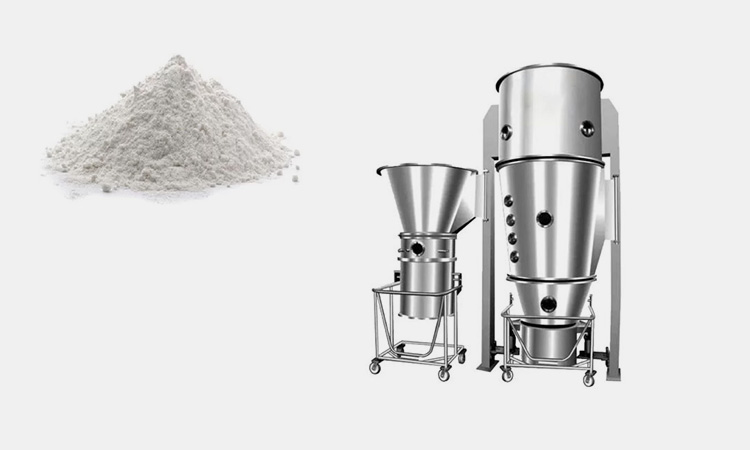
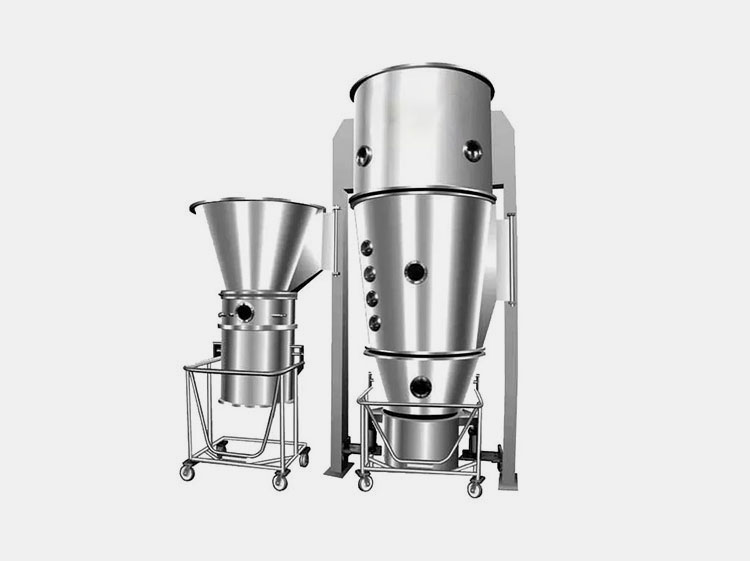
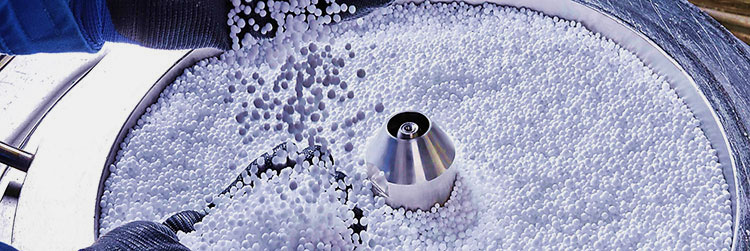
A glimpse from fluid bed granulation process-picture courtesy: ThyssenKrupp uhde
Fluid bed granulation process is a technique to convert loose and dusty powder into solid granules for better usage. In this process, the powder is fluidized by blowing the air from below into the powder containing chamber. This air makes the powder move and float around making a fluidized bed of powder. Hence, the process is termed is fluidized bed granulation process.
The binder is sprayed over the fluidized powder particles which cause them to stick together and form granules. The use of steam or heated air to fluidize the powder particles allows a uniform and efficient mixing and drying of the ingredients.
2.What do you know about fluid bed granulation process?
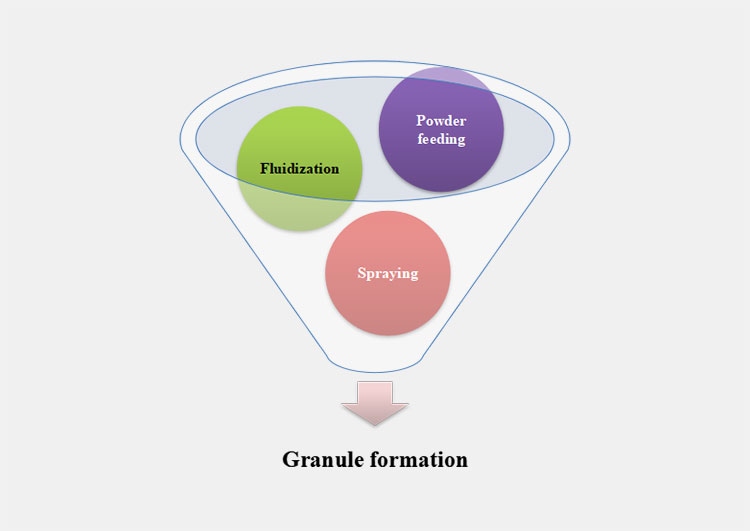
The above image shows formation of granule in fluidized bed granulation process
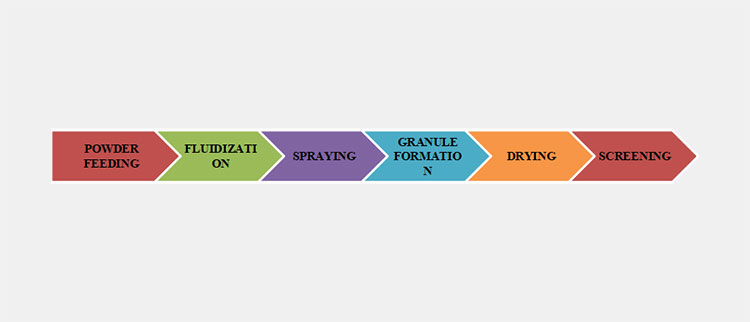
The fluid bed granulation process is a one pot procedure of making granules using fluidized bed granulator. This fluid bed granulation process comprises of the following main steps:
Powder feeding:
This is starting point of fluid bed granulation process. The mixture of powder which contains all the excipients and active ingredients is loaded from above head into the granulator which is product container of the fluid bed granulation process.
Before feeding the powder into the machine, it is ensured that the powder is blended well and there is uniform mixing of the ingredients. It is also recommended to ensure that there are free flowing powder particles for efficient fluidization. These qualities make a uniform powder bed for granulation.
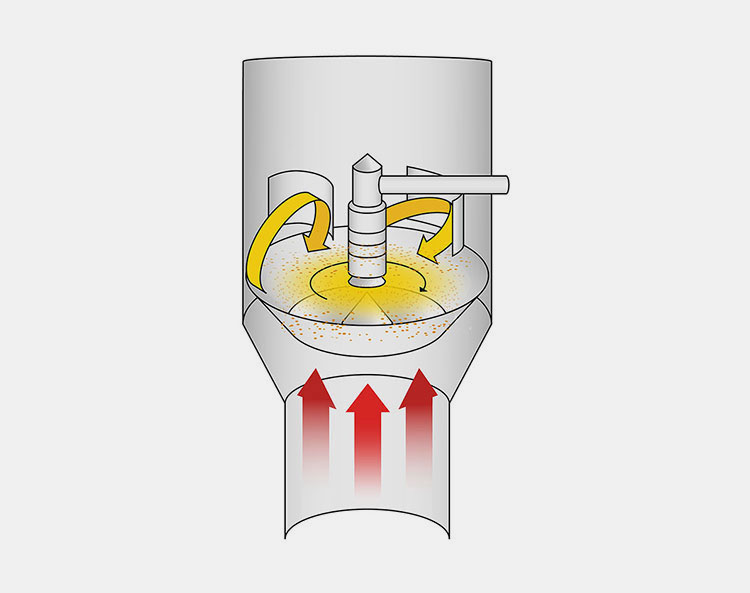
Fluidization:
Fluidization of powder into granules-picture courtesy: research gate
This is the step which makes the powder particles act like a liquid, called fluidization. Once there is successful feeding of powder into the granulator, air is introduced into the granulator chamber. It is heated air which is blown from bottom of the granulator, already containing dry powder. The airflow is strong and exerts enough pressure on the powder particles to lift them and make them float in the chamber.
The drag force of the air flow becomes equal to the particles weight and powder particles float and move freely in the granulation chamber. These free floating powder particles just behave like a liquid and become fluid like. The have swirling and mixing movements without any are clumping.
This free mixing movement is essential so that the powder is properly mixed and prepared for binder spraying step. This fluidization of the powder particles evenly suspend and expose each and every powder particle to the binder which helps in effective granulation of the powder.
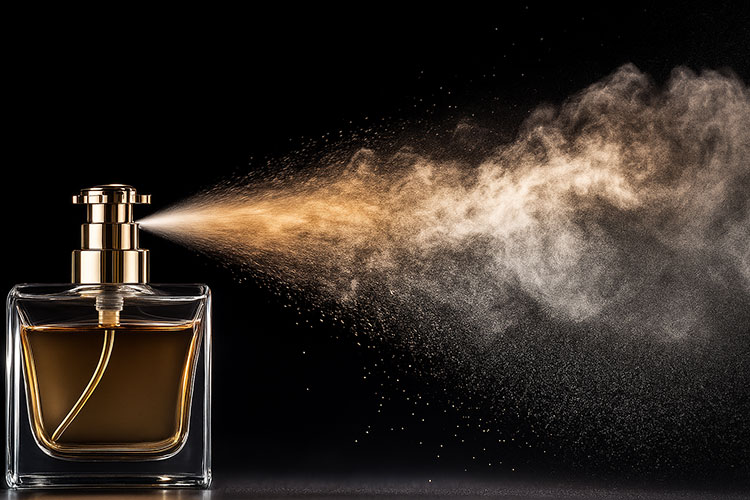
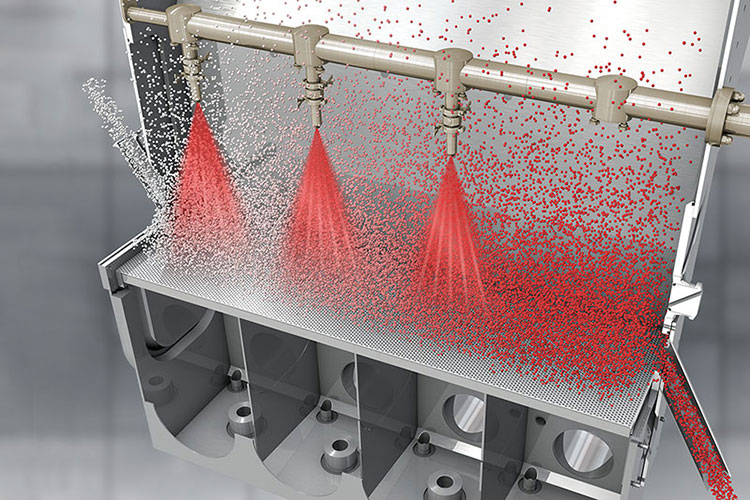
Binder atomization-Spraying :
Spray atomization phenomenon-picture courtesy: adobe
After the powder is fluidized and heated to the required temperature. This fluidized powder bed is sprayed with binder solution. The binder solution can be water or a sticky substance like starch or PVP. The spraying of binder is done through a nozzle attached in the granulation chamber. The spraying of binder through nozzle in form of fine liquid droplets is termed as binder atomization.
These liquid droplets come in contact with the fluidized powder particles. As soon as the powder particles contact the droplets, the liquid spread over the particles surface and bind them together in the form of agglomerates. As the binder is a sticky liquid it helps the powder particles to stick together upon contact.
The purpose of binder spraying is to make an initial contact among the powder particles to achieve the formation of granules.
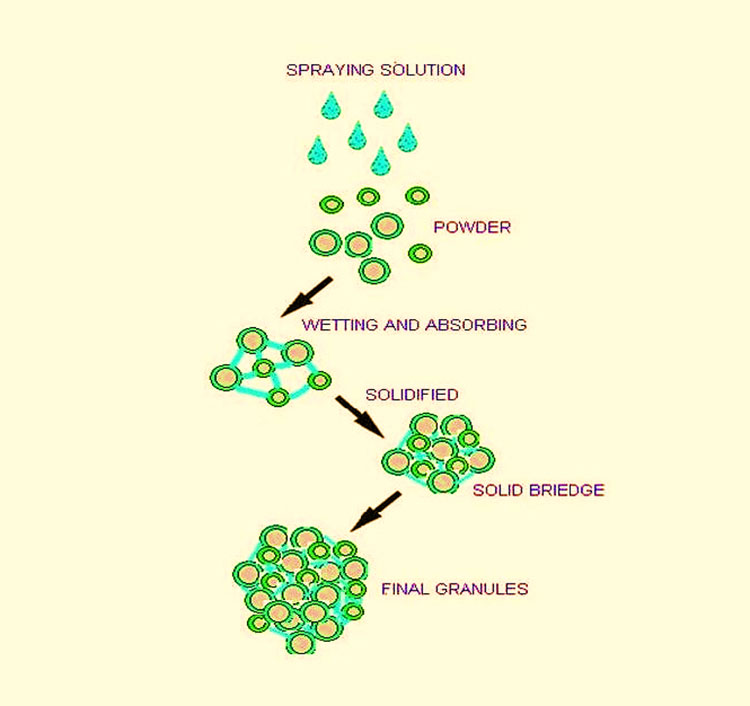
Granule formation:
Granulation of coffee powder-picture courtesy: 123 RF
The binder wets the powder particles and makes them collide with each other and stick together. Over time, as more the liquid binder is being added, these small clumps start to grow in size and as more particles attach irregular shape granules start to form. This process is termed as nucleation and growth of granules. The size of the granules is controlled by operating system.
The binder spray and fluidization is well controlled. This ensures the growth of granules to a desired size. When the required binder spraying rate is achieved and there is required binder saturation of the particles, desired and properly formed granules are achieved. This is the fluid bed granulation of powder. The granules thus achieved are of a uniform size.
Drying:
Drying-picture courtesy: vecteezy
Drying is the step which makes the freshly made granules solid and stable. While the granulation is being carried out, the hot air is consistently being circulated through the fluidized bed. This hot air evaporates any excess moisture from the binder and granules formed. This makes the granules dry out and become hardened.
Drying not only solidifies the granules but it makes them stable and strong. The result of drying provides us with free flowing granules.
Screening:
Separation of different particle size through sieving
Screening of the finally prepared and dried granules is done to ensure a uniform and required granular size. This screening is done through specified size sieves which removes any oversized lumps as well as over fine granules or if there is any fine powder. This is important to ensure uniform size to improve the flow properties and compressibility of the granules.
3.Machine involved in fluid bed granulation process:
AIPAK multi-function fluid bed granulator
The following table will provide you with breakdown of major components inside fluid bed granulation process machine and the role of each part:
| Machine components | Role in fluid bed granulation process |
| Fluid bed granulator | This is main core machine in which this whole fluid bed granulation process is being carried out. All the stages fluidization, binder spraying, granulation and drying is carried out in this fluid bed granulator. It is made up of stainless steel for effective hygiene and durability.
It is equipped with air handing unit, spraying nozzle, filters and product chamber. The binder solution is sprayed through this spray nozzle system into the granulation chamber. It has a perforated base through which air flow distribution is carried out. The fluid bed granulator processing system has a human machine interface (HMI) system. This is the control panel through which all the commands and required parameters are fed into the granulator. It is a well suitable structure to support free movement of the powder avoiding nay dead zones. |
| Binder Solution Preparation Tank / Mixing Tanks | These are mixing tanks used to prepare and hold the binder solutions, before it is added to the fluid bed granulator. They are stainless steel tanks equipped with mixers and agitators for effective mixing and homogenization of binder solution. They have heating features to maintain a desired binder temperature. |
| Peristaltic Pump | They are also called diaphragm pump. They are used to deliver the binder solution from the mixing tank to the spray nozzle in fluid bed granulator. They deliver a uniform and required adjustable flow rate of binder to the nozzle. They are gentle and can be adjusted to a less shear in case of sensitive binder solutions, to avoid degradation. |
| Air Handling Unit | Air handling unit (AHU) is responsible for the filtered, heated and controlled supply of air for effective fluidization. It contains pre filters, HEPA filters, heater and fans. The pre filters are first line of filtration in the AHU.
They prevent the large dust particles from reaching the sensitive HEPA filters. The HEPA filters are placed after the pre filter, just before the air entrance unit. They clean the air and remove ultra-fine dust particles, up to 99.97% of 0.3 microns. The humidity, pressure and temperature of introduced air controlled by AHU. |
| Dust Collector / Exhaust Filter System | This air exhaust system provides exhaust to the granulation chamber by pulling out excessive moist and warm air after the drying procedure is completed. It collects the fine dust particles and prevents them from being exposed in environment.
In this way it controls the emission of dust in the air as well as air pressure in the system and prevents any recirculation of the humid air into the granulation chamber. It effectively controls the drying rate and moisture of the granules. |
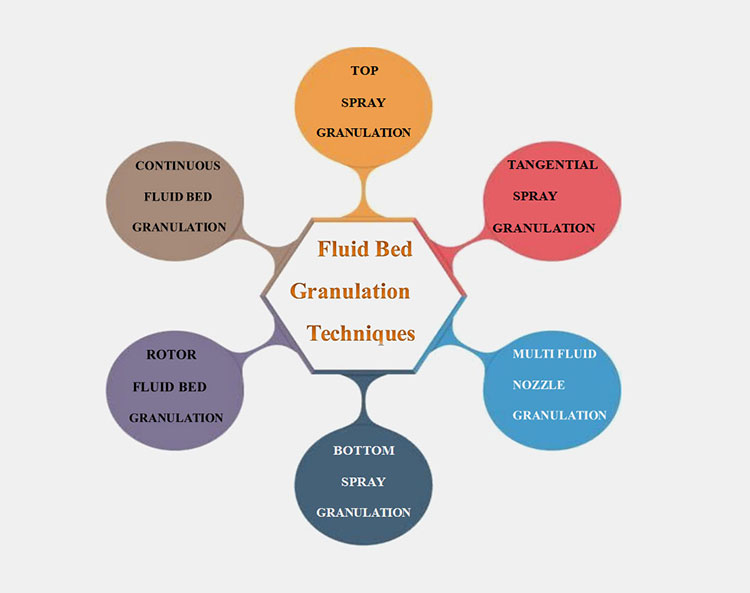
4.Different techniques of fluid bed granulation:
There are different techniques and variation of fluid bed granulator which you can find in different manufacturing industries. Let’s discuss the most commonly seen techniques of fluid bed granulators.
Top spray granulation:
This is the most widely used technique and often seen in manufacturing and processing industries. As the name suggest, it operates by spraying the binder solution from top of the granulation chamber. The hot air for fluidization is introduced from the bottom. It gives uniform granular size with good flow properties. They are common in pharmaceutical and food industry.
Bottoms spray granulation:
The atomizing nozzle is placed at the bottom of granulator chamber. The fluidized particles move upward under the influence of hot air and behave like an upward moving fountain of fluidized particles. The binder solution is sprayed from the bottom and particles are coated as they pass through the spray zone. They give precise coatings and used in controlled release or masked taste formulations.
Tangential spray granulation:
The binder spraying nozzle is attached at a tangential angle to the rotating fluidized powder bed. It creates a swirling liquid-particle interaction momentum. This system is integrated with rotary fluid bed systems. They provide a better control over the structure and thickness of layer. This technique is used with larger size particles.
Rotor fluid bed granulation:
Rotor fluid bed granulation technique-picture courtesy: food feed fine chemicals
This fluid bed system has a rotating disc placed at the bottom of the granulator. The powder particles are fed into this rotating disc which creates a centrifugal force upon rotation and throws the particles outside in granulation chamber creating a spinning fluidized ring of the powder. The binder is sprayed at center or tangent angle colliding with swirling particles. It is used for granules with high mechanical strength and pelletization.
Multi fluid nozzle granulation:
This fluid bed granulation technique has a specialized nozzle which allows multiple fluids to mix. These different liquids can mix inside the nozzle or they mix as they came out of the nozzle creating a fine mist. This technique is used for complex formulations and takes less processing times with fewer steps. It is used with fertilizers, sensitive chemical granules or combination tablets.
Continuous fluid bed granulation system:
Continuous fluid bed system-picture courtesy: food feed and fine chemicals
This fluid bed granulation system has a continuous operation of powder feeding, binder spray, drying and discharge. It is not like other fluid bed granulation techniques in term of batch systems. It has a nonstop and continuous operating system. They are best suited with high scale industries production and provide a consistent quality.
5.Applications of fluid bed granulation process:
| APPLICATIONS | FEATURES |
| Pharmaceutical Industry
Granules compressed to form tablets |
This is the main application that comes to mind when you hear about fluid bed granulation. It is used to make granules for tablet compression and capsule filling. It improves the flow properties, compressibility of powders. The controlled released and taste masked granules are prepared through it. It gives effective combination of multiple active ingredients in a single granule. |
| Chemical Industry
Chemical granules-picture courtesy: dissemination of IT |
In the chemical industries, fluid bed granulation process is used to make stable and dust free granules from chemical powders. It provides uniform and safe distribution of active chemicals. The sensitive and reactive chemicals are efficiently coated in it. |
| Food Industry
Picture courtesy: cryo drying |
In food industry, there are powdered food ingredients like cocoa, milk powder or instant soup which granulated through fluid bed granulation process. The instant and rehydrate able processed foods are made through this technique. It allows the encapsulation of flavors and nutrients in granule form. |
| Agriculture & Fertilizers
Fertilizer granules-picture courtesy: METSO |
The production of granulated fertilizers and pesticides is made through fluid bed granulation process. These fertilizers granules are used for a controlled release in the soil. This technique reduces the dustiness and keeps the environment free from pungent fertilizers. |
| Detergents & Cleaning Products
Detergent granular powder-picture courtesy: toms guide |
There are detergents available in the form of granules. These detergent granules are made free flowing and water soluble using fluid bed granulation process. This technique also allows the addition of fragrance or enzyme encapsulation of the granules. There is no caking or clumping in the detergents and cleaning products make this way. |
| Nutritional & Herbal Products
Matcha tea powder granules |
The plant extracts, herbal powders or multivitamins are granulated using this fluid bed granulation process. The shelf life and uniformity of these dense and difficult powders is improved through granulation. The granules are easy to use, easier to swallow in the form of capsules, filled sachets or can be compressed into tablets. |
6.Parameters that matters! (critical process parameters):
There are several critical parameters in fluid bed granulation process which must be monitored and carefully controlled. These parameters hold a significant importance because they directly affect the quality of granules produce through fluid bed granulation process.
These are the following parameters:
| Parameters | Why It Matters | Typical Range |
| Inlet Air Temperature | It is the temperature of hot air entering the granulator chamber. If it is too high it will over dry the granules or even melt them. If it is too low there will be wet granules at the end with sticking issue. | 60-90̊C |
| Air Flow Rate | This is the amount of air which is utilized to fluidize the powder particles. If it is too much, the powder bed will not be stable or may blow out. Too little air will cause incomplete fluidization with poor mixing and wet spots. | 200-400m³/h |
| Binder Spray Rate | This is the rate at which the binder liquid is sprayed over the particles. If the rate is very high it will cause the granules to sticking, agglomeration or over wetting. Very low rate can result in weak and poorly bonded granules. | 10-50g/min or ml/min |
| Atomization Air Pressure | It is the pressure of air that converts the binder into fine droplets. Very low pressure can cause large droplets and thus over wetting of the powder. High pressure is good and gives a fine mist with better distribution of binder but excessively high has risk of spray drying. | 1.5-3.0 bar |
| Granulation Time | It is the total time which is utilized for spraying and granule formation. Optimum time should be followed, because if time is too short it will cause incomplete granulation. Very long time can also damage the granules making the, dense or over growth. | 20-40 minutes |
| Product Temperature | It is the temperature of fluidized powder bed. It is the key feature to prevent over heating or under drying. It should be kept in a valid range for consistency in quality and proper binder activation. | 40-60̊C |
| Binder Concentration | It is the percentage of binder which solidifies in the liquid spray. It should be a balanced binder mix for an ideal hardness of granules. A very high concentration can cause highly viscous clumps and also poor sprayablity. If the concentration is very low it will give weakly bonded dusty granules. | 5-15% w/w (solid content) |
It should be kept in mind that all these parameters are interdependent. It means they are directly linked and dependent upon each other. The change in one parameter will exert a direct effect on the other parameter. Therefore, it is recommended to carefully optimize this parameter together in order to achieve successful and efficient granulation.
Conclusion:
Now you must have been well familiar with the fluid bed granulation process. The versatility, efficiency and advancement of fluid bed granulation process is widely adopted and extensively utilized in pharmaceutical industry, chemicals manufacturing, food processing industries and even agriculture. The combining of all the multiple stages of fluidization, atomization, granulation and drying in a single system make it a granulation favorite. To ensure production of fine quality granules, it is important that operator is well familiar and completely understands each stage. Each stage is equally important and has a significant role in maintaining process consistency. For more interesting information feel free to visit our AIPAK website.
Granulator Machine Related Products
Granulator Machine Related Posts
Granulator Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586

Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box? Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter, we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machin