Tablet In Pharmaceutics: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Are you looking for effective discussion related to tablets in pharmaceutics? This blog is mainly created to explore basic aspects of tablet dosage formulation. The aim is to provide fundamental details such as types, specification, major characteristics, and all significant tips and tricks hidden behind the core of pharmaceutics.
So don’t crush the pill to find what’s inside it! First, learn about the major points described in ‘Tablet in pharmaceutics: The Complete FAQ guide in 2025’. Let’s learn!
1.What is tablet in pharmaceutics?
Tablet In Pharmaceutics
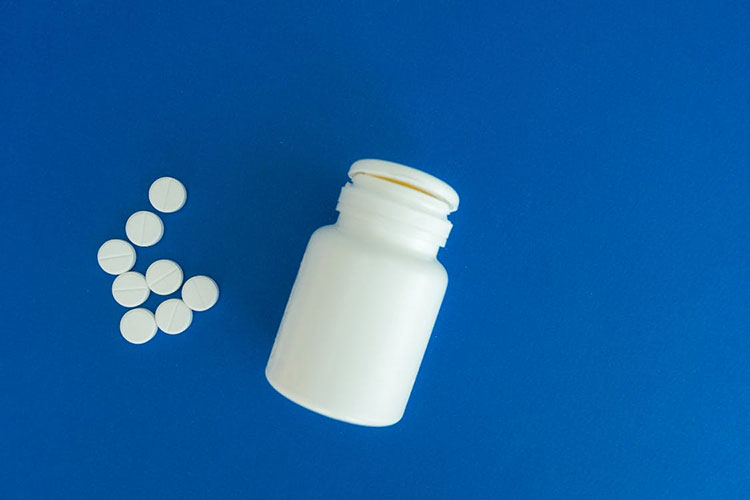
A solid medicine that you take orally is known as a tablet in pharmaceutics. However, it may contain one or more active ingredients along with extra substances that help shape or protect it. Thus, all ingredients are compressed into a firm and uniform shape using a tablet press. Each type is designed to release the medicine in a specific way, based on the treatment goal.
Tablets are produced in large quantities in pharmaceutical industries and indicated in clinics, hospitals, and homes, making them the most common dosage form in modern pharmaceutical practice.
2.What is the history of tablet in pharmaceutics?
History of Ancient Tablet in Pharmaceutics
Today, tablets remain the most widely used and advanced oral dosage form worldwide but the history of tablets dates back to ancient Egypt, Greece, China, and India, where crushed herbs and minerals were mixed with honey or fats to form pill-like doses.
During the Islamic Golden Age and medieval Europe, apothecaries, people who made and sold drugs, refined these into powders and lozenges, though remained inconsistent was still a problem.
In 1843, William Brockedon invented the first tablet press, making mass production possible. By the late 1800s, companies like Bayer and Merck produced uniform tablets. The 20th century brought innovations like sugar coatings, enteric protection, and extended-release systems.
3.Why Tablet in Pharmaceutics Always High in Demand?
For doctors, pharmacists, and patients, tablets became the most practical choice. As healthcare systems modernized, tablets became the global standard and offered the following key benefits.
Easy to Carry and Store
Compact And Travel Friendly Tablet
Tablets are small, lightweight, and stable, which makes them easy to carry in your bag or store at home without needing special conditions like refrigeration. Their solid form also helps preserve the drug's strength over time.
User-Friendly and Non-Invasive
User Friendly
Taking a tablet is simple, quick, and doesn’t require any help or special equipment, which is why most people recommend swallowing a tablet over taking an injection or syrup. This ease of use improves patient compliance, especially for those on long-term treatments.
Accurate and Consistent Dosing
Precision in Every Dose
It is easier for your doctor to prescribe and monitor your treatment every time using tablets, as each tablet contains a specific amount of the active ingredient. It also reduces the risk of underdosing or overdosing, which is especially important in long-term or critical care.
Cost-Effective for Mass Production
High-Speed Tablet Machines
Pharmaceutical companies can make millions of tablets a day using automated machines, which lowers the cost and increases availability, plus tablets are faster and cheaper to produce in large quantities.
Wide Range of Options
Wide Range Of Options
As you know, tablets come in many forms: coated, chewable, sublingual, and extended release. This variety helps tailor your treatment based on how quickly or slowly the medication needs to act in your body.
Long Shelf Life
Long Shelf Life
Unlike liquid medicines, tablets are less likely to spoil or degrade over time. This stability makes them ideal for storage, transport, and emergency medical supplies. Their extended shelf life also reduces waste and ensures medicines remain effective until the expiration date.
4.What are common types of tablet in pharmaceutics?
Tablets are solid dosage formulation in pharmaceutics designed to deliver specific amount of required active ingredients into the body through various routes, for treatment purposes. Below are some common types of tablets in pharmaceutics:
Based on Disintegration Profile
In pharmaceutics, the term disintegration refers to how fast a tablet breaks down into smaller particles after it is administered, which affects the level of absorption. Based on disintegration, the tablets are classified as follows.
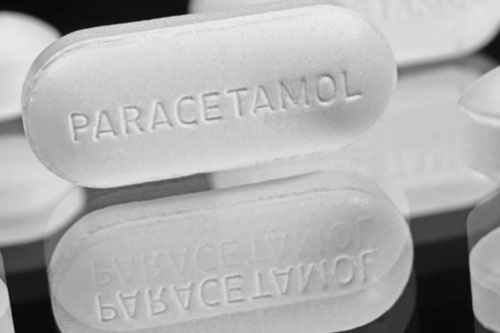
| Immediate Release Tablets
Paracetamol Tablets-Picture Courtesy: The Guardian |
Immediate release tablets are designed in such a way that they will break apart rapidly after swallowing them. They release active ingredients of the drugs into the bloodstream without any delay leading to faster absorption and quick onset of action. Common examples of immediate release tablets are pain killers and fever medicines, in which immediate relief is required. |
| Extended Release Tablets
Extended release tablets-Picture Courtesy: KrKa |
These types of drugs are specially designed for their gradual release over an extended period of time. The extended release of medication ensures uniform drugs supply in the bloodstream, reducing the need for frequent dosing which leads to effective treatment process. Remember to not chew or crush these tablets as it would destroy its specified time-release mechanism. |
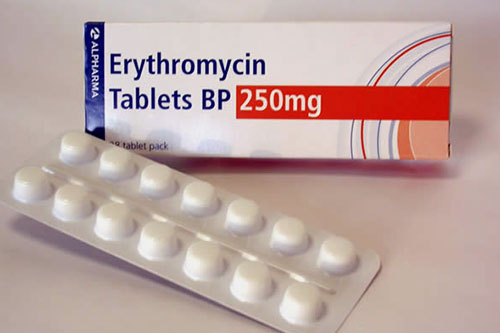
| Delayed Release Tablets
Erythromycin: Delayed release tablets-Picture Courtesy: African Health Sciences |
Delayed release tablets are manufactured to release the active ingredients after specific time, usually when they reach a certain part of digestive system such as intestines. These tablets have an enteric coating which protects them from stomach acid. Their delayed action helps the body prevent stomach ache and irritation. |
Based on Types of Intakes
In pharmaceutics drugs are specially designed according to their specifications. Some of the drugs have a certain mode of intake, according to which they are classified as follows.
| Chewable Tablets
Chewable Tablets-Picture Courtesy: sagar medpharm |
Chewable tablets are designed to be chewed properly before swallowing them. They are offered in different flavors, making it ideal for children, elderly patients or anyone who faces difficulty in swallowing tablets. The chewing process breaks down the drugs, allowing the absorption process to start sooner. |
| Sublingual Tablets
Sublingual Tablets-Picture Courtesy: dixie |
Sublingual tablets are placed under the tongue where they are dissolved quickly with the help of a tissue under the tongue called sublingual mucosa, this helps rapid absorption of the drugs into the bloodstream. |
| Buccal Tablets
Buccal tablets- Picture Courtesy: Persona Nutrition |
Buccal tablets are designed to be placed in the buccal cavity, an area between gum and inner cheek, where they are slowly dissolved with the help of buccal mucosa into the bloodstream. These kinds of tablets prevent stomach irritation by their sustained release. |
| Effervescent Tablets
Effervescent Tablets-Picture Courtesy: Wallabay wellness |
Effervescent tablets are designed to be administered after dissolving in water. When they are dissolved in water, they release carbon dioxide, turning the water into a fizzy solution. This process makes the absorption quicker and easier. |
Based on Composition
Tablets based on composition are group according to their ingredients, especially combinations and excipients. Composition based tablets are as follows.
| Single-layer Tablets
Single-layer Tablets |
These kinds of tablets are designed to have a single consistent layer, which consist of active ingredients and excipients. Single-layer tablets are the most basic form of tablets; they are most commonly used because of their immediate release and faster onset of action. |
| Multi-layer Tablets
Multi-layer Tablets-Picture Courtesy: Pharmaceutical Technology |
These kinds of tablets are designed to have two or more discrete layers, each layer contains different combination of active ingredients and excipients. The different layers are because of incompatible drugs or specific release rate effects. They are frequently used when there is a need to administer multiple drugs in one tablet. |
| Compressed Tablets
Compressed Tablets-Picture Courtesy: Colorcon |
Compressed tablets are the most frequent type of tablets. They are meant to compressed into a uniform mixture into a solid dose, with the help of high-pressure automated tablet machine.
They are immediate release drugs, allowing the active ingredients of the tablets to be quickly absorbed in the bloodstream for a fast onset of action. |
| Orally Dispersed Tablets (ODTs)
Orally dispersed tablets-Picture Courtesy: Dec Group |
Orally dispersible tablets are designed in a way that they disperse in water before administration. after dissolving the tablet, the solution is consumed orally. They are ideal for children or elderly patients, who find it difficult to swallow tablets. |
| Specialized Tablets
Specialized Appealing Tablets- Picture Courtesy: Mydr.Au |
Specialized tablets are designed to have a unique and distinct formula; they are manufactured to meet specific therapeutic requirements or to enhance drugs efficiency. These tablets consist of advance technologies such as protective coatings and controlled release system, to avoid stomach irritation. |
5.What are the common shapes and sizes of tablets in pharmaceutics used?
Shapes And Sizes Of Tablets In Pharmaceutics
The common shapes and sizes of tablets in pharmaceutics are:
Common shapes of tablets in pharmaceutics
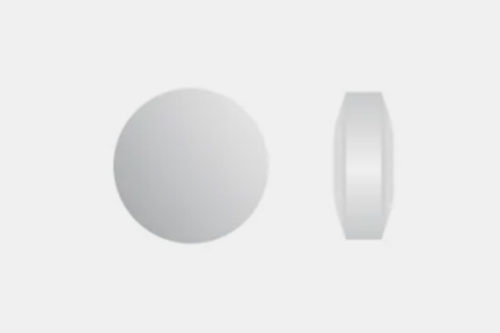
| Standard convex
|
A standard dome shape pill in round or circular edges, such as paracetamol. |
| Standard convex bisect
|
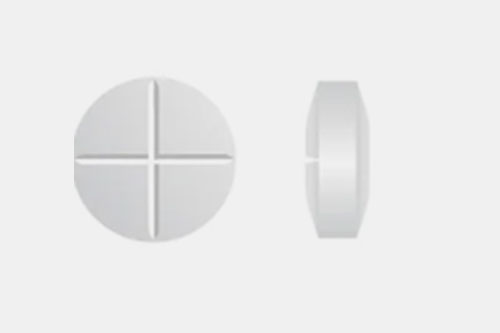
This is a standard shape with a provided section for easy breaking, such as the antihypertensive agent metoprolol. |
| Standard convex straight through bisect
|
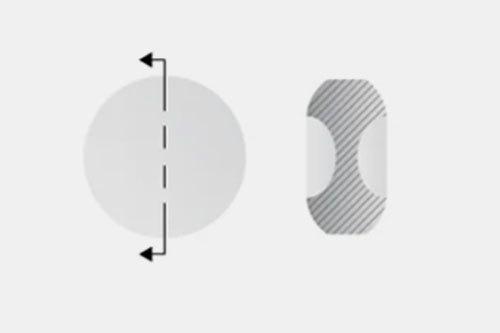
A convex shape with a straight cut line, such as levothyroxine. |
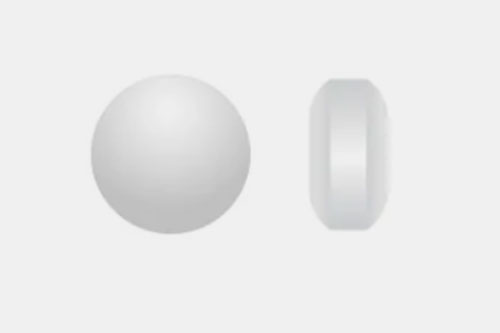
| Compound cup
|
This is mostly designed for supplements presenting a concave cup shape, such as docusate calcium. |
| Standard convex quadrisect flush
|
The tablet is presented with 4 breakage lines and mainly available genera are tizanidine hydrochloride muscle relaxant. |
| Convex bevel
|
This is domed at the upper sides with flattened corners, such as vitamin C tablets. |
| Flat faced plain
& with edges |
All around tablet shape is flattened, such as the calcium channel blocker amlodipine. |
| Flat-faced radius
|
This is presented with flat face and smooth light curves, such as the blood thinner clopidogrel. |
| lozenge
|
These are mainly oval shape tablets that looks like lozenges, such as antidepressant Xanax. |
| Capsule shaped tablet
|
A capsule-shaped tablet is commonly available in muscle relaxant genera such as methocarbamol. |
| Square
|
An attractive shape with a four-sided corner tablet that looks like a square such as montelukast singulair 117. |
| Diamond
|
This exactly looks like a rhombus-shaped tablet, such as Viagra. |
| Pentagon
|
A tablet with five corners or smooth edges, such as Cyclobenzaprine which is muscle relaxant. |
| Hexagon
|
A six sides shaped tablet with or without sectional line such as Inderal a commonly used antihypertensive agent. |
| Almond
|
The tablet shape in almond, which is round with sharp edge, such as tadalafil that’s used as impotence agent. |
Common sizes of tablet in pharmaceutics
Common Sizes Of Tablets In Pharmaceutics
Generally, tablets in pharmaceutics sizes vary between 1 mm and 22mm. It is all about based on the requirements, the type of population, and the materials to be incorporated into it. The designed studies are done before it's made and consider the necessary changes. According to based on size the tablet in pharmaceutics is categorized into the main types:
Large Size Tablet in Pharmaceutics

Large tablets in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: Oaklife vitamin |
According to the guidance published in June 2015, the large-sized tablets in pharmaceutics must not exceed dimensions of 22mm.
For example, a calcium supplement tablet is considered a large tablet with a size of 18mm. However, the size of the tablet cannot be swallowed; rather, it is dispersed in water prior to intake. |
Standard-Size Tablet in pharmaceutics
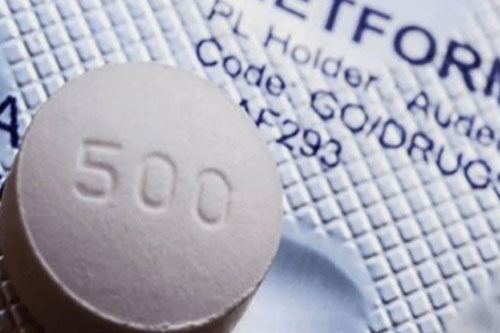
Standard Tablets In Pharmaceutics |
The standard size of tablet in pharmaceutics varies in between 5 mm to 10 mm where oblong or circular shape is mainly used. Moreover, it can hold the typical weight of 200 mg to 500 mg. the commonly used example in this case is aspirin, paracetamol, or ibuprofen. |
Mini Tablet in pharmaceutics

Mini Tablets in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: Losan Pharma |
This is usually considered as a slow-running tablet in pharmaceutics, which is not used in general applications.
The sizes of these tablets vary between 2 to 4 mm in dimension. The commonly used examples used in these categories are contraceptive tablets, hormonal therapy, enzymatic therapies such as thyroxine, and others. |
6.What is basic composition and material properties of tablet in pharmaceutics?
Composition of Tablet In Pharmaceutics
Despite to contrary belief, tablet in pharmaceutics isn’t just drug material but rather, there are other useful components called excipients present in them. They’ve a role in maintaining the stability of the tablet and supporting its desired formation and delivery. So, let’s have a look at basic composition and excipient properties of tablets:
Active Ingredients
First and foremost are active ingredients and are considered the star of the show when it comes to tablets in pharmaceutics. Indeed, they’re the active drug ingredient that confers therapeutic effect. They’re potent substances that are used for treating disease condition or relieving symptoms of disorder in body.
Excipients
As you probably know that they’re inactive component in tablet, not used for their therapeutic activity instead they help in tablet disintegration in gut or keep it stable until its consumption. Some excipients are:
| Binders | Also termed as adhesives and are the ingredients that provide cohesion to tableting materials. They’re integral in compressing powders and offer mechanical strength that holds the materials together in the tablet. |
| Disintegrants | As the name suggests, they help in breaking, fragmentation, or disintegration of tablets into their consistent components when the medication is exposed to the fluid of the gastrointestinal tract. Yes, they help release API in the stomach or intestine, consequently facilitating their absorption. |
| Bulking Agents | To bulk up tablet materials, typically, excipients called bulking agents, binders, or fillers are used. With these substances, pharmacists increase the mass of the active ingredient dose so that it is easily handled and compressed. Moreover, fillers also boost the cohesivity of powders in tablets. |
| Glidants | Sometimes, tablet powders have minimal fluidity, so to counter this issue, you generally use glidants when making tablets. This not only increases the flow of materials from the hopper into the die cavity but also allows evenness of material fill in a cavity, leading to uniform tablet weight. |
| Absorbents | In some cases, you also add absorbent materials, for instance, colloidal silicon dioxide or kaolin, to the tablet blend. These substances are integral moisture or liquid, producing dry powder. |
| Lubricants | Friction is a common phenomenon when you’re compressing powders in a die cavity. Therefore, lubricants are included in powder blends to produce tablet in pharmaceutics. With this, frictional forces between powder ingredients and components of the tablet press are reduced. In this way, issues like sticking and wear of tooling are reduced. |
| Flavoring Agents | This is no secret that tablet ingredients are quite bitter; therefore, they are deemed unpleasant by patients. So, tablet in pharmaceutics is made with flavoring agents that mask the taste of bitter compounds. They also increase the pliability of chewable or oral disintegrating tablets. |
| Coloring Agents | They are used not only for aesthetic purposes but also help patients in distinguishing between various tablets and their doses. |
7.How to manufacture tablet in pharmaceutics?
Manufacture Tablet In Pharmaceutics
After learning about the composition of tablet in pharmaceutics, you might be wondering how tablets are formed in the pharmaceutical industry. So, to put your mind at ease, here we’re describing some basic steps in making this dosage form:
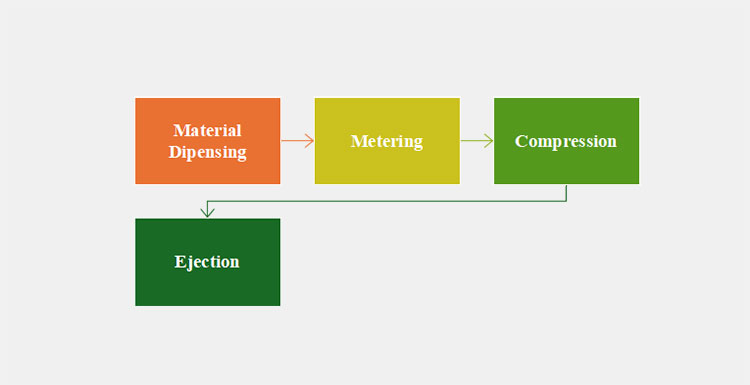
Steps in Manufacturing of Tablet in Pharmaceutics
Material Dispensing
In this first step, the powder or granule materials are carefully weighed and then dispensed inside the die cavity from the hopper. They flow inside the die bore of tablet press, either by gravitational force or with mechanical assistance.
Metering
Once, the die core is filled with tablet materials, the lower punch of the tablet press is pushed upward or raised to metering position. Owing to this, surplus material is removed from the die bore. Using swipe blade, this excess powder is scrapped off from die surface. This step is integral in controlling powder volume and thus, regulates weight and dosage of final tablets.
Compression
Now that die cavity is precisely filled, the upper punch descends down into the die, and at this exact time, the lower punch moves up. You can imagine this step as both punches moving towards each other. This movement leads to exertion of intense pressure on the powder or granules, resulting in their compaction or compression.
Hence, the materials in the die cavity are converted into a tablet.
Ejection
Finally, as soon as compression of the tablet is successfully performed, the upper punch moves back in its original position (upward towards turret). Simultaneously, lower punch ascends, leading to the ejection of newly created tablet from die bore. Scrapper then moves the ejected tablet into the collecting bin.
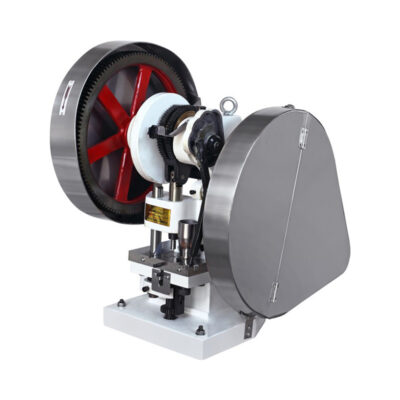
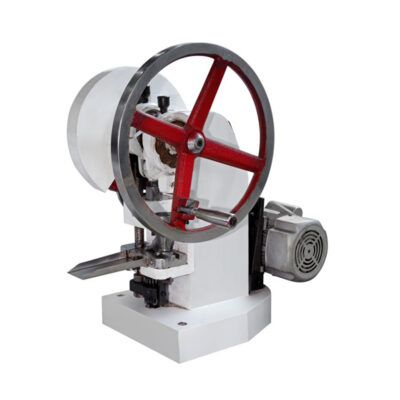
8.What machine is used for compressing the tablet in pharmaceutics?
You can find the main units utilized in to manufacture tablet in pharmaceutics are described below:
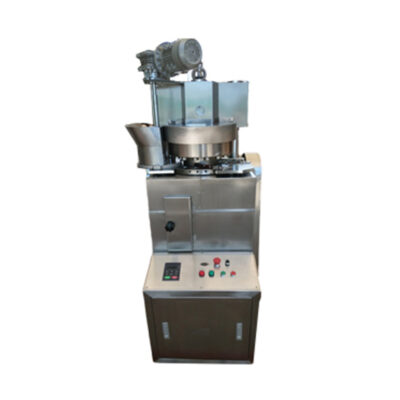
| Single Punch Tablet Press Machine | ||

AIPAK Single punch tablet press |
This is a very simple addition and used for limited production of tablets in pharmaceutics.
The single punch machine is also popular as an eccentric press’. It is designed with one die and a pair of punch. The fixed quantities of ingredients are measured and direct poured into the punch. Upon pressing the manual handle the punch die fixes the material and can form a tablet which is ejected from the die via manual ejection. |
|
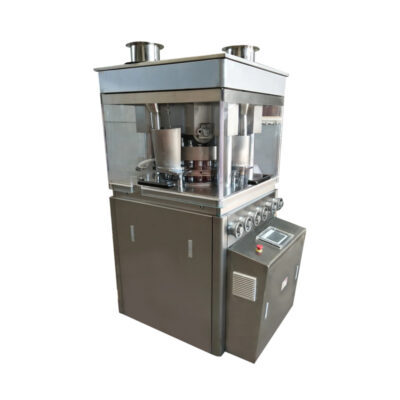
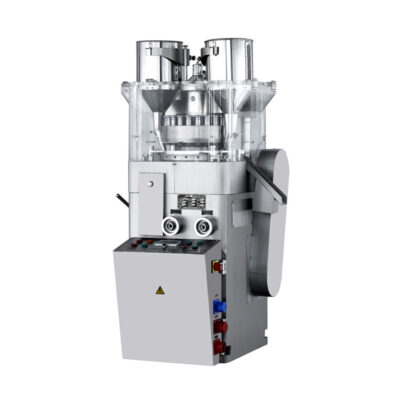
| Multi Station Rotary Tablet Press Machine | ||

AIPAK Rotary Tablet Press Machine |
The machine is considered as an ideal option when it is required to manufacture the large quantities of tablets in pharmaceutics.
The rotary tablet press is composed of multiple punches around the circulatory turret. Upon rotation of turret the punches moves, and each punch fills the powder and compression of other punch makes firm tablets of the same sizes. |
|
9.What are the machines of tablet in pharmaceutics production line?
Industrial Production Of Tablet In Pharmaceutics
The commonly utilized industrial production line for tablet in pharmaceutics are enlisted below:
| Tablet Metal Detector
|
This machine is mainly installed to pick or detect the presence of metallic particles attached to the surface of tablet. By this, metal cross contaminants are also detected and eliminated with the help of metal detectors. |
| Tablet Deduster
|
During manufacturing tablet in pharmaceutics, the tablets surfaces are encountered with various dust particles of powders. This could be either APIs, excipients or from atmospheric dust. The tablet deduster helps in the brushing over the surface in a delicate manner and ensuring excessive dust is removed completely. |
| Tablet Coating Machine
AIPAK tablet coating machine |
A tablet coating machine is often used when you make sustain or controlled release tablets and other. The machine is specialized in customized coating including sugar coating, enteric coating etc. the machine used are standard coating, fluidized bed coating etc. |
| Tablet Counting Line
AIPAK Tablet Counting Line |
The tablet counting line is the extensive solution of subjecting wholesome setup of integrated machines instead separate units. This is included with bottle unscrambler, tablet counting machine, desiccant insertion machine, capping machine, induction sealing machine and a labeling machine.
Therefore, the counting line offers an excellent solution that 100 % satisfies your production needs error free and fast workflow. |
| Blister Packaging Machine
AIPAK Blister Packaging Machine |
The blister packaging machine is a compact unit with comprehensive operating features. It helps in the formation of molding pockets or cavities for individual tablets by utilizing the features of mesh heat seal. Hundreds to thousands of tablets per hour can be treated for packaging using this machine. |
| Cartoning Machine
AIPAK Automatic Cartoning Machine |
The cartoning machine is an advanced unit that is responsible for the formation of boxes/cases/cartons to place primary packaging content. For example, tablets or capsules in blister/strip packaging or in bottles, they’re packed in cartons respectively. |
10.What are the major processing problems of tablet in pharmaceutics?
The Main Problem Of Tablet In Pharmaceutics
Tablet processing is a complex procedure that requires precision and attention; several problems could occur during the process. Some of them are mentioned below.
| Problems | Description |
| Capping
Tablet Capping Issue |
Capping is the most common problem while processing tablets; it occurs when either the top or bottom part of tablet breaks. This can affect drug uniformity and efficiency.
In order to prevent capping, use accurate compression force and an appropriate formulation. |
| Lamination
Laminated Tablet |
Lamination occurs when the tablet is split into two or more layers during or after the compression process, which affects the tablet's integrity.
To avoid lamination, ensure there is no air trapped in the powder blend during the process of compression. |
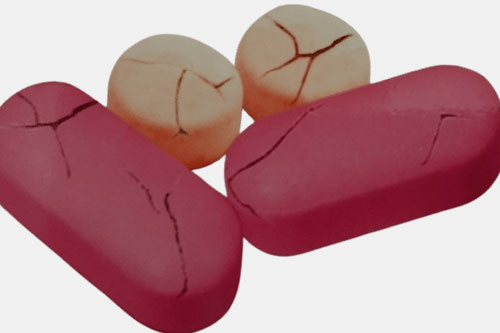
| Cracking
Visible tablet cracks |
Tablet cracking refers to the visible fractures and cracks present on the surface of tablets, resulting from the stress on the tablet structure.
To avoid cracking of the tablet, you must adjust the compression force and enhance drying conditions. |
| Sticking
|
Tablet sticking happens during the compression process, when the tablets sticks to the punch faces due to excessive moisture. This issue leads to defects and tablet degradation.
To prevent the tablet from sticking, use appropriate lubricants, reduce excess moisture and adjust the formulation. |
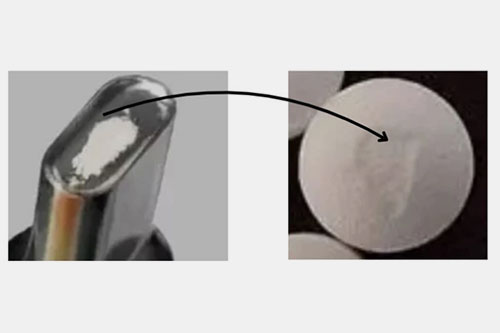
| Picking
Engraved logos on tablets |
Picking issue occurs when a piece of tablet sticks to the punch, particularly to engraved letters or logos.
To avoid picking issue, use fine polished punches and use anti-adherents. |
| Chipping
Tablet chipping |
Chipping occurs when small pieces from the tablet edges are broken, affecting the tablet integrity.
By enhancing binder concentration and drying conditions, chipping can be avoided. |
| Mottling
Mottling |
Mottling occurs when the tablet has uneven distribution of colouring, leading to a spotted or defected look, it usually happens due to mixing or formulation issues.
To prevent mottling issues, improve blending consistency and use proper colorants. |
| Weight Variation
Weight Variation |
The weight variation problem occurs when there is inconsistent granule flow or fluctuations in feeder performance, leading to distinct tablet weights.
Ensure consistent and equal granule size and continuous feeder calibration to prevent weight variation issue. |
11.What are the evaluation points of tablet in pharmaceutics?
Quality Assessment Of Tablet In Pharmaceutics
In pharmaceutics, there are several ways a tablet is evaluated to ensure its safety and stability. The key evaluating parameters include.
| Hardness
Tablet Hardness Tester |
Tablet hardness refers to the pressure level that is required to break the tablet during the compression process. It shows the tablet’s mechanical strength and resistance. This evaluation test is carried out to ensure that the tablet is strong enough to resist defects during the manufacturing process. The instruments used for testing tablet hardness are Monsanto hardness tester, Pfizer hardness tester, and more. |
| Disintegration Time
Disintegration test apparatus-Picture Courtesy: Electronics India |
Disintegration time is the amount of time a tablet takes to break down into smaller granules when placed in water or simulated gastric fluid. The primary purpose of measuring disintegration time is to ensure that the tablet will start its action within a specified period after ingestion. A disintegration test apparatus is used for disintegration time evaluation. |
| Weight Variation
Weight, thickness and hardness tester-Picture Courtesy: VORTEX Sales Group |
Weight variation evaluation test ensures that each tablet in a batch contains a uniform and equal amount of active ingredients them, by checking their weight. This testing is crucial because difference in tablet weight will affect drug efficacy and lead to inconsistent dosing. Analytical balance instrument is usually used for weight variation testing. |
| Friability
Tablet friability tester-Picture Courtesy: Blibi |
The friability test evaluates how a tablet reacts when subjected to mechanical stress, how long the tablet takes to crumble, chip, or break under pressure. The instrument used for this test is called a friabilator. It shows the physical strength and durability of the tablet. |
| Diameter and Thickness
Vernier calliper- Picture Courtesy: Altronics |
Thickness and diameter are physical dimensions of a tablet. These measurements are taken through specialized instruments called callipers or micrometers. This measurement evaluation test is taken to ensure the tablet consists of an accurate dose and it is of a similar size and shape. The instrument used for evaluating thickness and diameter is called a vernier calliper and screw gauge. |
Conclusion
Today’s world of tablet in pharmaceutics is highly regulated and well demand. There are different types related to their target actions, sites, release, shapes, etc. What you need is prior knowledge and advanced machines. In this blog, we tried our best to talk about all aspects briefly. Are we still missing some points that you are looking for? Then please contact our team to get answers. Moreover, for excellent machines and learning, check AIPAK products and buying guidelines to explore.
Don't forget to share this post!
Tablet Press Machine Related Posts
Tablet Press Machine Related Products
Tablet Press Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine