Exploring Different Types of Tablets in Pharmacy
In pharmaceutical settings, tablets are the most convenient way of administering medicine. You may have come across tiny mint size tablets as well as large disc like tablets that creates a fizz in the glass of water. They have so much variation. These little power houses with so much pharmacological effects come in many shapes and sizes, definitely more than most people know and realize.
The shape, size and type of tablet are not just random decision but a well calculated plan, involving pharmaceutical technology and physiological parameters. The tablet is designed after complete assessment of how the tablet should work, how to make it easier to swallow or how to protect it from the stomach acid.

So next time whenever you come across a pill, there’s a lot more going on behind that little tablet you are looking at. Let’s explore more about the different types of tablets and the reason behind those different types in the following editorial!
1.What is a pharmaceutical tablet?
Different pharmaceutical tablets
A pharmaceutical tablet is an oral dosage form made by compressing of the fine powder or granule containing single or more than one active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). A tablet contains active pharmaceutical ingredient along with excipients which are disintegrants, binders, lubricants, colorants and coating sometimes. The compression of powder into tablet form can be in any shape including round, sphere, and square, oval.
2.Exploring different types of tablet in pharmacy – Main types:
The tablets in pharmacy come in a wide variety with different shapes, sizes and types. The following classification explains different main types of tablets in pharmacy.
Based On The Release Mechanism:
Immediate Release:
Paracetamol is the most commonly available immediate released tablet-picture courtesy: pharma excipients
The immediate release tablets are produced in such a way that they disintegrate and dissolve quickly in the body after ingestion. As the name suggests, the active drug is immediately released in the body and becomes available for the absorption without any intentional delay. This release is within minutes of administration.
There is no special kind of coating on these tablets. The coating if present is a very thin film coat which masks the pungent taste or smell of the drug. The purpose of these immediate release tablets is to provide a fast onset of action especially in case of pain killers, infections or other emergency medical conditions. They are best suited for drugs that do not require a prolonged or controlled release.
Composition & Mechanism of Immediate Release Tablets:
The main composition is the active pharmaceutical ingredient which is the actual drug. It is accompanied by excipients among which disintegrants plays the most crucial role for immediate release of the tablet. Disintegrants like sodium starch and croscarmellose sodium helps the tablet to disintegrate rapidly when they come in contact with gastric fluids.
This leads to dissolution of API and absorption starts in the blood stream. The immediate release tablets have a simpler manufacturing and give a quick relief from the symptoms of disease or infection. But the drugs with short half-life may require a frequent dosing and they may not suitable with drugs that require slow absorption.
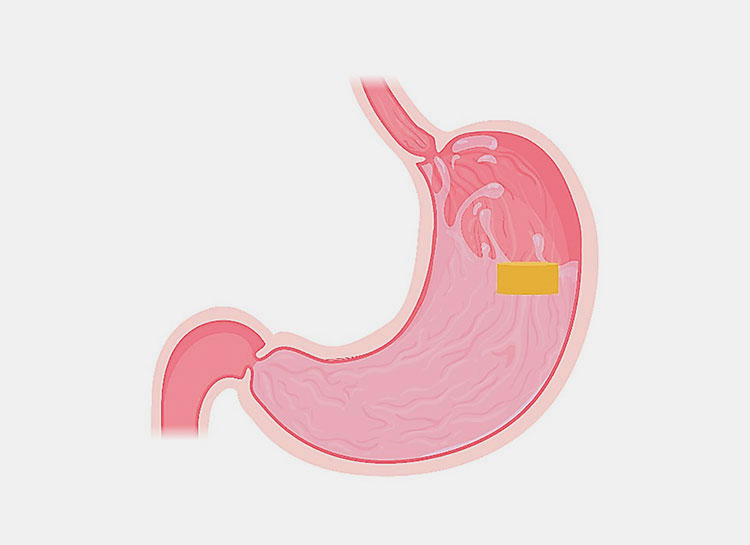
Delayed Release / Enteric Coated :
Aspirin delayed release tablets-picture courtesy: healthiza life sciences
Delayed release tablets are designed in a specific way so that the drug is not released immediately after ingestion. The release of the active ingredient in delayed release tablet requires a specific time delay and they require a specific pH for absorption. They usually release the API once the tablet reaches the intestine
The coating is special and pH sensitive. It protects the tablet from acidic stomach pH and prevent from dissolving. The dissolution occurs when the tablet reaches the alkaline environment of the small intestine with pH ranging from 5-7. The release of API happens after a lag time which is the time taken for the tablet coating to dissolve.
Composition & Mechanism of Delayed Release Tablets:
The API of the delayed release tablets can be irritating to the stomach and also sensitive to the stomach acid. This is why they have coating polymers like Cellulose acetate phthalate or methacrylic acid copolymers which remain intact in the stomach. The dissolution start upon reaching a higher pH and there API is release in the intestine.
The delayed release tablets protect the drug from stomach acid and also well suited when target intestinal drug delivery is required. The manufacturing of delayed release tablets is more complex and costly and they may cause dose dumping if the coating of tablet is damaged.
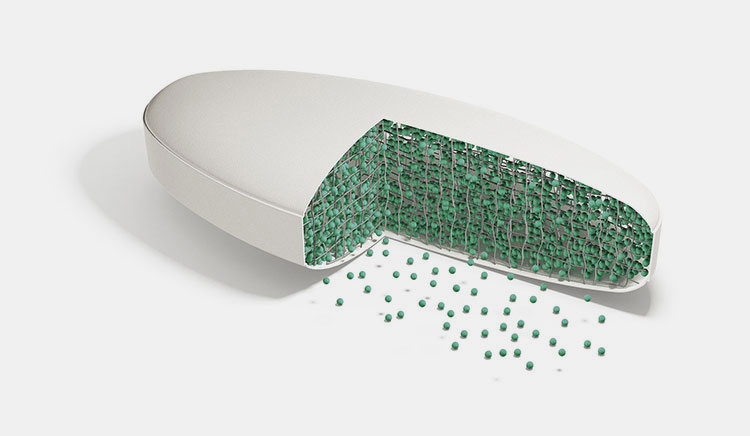
Extended Release /Sustained Release (SR, ER, XR):
Internal view of extended release tablet-picture courtesy: Krka
The extended release, sustained release or controlled release is the name given to all those form of tablets which are designed in such a way that they release the drug over a controlled and extended period of time. These tablets release the drug slowly over an extended period of time and also maintain a steady drug concentration in the body for a longer period of time.
Composition & Mechanism of Extended Release tablets:
There are special drug control release systems which are applied in the composition of the extended release tablets. These systems instead of dumping the entire drug into the body control the escape speed of drug. It can either be diffusion of drug or tablet slowly breaks down which is erosion or it could be due to osmotic pressure in which water gets into the tablet and slowly pushes out the drug.
These extended release tablets do not require frequent dosing and maintains a steady drug levels in the body so there is very less risk of side effects. But they also come with most expensive manufacturing coast and also cause dose dumping if tablet is chewed or broken.
Based On The Type Of Compression:
Standard Compression Tablet:
Standard compress tablets
These are the standard and most basic compressed tablets. They are made using wet granulation or single compression method. All the ingredients including API and excipients are collectively compressed in a single compression step. These tablets don’t undergo further coating procedures. They provide rapid disintegration and release for localized action in the GIT.
Multiple Compression Tablet:
The multiple compression tablets are made by more than one compression cycles. The reason for multiple compression cycles is to give multiple layers, coatings and core of tablet. The active ingredients also required to be separated for stability and for the controlled release rate. These multiple compressed tablets are classified in further 3 categories of coated, layered or in lay tablets.
Coated tablet:
The compressed tablet is further covered with a layer giving a coating to the core of tablet. These coated tablets are produced to mask the smell and taste, protect and the drug and above all these coatings allow the controlled release of mediation. The following explains the type of coated tablets produced:
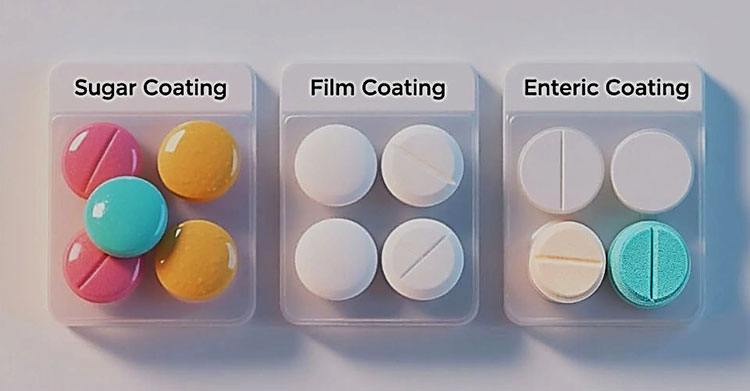
Different types of tablet coating-picture courtesy: jinlu packaging
| TYPE OF COATING | FEATURES |
| SUGAR COATED TABLET | These tablets are coated with sugar syrup to mask the unpleasant taste and smell of drug. This coating also improves the appearance and protects the drug. Sugar coated drugs are larger in size due to multiple layers of sugar syrup and production cost is also increased with longer manufacturing time. |
| FILM COATED TABLET | Film coated tablets are covered with a thin layer of polymer film coating which can be water or organic based. The drug in film coated tablet does not require coating. In fact the coating is done to give structural support to the tablet. Film coating has a faster production than the sugar coated tablet and they are also less bulky. |
| ENTERIC COATED TABLET | The enteric coating in this tablet is resistant to stomach acidic medium and they are dissolved in intestine. Therefore, they are delayed release tablets. They prevent gastric irritation by preventing release of drug into stomach. |
| GELATIN COATED TABLET | These tablets are enclosed in a gelatin layer which can be colorful or opaque. These gelatin coated tablets are much easier to swallow and they offer an attractive appearance |
Layered tablet:
Bilayer tablets with two different active pharmaceutical powders
The layered tablets are produced with compression of two or more layers in a sequence. Thus they can be bilayer or tri layer tablets. They are just like a sandwich in which two or more layers are compressed together. Layered tablets are made when there are incompatible drugs or drugs with different releaser rate are to be compressed in a single dosage. The different layers are given different colors to give a distinction to the tablet.
In lay tablet:
In-lay tablets-picture courtesy: IJCRT
These in-lay tablets are also referred as bull’s eye or dot tablet. These in-lay tablets are very unique in a way that they are not completely coated. The top surface of the tablet is completely exposed. In this way these in-lay tablets can give different release rates. One drug is placed in the core of tablet and other drug is placed in the coating.
The coating of in-lay tablet gives a slow release of drug and core of the tablet gives a fast release of the drug. In this way they are a good choice in sustained released dosage forms due to their less weight and reduced size. They give a combination of fast and slow release medication.
Based On Method Of Administration:
The tablets in pharmacy are although an oral dosage form but these tablets are very versatile and they come with different forms and routes of administration. A few of the form and routes of administration are given below:
Administered In The Oral Cavity:
The tablets administered in the oral cavity are not only simply compressed tablets, but there are other forms also available, these types are given below:
Lozenges and troches:
Honey and lemon lozenges
Lozenges are the type of solid tablet dosage forms which are required to be dissolve slowly in the mouth and gradually release the medication. They are usually designed for local effects required in mouth or throat, like antiseptic or anesthetic purposes. There are no disintegrants in the lozenges because these are not meant for disintegration.
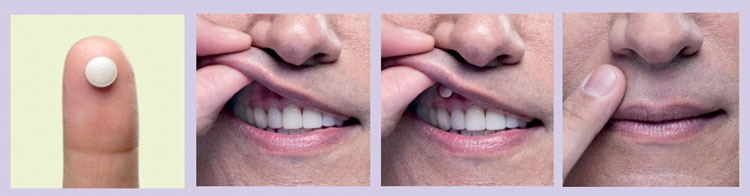
Sublingual tablets:
Sublingual tablet for blood pressure-picture courtesy: shutterstock
Sublingual tablets are just as the name suggest, they are placed under the tongue for an immediate effect. These tablets undergo rapid disintegration and absorbed directly in the blood stream through sublingual mucosa. These tablets are used when rapid action is required. These sublingual tablets by pass the stomach and first pass metabolism which slow down the absorption in other cases.
Buccal tablets:
Buccal tablets have been a rescue from migraine
These Buccal tablets are placed in between the gums and cheeks in the oral cavity. They are designed for a sustained and slow release of medication in the blood stream. Buccal tablets are mostly used in the hormonal therapy and for treating migraines and schizophrenia. There is fast acting as well as long acting buccal tablets from which the medication is slowly release and becomes available for absorption through buccal mucosa.
Dental cones:
Dental cone tablets are a fast way for treating toothache-picture courtesy: spring hill dentistry
These are small cone shaped tablets designed to provide a local antimicrobial action to prevent any kind of further infection following a tooth extraction procedure. These dental cone tablets are placed in the tooth socket where they provide a slow dissolution and maintain antimicrobial effect.
Orodispersible tablets (ODT)
These Orodispersible tablets are rapidly disintegrated inside the mouth without water. They disintegrate under the effect of saliva and provide an easy administration in patients with swallowing difficulties.
Used As Solution:
Effervescent tablets:
Effervescence phenomenon-picture courtesy: yumda
These effervescent tablets are designed to disintegrate as soon as they come in contact with any liquid. These tablets disintegrate and completely dissolve in the liquid making a solution. These tablets contain the acidic and alkaline substances that react in presence of water and release carbon di oxide. This CO2 is the reason of forming bubbles or what you called fizz in the water.
These effervescent tablets mask the taste and provide complete dissolution before even administration of the tablet. This makes the absorption of the tablet faster and easier. This form of tablets is easier to administer in patients with swallowing difficulties.
3.The modern and advance innovations in tablets in pharmacy:
3.1) 3D-Printed tablet:
3-D printed chewable tablets for children-picture courtesy: pharmaceutical journal
3-D printing technology allows the manufacturing of specialized tablets with as required précised shape, size and drug release profiles. This technology allows customizing the dosage formulation as per individual patient needs. 3-D printing technology allows combining complex drug combinations into a single tablet which enhance the patient compliance. These tablets allow controlled release pattern of drugs.
3.2) Floating tablets:
Tablet floating in the stomach-picture courtesy: NDMI
These floating tablets remain afloat in the stomach for an extended period of time without causing an effect on the gastric emptying rate. These tablets have gas generating excipients which keep them afloat in the stomach. The purpose of these tablets is to prolong the retention time of drugs in the stomach. In this way the drugs which are required to be absorbed in stomach and upper intestine have an increase bioavailability.
3.3) Mucoadhesives tablets:
Mucoadhesive tablet for infection in mucosa of gums-picture courtesy: Taylor & Francis online
Mucoadhesives tablets are designed to stick to the mucosal layer inside the body.
These tablets stick with mucosal membrane in the oral, buccal, sublingual or gastro intestinal cavities. The purpose of these tablets is to provide a sustained and targeted drug release. They have polymers which create strong bond with the mucosal membrane for adherence. They not only increase bioavailability but allow a controlled drug release system.
4.How do pharmacists decide which tablet to use-factor affecting the choice of tablet:
Variation in types of tablets-picture courtesy: meer
It is correct to assume that tablets and their types are not just randomly decided but there are some factors behind. The factors which influence the decision of the pharmacist to choose a specific tablet type are given below:
Drug Properties:
The drug solubility, stability and bioavailability are the factors which are needed to consider while deciding the type of tablet. The drugs with poor solubility and stability values are tend to be designed for rapid disintegration or in effervescent form. The drugs are sometimes sensitive to stomach acid due to which they are made enteric coated and designed to be released in large intestine.
Drug Release Profile:
There are immediate and controlled release profiles of the tablets. The pain killers are usually designed in immediate release tablet forms for a rapid relief from the pain. The delayed release drugs offer a long term and sustained effect in the body usually made for once a day drugs. Floating drugs are made for stomach purposes and muchoadhesive drugs targets mucosal issues.
Patient Factors:
Age is a very important factor among other factors that influence the choice of drug. Disintegrating or chewable tablets are preferred for young children while elderly with swallowing difficulty prefers Orodispersible tablets. The patient compliance with smell and taste as well as special needs of the patient is to be considered while deciding the tablet type.
Drug Release and Potency:
The drug release and potency are directly to each other. The highly potent drugs are required to be made modified release or multi layers form for a precise control of the drug levels in the body. The drug requiring high dose may not be suited with small tablet formats hence they are designed as per the requirement.
Manufacturing Cost:
The specialized and tablets requiring advance techniques like 3-D tablets may be expensive and require complex manufacturing. This is the reason they may not be suitable for mass use. The manufacturing capabilities can also influence the designing of a specific form of tablet.
Therapeutic Urgency:
There are emergency conditions like very high blood pressure which require a rapid treatment. The sublingual tablets provide an instant absorption in the blood by rapid disintegration. In case of chronic treatments, once daily or controlled release tablets are preferred.
Patient Lifestyle and Preference:
Last but not the least; patient preference can never be ignored while deciding a tablet. The more the patient complies with the medication and is suitable with his lifestyle the more positive results will be achieved. A good tablet size, ease of administration and single daily dose requirement are preferred by the patients.
Conclusion:
Tablets are versatile and convenient while offering a large variety to attend different therapeutic and patient needs. All these different types of tablets, from conventional compressed tablets to advance 3-D printed tablets, each of them has a specific need. These different types offer different bio availability, drug stability and compliance with the patient. There are many factors which influence the choice of tablet which includes patient age, swallowing ability, drug release profile and goal of treatment. The more advance techniques and variety in the manufacturing of tablet types is making the tablets more patient friendly and first choice of treatment. For more such interesting information you can visit our AIPAK website.
Don't forget to share this post!
Tablet Press Machine Related Posts
Tablet Press Machine Related Products
Tablet Press Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 156 0710 8630
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine