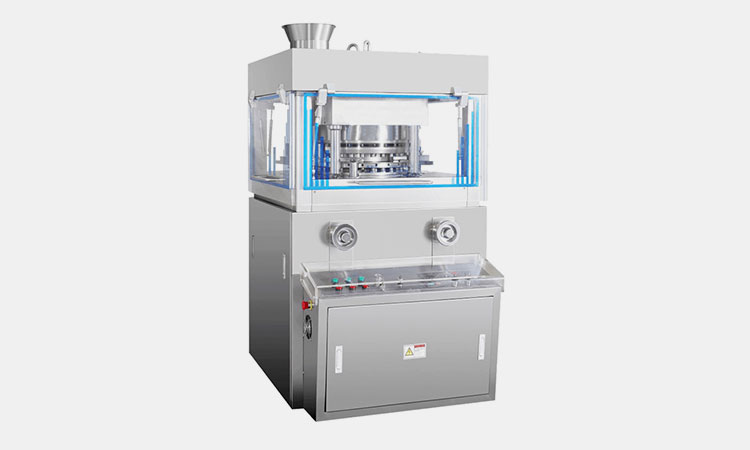
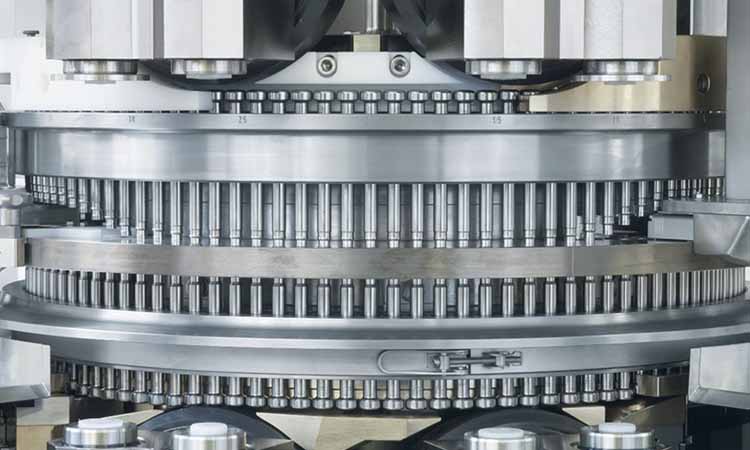
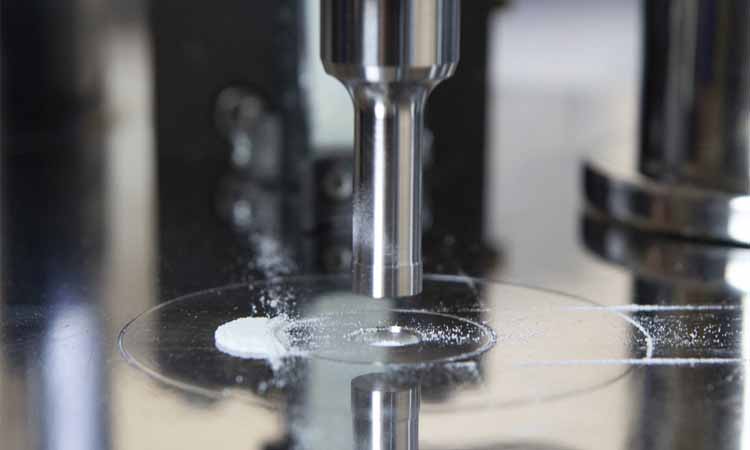
How To Deal With Uneven Pressure In Your Tablet Pressing Process?
Do you know that your tablets are pressed with high skills? The little round and inconspicuous pills are made with great test and complicated manufacturing process. The little ignorance may lead large problem for your tablets appearance and effect. And pressure makes the irreplaceable important work here.
How to determine the appropriate main pressing pressure in pressing tablets? How does uneven pressure affect your tablet? How to deal with uneven pressure in your tablet pressing process? What are the machines applied for tablet pressing? Here welcome to get the comprehensive answers.
1.What Is Pressure Applied For Tablet Pressing?
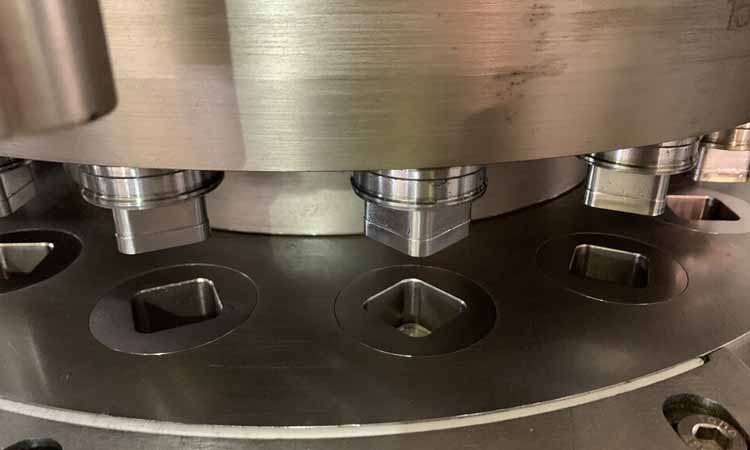
Pressure Applied For Tablet Pressing-Sourced:baumueller
The pressure applied for tablet pressing ranges from 1 to 10 tons which is suitable for tablet pressing of different material and formulation. It can press the loose powder to the stable and tough tablets. The specific pressure connects greatly to tablet feature, machine performance, material applied.
There are different tablet pressing machine. And for different tablet pressing machine, there is different pressing pressure. You may adjust the machine for the better tablet products manufacturing according to your different need. And you may also make several times of test for your right tablet pressing pressure.
2.Why You Should Pay Much Attention On The PressingPressure?
Why you should pay much attention on pressing pressure in your tablet pressing work? Here are the main reasons.
Product quality
Product Quality-Sourced:pharmaceuticalmanufacturer
The unsuitable pressing pressure may make problem for your tablet product quality. You should pay much attention on the pressing pressure for the completeness and hardness of your tablet products. Your tablet products quality concerns a lot on the pressing pressure or your tablet pressing machine.
Machine wearing
Excessive compression pressure may lead the tear and wear of your machine. And this is the work which may improve your maintaining cost. To make the great maintaining work for your tablet pressing machine, you should pay much attention to the pressing pressure.
Manufacturing efficiency
Manufacturing Efficiency-Sourced:pharmaceuticalmanufacturer
The optimized pressing pressure can make the nice corporation of tool, mold, tablet material and so on. And it can make great work in improving manufacturing efficiency of your tablet pressing work.
3.How To Determine The Appropriate Main Pressing Pressure In Pressing Tablets?
How to determine the appropriate main pressing pressure in pressing tablets? You may try the process of characteristics analysis, preliminary setting, gradual optimization or precise control.
According to compressibility of material
Compressibility Of Material-Sourced:merlin-pc
High Compressibility Materials (Easy to Form)
| Typical Materials | Lactose, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), starch, dextrin, and other excipients, or particles with a high content of the above excipients. |
| Characteristics | Strong interparticle bonding, easy deformation under pressure, and tight bonding. Can be formed with low pressure. |
| Method for Determining Main Compression Pressure | For standard tablet hardness requirement of 3-6 kgf (approximately 30-60N), the pressure can be set to 8-12 kN.
For rapid disintegration (e.g., dispersible tablets), the pressure can be further reduced to 5-8 kN, reducing particle densification and lowering disintegration resistance. Preliminary Range: 5-15 kN (for rotary tablet presses, convert proportionally for single-punch tablet presses). Optimization Logic: The upper limit is “achieving target hardness,” avoiding excessively high pressures. |
Medium Compressibility Materials (Require Moderate Pressure)
| Typical Materials | Most active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) such as aspirin and ibuprofen, mixed with excipients, or mixtures of traditional Chinese medicine extracts with fillers. |
| Characteristics | Moderate ability to form on their own, dependent on excipients, low pressure may cause the tablet to be too loose, while high pressure may delay disintegration. |
| Method for Determining Main Compression Pressure | If hardness is only 2 kgf (risk of loose tablets) at 15 kN, the pressure should be increased to 18-20 kN.
If the hardness meets the standard at 20 kN but disintegration exceeds 30 minutes, it can be adjusted back to 16-18 kN, while increasing the amount of disintegrant (e.g., cross-linked polyvinylpyrrolidone) to balance. Preliminary Range: 10-25 kN. Optimization Logic: Adjust based on the combined indicators of “hardness” and “disintegration time.” |
Low Compressibility Materials (Difficult to Form)
| Typical Materials | Crystalline APIs (e.g., sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate), hydrophobic powders (e.g., stearic acid), and non-adhesive mineral-based materials. |
| Characteristics | Hard, elastic particles with minimal deformation under pressure, weak interparticle bonding, prone to loose or cracked tablets. |
| Method for Determining Main Compression Pressure | If the tablet is loose (hardness < 2 kgf) at 25 kN, gradually increase to 30-35 kN until the hardness meets the standard.
If cracking occurs at pressures over 35 kN, excipient adjustments (e.g., adding MCC to increase plasticity) should be made, rather than simply increasing pressure. Preliminary Range: 20-40 kN (requires pre-compression, with pre-compression pressure set at 30%-50% of the main compression pressure, to expel air and initially form the tablet). Optimization Logic: The baseline is “no loose tablets,” while avoiding excessively high pressures that cause “elastic recovery” (where the tablet expands and cracks after pressure is released). |
According to viscosity of material
Viscosity Of Material-Sourced:powdertechnology
High Viscosity Materials (Prone to Stick and Punch Issues)
| Typical Materials | Chinese medicine extract powders, particles containing a large amount of dextrin, certain resin-based drugs. |
| Characteristics | Excessive pressure may cause the material to tightly adhere to the punches, leading to sticking issues, and may also negatively affect disintegration due to excessive densification. |
| Method for Determining Main Compression Pressure | If sticking occurs at 12 kN, reduce the pressure to 10 kN, and compensate for the stickiness by adding a lubricant (e.g., magnesium stearate at 1.5%). Then, try a slight increase in pressure to 11 kN.
Preliminary Range: Lower than the typical pressure for low-viscosity materials with the same hardness requirement (e.g., for a target hardness of 4 kgf, pressure will be 20%-30% lower than usual). Limitations: The priority is “no sticking,” even if the hardness is slightly lower. The demolding ability must be prioritized. |
High Brittleness Materials (Prone to Cracking)
| Typical Materials | Crystalline drugs (e.g., sulfonamides), inorganic acid salts (e.g., ferrous sulfate), Chinese medicine granules rich in fiber. |
| Characteristics | Excessive pressure can cause internal stress concentration, leading to cracking. Insufficient pressure can cause the tablet to be too loose. |
| Method for Determining Main Compression Pressure | Pre-compression must be applied (pressure should be 30%-40% of the main compression pressure). The main compression pressure should be tested in a “stepped” manner: Start with a lower pressure (e.g., 15 kN), increase by 2 kN each time, and observe whether cracking occurs. Continue until the “maximum non-cracking pressure” is found.
Example: For a certain crystalline drug, cracking occurs at 20 kN, but at 18 kN, the hardness meets the standard without cracking. Therefore, the main compression pressure is set to 18 kN, while pre-compression (6 kN) is applied to reduce internal air. |
According to tablet type
Tablet Type-Sourced:istockphoto
| Tablet Type | Typical Material Characteristics | Main Compression Pressure Features | Example Range |
| Standard Oral Tablets | Medium compressibility, low viscosity | Targeting “hardness 3-6 kgf + disintegration within 30 minutes,” moderate pressure. | 10-20 kN |
| Extended-Release Tablets | Contains extended-release materials (e.g., ethyl cellulose) | Requires high pressure (to increase densification and delay release), but avoid excessively high pressure that fully obstructs drug release. | 20-30 kN |
| Dispersible Tablets | High porosity, rapid disintegration requirement | Low pressure (maintains particle spacing), relies on disintegrants for expansion; hardness can be slightly lower (2-4 kgf). | 5-10 kN |
| Chewable Tablets | High sweetness excipients (e.g., mannitol) | Moderate pressure, balancing hardness (to avoid breaking during chewing) and taste (not too hard). | 8-15 kN |
According to process in practice
Process In Practice-Sourced:sigmaaldrich
Small-Scale Testing
Take a small amount of material (500g) and perform a pressure gradient test using a single-punch tablet press (e.g., 5, 10, 15, 20 kN). Measure the tablet hardness, disintegration time, and appearance (e.g., whether there is cracking or sticking) at different pressures.
Correlation Analysis
Plot the “Pressure - Hardness” curve to find the minimum pressure at which the hardness meets the standard. Simultaneously, exclude any appearance defects (such as cracking or sticking) at this pressure.
Pilot Scale Verification
On a rotary tablet press, set the pressure to 80%-90% of the small-scale test pressure as a preliminary setting. Adjust in conjunction with the tablet pressing speed (which may require slightly higher pressure when speed increases). The final qualification standard is: “The weight variation of 1,000 continuous tablets ≤ 5% and hardness fluctuation ≤ 10%.”
4.How Does Uneven Pressure Affect Your Tablet?
Uneven pressure distribution is a common process issue in tablet pressing and can directly lead to multiple defects in the tablet quality, affecting its mechanical properties, appearance, and drug efficacy stability.
Mechanical strength defects
Large Hardness Differences
Large Hardness Difference-Sourced:asad-ali
| Phenomenon | In the same batch of tablets, some have the required hardness while others are too soft, or there are significant hardness differences in different regions of the same tablet. |
| Cause | Uneven pressure distribution leads to inconsistent compression of the material—regions with higher pressure have tightly bonded particles (higher hardness), while regions with lower pressure have more gaps between particles (lower hardness). |
| Impact | Tablets with insufficient hardness are prone to breakage during transportation, while areas that are overly hard may cause slow disintegration. |
Loose Tablets
Loose Tablets-Sourced:istockphoto
| Phenomenon | The tablets are loose and can easily break apart with a finger press, or the cross-section shows obvious gaps (especially in the center). |
| Cause | Insufficient pressure in the core region, leading to inadequate binding force between particles. |
| Impact | Large diameter tablets (e.g., diameter > 15 mm) are more prone to “center loosening” due to low efficiency in pressure transmission to the center. Tablets with high elastic materials (e.g., crystalline drugs) also experience significant pressure loss, making them more likely to be loose. |
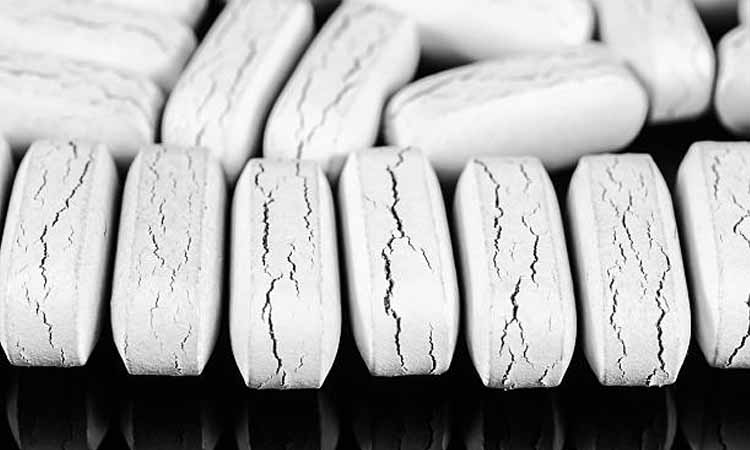
Cracking
Cracking-Sourced:istockphoto
| Phenomenon | Radial cracks appear on the surfaces of the tablet that come into contact with the upper and lower punches (often caused by excessive surface pressure and insufficient internal pressure, leading to uneven stress on the surface when the tablet attempts to return to its original shape). |
| Cause | Horizontal or ring-shaped cracks appear in the middle of the tablet (due to a sudden decrease in pressure in the middle layer, weak particle bonding, and inconsistent elastic recovery during decompression). |
| Impact | Excessive pressure gradient causes significant differences in elastic/plastic deformation between different areas of the tablet—regions with higher pressure are tightly compressed and have less elastic recovery, while regions with lower pressure are loosely compressed and have more elastic recovery. This leads to shear forces between the two regions, ultimately resulting in fractures. |
Appearance defects
Appearance Defects-Sourced:sensum
Uneven Surface
| Phenomenon | The surface shows local depressions or protrusions, or color spots caused by uneven particle distribution (e.g., pigment particles concentrated in low-pressure areas, leading to uneven coloration). |
| Reason | In areas with insufficient local pressure, the material fills loosely and cannot extend evenly after compression, leading to depressions; or particle aggregation (e.g., sticky material clumping) causes concentrated local pressure, resulting in protrusions. |
Edge Defects
| Phenomenon | The edges of the tablet are rough with burrs, or there are missing corners or broken edges. |
| Reason | Uneven radial pressure distribution—when pressure is insufficient in the edge areas, the bond between particles and the mold wall weakens, causing the tablet to be scratched by the mold wall during ejection; if local radial pressure drops suddenly (e.g., edge gaps caused by uneven particle distribution), edges may break. |
Surface Cracks
| Phenomenon | Fine cracks appear on the surface (difficult to see with the naked eye, but affecting strength) or visible radial cracks (especially near the edges). |
| Reason | A large gradient difference between axial and radial pressures leads to stress concentration on the surface and edges, causing surface tearing during elastic recovery after decompression. |
Functional defect
Functional Defect-Sourced:lfatabletpresses
Slow disintegration or uneven dissolution
| Phenomenon | Some tablets have a disintegration time that is too long, or the disintegration time variance within the same batch exceeds the standard (e.g., ±10% as specified by pharmacopeia); the dissolution curve shows a “fast - slow” polarization. |
| Reason | In high-pressure areas, the material is compressed too densely, forming a “hard shell” or “dense layer” that hinders water penetration (this is more pronounced in hydrophobic drugs in high-pressure areas).
In low-pressure areas, the material is loose, allowing water to enter quickly, causing disintegration/dissolution to happen too fast and leading to fluctuations in the overall dissolution curve. |
Content uniformity exceeds the standard
| Phenomenon | The active ingredient content in the tablets varies beyond the specified limits (e.g., one component in a compound formulation is locally too high or too low). |
| Reason | If the material is unevenly mixed (e.g., a significant density difference between the API and excipients), uneven pressure distribution can exacerbate the issue — high-pressure areas may accumulate denser particles (e.g., API crystals), while low-pressure areas may accumulate lighter excipients, causing content deviations. |
Production stability
Production Stability-Sourced:colorcon
Difficulties in Ejection
| Phenomenon | The tablet cannot be smoothly ejected from the mold cavity, or the tablet surface sticks to the punch (sticking to punch), or even cracks due to excessive ejection force (top cracking). |
| Reason | Excessive local radial pressure (e.g., local pressure concentration due to particle aggregation) causes a sharp increase in friction between the tablet and the mold wall.
Uneven pressure distribution (e.g., an uneven punch) results in the tablet tightly adhering to one side of the mold wall. |
Abnormal Equipment Wear
| Phenomenon | Localized wear on the punch or mold cavity (e.g., at the edge of the punch or one side of the mold cavity) accelerates, shortening the equipment’s service life. |
| Reason | Uneven pressure distribution leads to unbalanced force on the equipment (e.g., excessive pressure on one side of the punch), and prolonged operation causes mechanical parts to wear unevenly or deform. |
5.How To Deal With Uneven PressureIn Your Tablet Pressing Process?
Uneven pressure is a big problem for your tablet pressing process. So how to deal with uneven pressure in your tablet pressing process.
Regular Maintenance and Calibration
Regular Maintenance And Calibration-Sourced:clustermarket
You should make the regular maintaining and calibrating for your tablet pressing machine. The regular maintenance and calibration can make the quick and efficient troubleshooting for the various problem of your tablet pressing machine. And you may have the worn parts removed for the even pressing for your tablet pressing process.
Optimizing Granule Properties
Optimizing Granule Properties-Sourced:anishpharmaequippvtltdindia
You should optimize the properties for the even pressing of your tablets. The uniform particle size, suitable lubricants and binders are the important factor which affect the granule properties. The uniform mixing and so on can also make the great granule properties for the even pressing work.
Adjusting Compression Force
Adjusting Compression Force-Sourced:tekscan
You should also adjust your compression force for the even pressure of your tablet pressing work. The suitable compression force can make the ideal work for your even pressing of your various tablet products. You should adjust the compression force according to the different material properties.
Using Precision Tools
Using Precision Tools-Sourced:repassa
You should apply precision tools in your process of tablet pressing work. The accurate punch, mold and other pressing parts can affect your tablet problem greatly. The applying of precision tools can make the great impact for your tablet pressing work here.
Checking for Air Entrapment
Air entrapment may make the uneven tablet products for your tablet pressing work. The entrap air may lead series of problem for your tablet pressing work. You should thus pay much attention on air entrapment for the even pressing of your tablet pressing work.
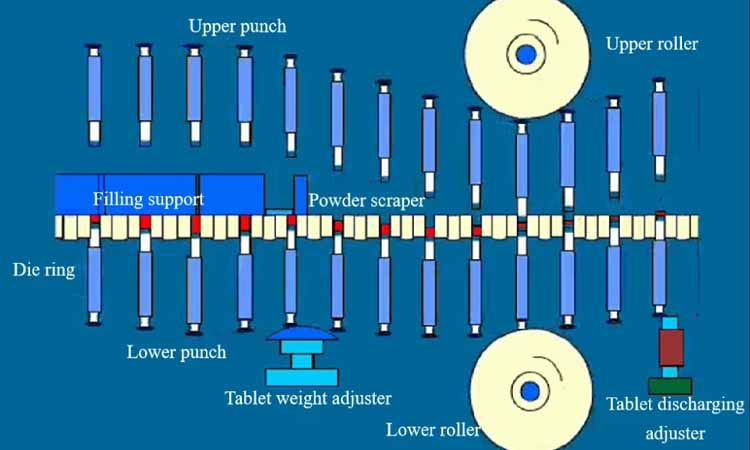
6.What Are The Machines Applied For Tablet Pressing?
What are the machines applied for tablet pressing? Here you may check the tablet pressing machine which make the irreplaceable work in tablet pressing.
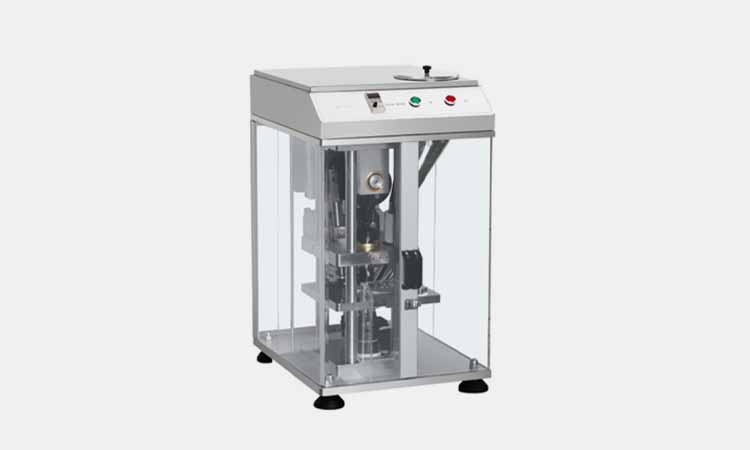
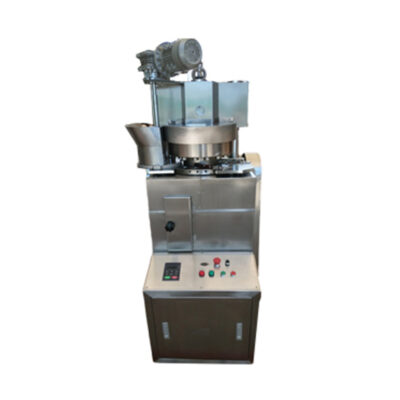
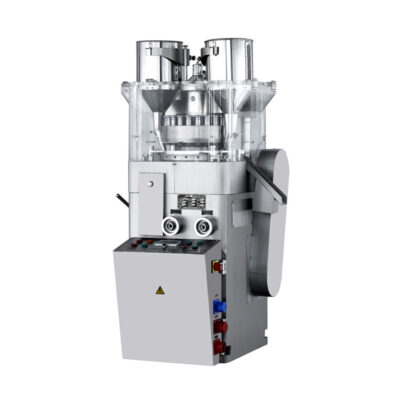
Single punch tablet pressing machine
AIPAK Single Punch Tablet Pressing Machine
Single punch tablet pressing machine is the machine which applied for the small scale production of various tablets, sugar pieces, calcium tablets and so on. The single punch tablet pressing machine is suitable for the precise filling work and can make the pressing with low noise and low consumption.
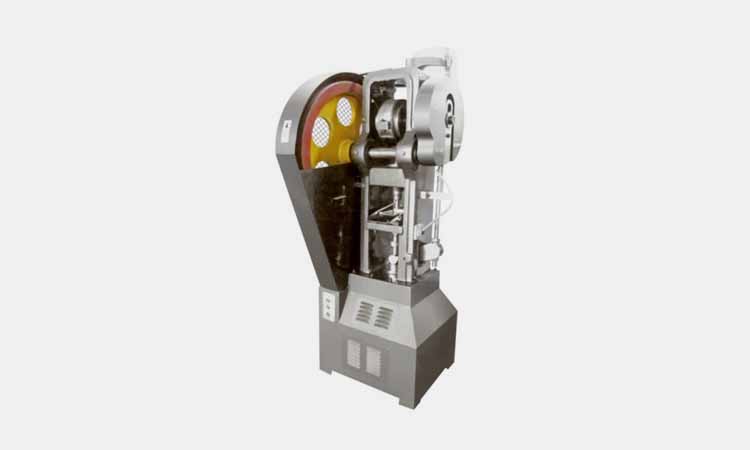
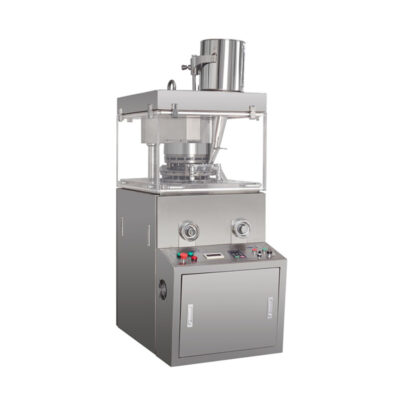
Flower basket tablet pressing machine
AIPAK Flower Basket Tablet Pressing Machine
Flower basket tablet pressing machine can pack various granule particle into round shape and this is the equipment which is suitable for the batch production most. It can be applied for the production of double layer tablet products or large diameter tablet products. You may apply it for the production of sugar, electronic parts and so on.
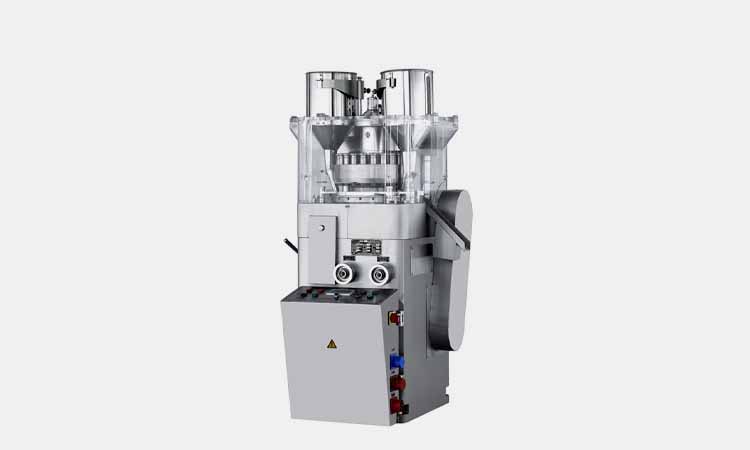
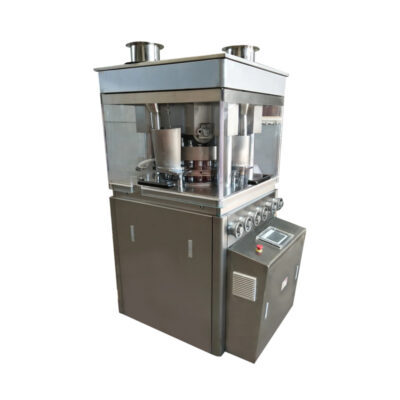
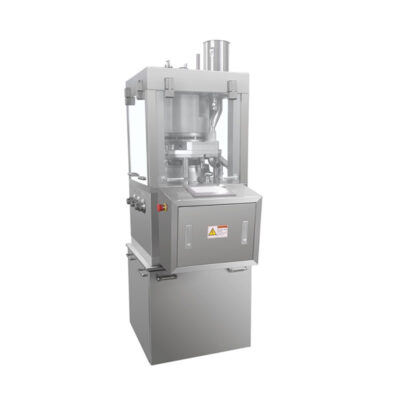
Rotary tablet pressing machine
AIPAK Rotary Tablet Pressing Machine
Rotary tablet pressing machine can make round shape tablets, irregular tablets, double-side engraved tablets and so on. Rotary tablet pressing machine has large power, large pressure, excellent performance and smooth operation. The products are compatible with GMP standard and can be customized mold.
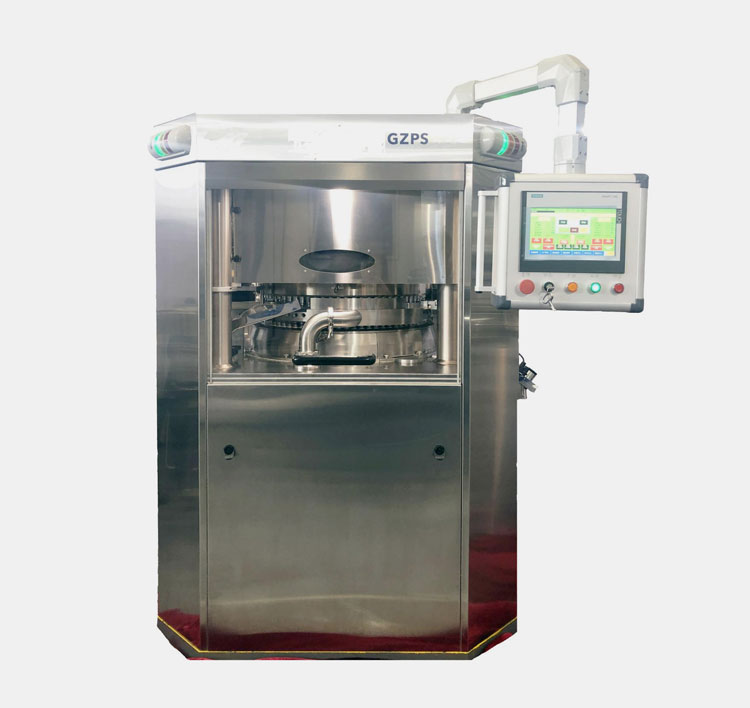
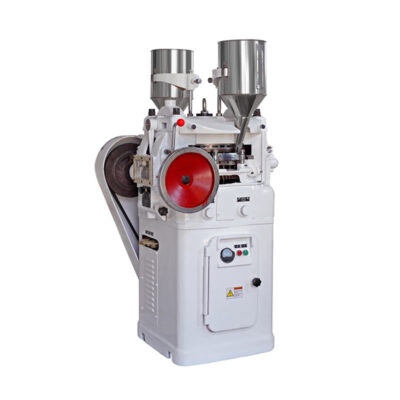
High speed tablet pressing machine
AIPAK High Speed Tablet Pressing Machine
High speed tablet pressing machine is the machine which is applied for the production of various irregular tablet products. The machine is easy to clean and maintain and can make the products of GMP standard. The excellent performance is so great and rather suitable for mass production.
7.How Does Pressure Transmit And Distribute During TabletPressing?
How does pressure transmit and distribute during tablet pressing work? Here you may find get the compressive answers.
The Core Path of Pressure Transmission
Pressure Transmission-Sourced:chinacanaan
During tablet pressing, the transmission of pressure follows the path: Equipment → Punch → Material → Die Hole. The specific process is as follows:
Equipment Applies Initial Force
The main pressure wheel of the tablet press (or the crankshaft of a single punch tablet press) applies axial pressure to the upper and lower punches (typically, the upper punch is the active one applying force, and the lower punch is supported by a spring or hydraulic system, creating a reactive force).
Punch Transmits Pressure
The upper and lower punches transfer the external force to the material inside the die hole, creating axial pressure (a force perpendicular to the surface of the punch). This pushes the material particles to compress, shift and deform.
Transmission of Internal Force in Material
The axial pressure is transmitted through the contact points between the particles (“force chain”) to the interior of the material. At the same time, due to the radial expansion of the material when compressed and the constraint from the die wall, radial pressure (a force perpendicular to the die wall) is generated.
Final Dissipation of Pressure
Once the pressure reaches its peak, the punches gradually lift, relieving the axial pressure. The material retains some internal stress due to elastic and plastic deformation, forming the mechanical strength of the tablet.
Distribution Pattern of Pressure in the Material
Pressure Distribution-Sourced:pharmtech
Pressure within the material is not evenly distributed; it follows specific patterns, mainly reflected in the following dimensions:
Axial pressure distribution
| Phenomenon | The material near the upper and lower punch surfaces experiences the highest pressure, which gradually decreases towards the center of the tablet, forming a pressure gradient: Surface > Middle Layer > Center. |
| Reason | Frictional forces exist between material particles. During pressure transmission, energy is lost due to particle sliding and friction, resulting in greater pressure loss as it moves towards the center.
If the material contains air, the expulsion of air during compression further hinders the pressure transmission towards the center (especially in the absence of pre-compression). |
| Impact | Insufficient pressure at the center may cause the tablet’s “core to be loose”, leading to “layering” or “central tablet crumbling” (this is more likely to happen in large-diameter tablets). |
Radial pressure distribution
| Phenomenon | Radial pressure (force perpendicular to the die wall) is greatest in the edge region where the material contacts the die wall, gradually decreasing towards the center. The ratio of radial to axial pressure (“side pressure coefficient”) is influenced by the material’s Poisson’s ratio (the higher the Poisson’s ratio, the closer the radial pressure is to axial pressure). |
| Reason | Under axial compression, the material undergoes radial expansion due to the Poisson effect, and the constraint of the die wall forces the edge regions to bear higher radial pressure. |
| Impact | Insufficient radial pressure can lead to weak bonding between the tablet and the die wall, potentially causing “edge brittleness”.
Excessive radial pressure (e.g., in materials with a high Poisson’s ratio) could lead to difficult ejection due to excessive friction between the tablet and the die wall. |
Overall uniformity
| Pre-Compression Stage | The pressure is lower (typically 30%-50% of the main compression force) and primarily serves to expel air from the material, reducing pressure fluctuations during the main compression phase. At this stage, the pressure distribution is rough but lays the foundation for more uniform pressure transmission during the main compression phase. |
| Main Compression Stage | The pressure rapidly increases to its peak. At this point, the material undergoes severe compression, with particles experiencing plastic deformation or breakage. Pressure is transmitted through tight particle contacts, significantly improving the uniformity of pressure distribution (though a gradient still exists). |
| Impact of Material Properties | Materials with good flow and uniform particle size lead to more uniform initial filling and more consistent pressure distribution.
Materials with excessive fine powders or particle aggregation tend to have uneven filling, resulting in localized pressure concentration (e.g., fine powder regions compress more densely, and pressure is transmitted more quickly in those areas). |
Key Factors Affecting Pressure Transmission and Distribution
Key Factors-Sourced:ianbrodie
The efficiency of pressure transmission and the uniformity of distribution are influenced by the material properties, equipment parameters, and process conditions, as detailed below.
Factors Influencing Pressure Transmission and Distribution
| Influencing factor | Effect on pressure transmission and distribution |
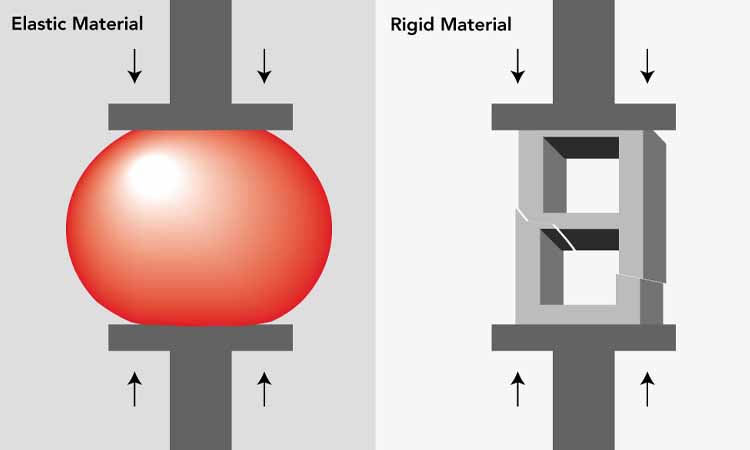
| Material Compressibility | Plastic materials (e.g., MCC) deform easily under pressure, with a large contact area between particles, leading to high pressure transmission efficiency and more uniform distribution. Elastic materials (e.g., crystalline drugs) rebound after compression, resulting in significant pressure loss and a more pronounced distribution gradient. |
| Material Flowability | Materials with poor flow (e.g., fine powders, sticky particles) tend to form “voids” or “uneven density” during die filling, leading to localized pressure concentration (pressure increases abruptly around voids), and poor uniformity in pressure distribution. |
| Particle Hardness | Hard particles (e.g., crystalline drugs) are less likely to break under pressure, and the force chain primarily transmits through particle surface contacts. This means the pressure distribution is more influenced by particle shape (e.g., angular particles), potentially causing “point contact pressure concentration.” Soft particles (e.g., granulated materials) are more likely to break, allowing more thorough particle contact and leading to more uniform pressure transmission. |
| Punch and Die Accuracy | Misalignment in punch concentricity (difference in concentricity between upper, middle, and lower punches) can cause excessive pressure on one side of the material, leading to a “tilted gradient” in pressure distribution. This could cause “tilted tablets” or “one side brittle” tablets. Rough die wall surfaces increase radial friction, reducing radial pressure transmission efficiency. |
| Compression Speed | When the compression speed is too fast, the material is compressed for a short period, and pressure is not fully transmitted to the interior before decompression begins. This results in insufficient central pressure (especially for highly elastic materials) and an increased gradient in pressure distribution. |
Practical Significance of Optimizing Pressure Transmission and Distribution
Practical Significance-Sourced:theo-dawson
Uneven pressure distribution is one of the core causes of tablet quality defects (such as cracking, loosening, and large hardness variations). In actual production, the following methods can be used to improve it.
| Optimization Methods | |
| Increase Pre-Compression | This helps expel air and reduce pressure loss during the main compression phase, especially for materials with high air content (e.g., lightweight powders), where the effect is particularly significant. |
| Control Material Properties | Improving the flow and uniformity of particles through granulation (e.g., wet granulation) or adding plastic excipients (e.g., MCC) can enhance pressure transmission efficiency. |
| Optimize Equipment Parameters | Using a “gradient pressurization” curve for tablet pressing (where pressure increases gradually) can extend the compression time. Additionally, ensuring the parallelism of the punches and smoothness of the die hole helps reduce distribution deviations caused by mechanical factors. |
| Adjust Tablet Design | For larger diameter tablets (e.g., ≥13mm), “shallow radius punches” or “central convex punches” can be used to enhance pressure transmission in the central region. |
8.How To Solve The Sticking Phenomenon In Tablet Production?
How to solve the sticking phenomenon in tablet production? “Punch sticking” refers to the phenomenon where a thin layer or a small part of the tablet surface is stuck to the punch, causing roughness, unevenness, or indentations on the tablet surface.
Improving Material Factors
Control Material Humidity
Control Material Humidity-Sourced:azom
Many materials have hygroscopic properties, and when the environmental humidity is high or the material itself contains too much moisture, punch sticking is likely to occur. Therefore, it is important to strictly control the moisture content of hygroscopic materials.
In terms of production environment, the relative humidity of the production workshop should be controlled. Dehumidifiers can be installed to maintain the relative humidity in the range of 40%-60% to reduce the likelihood of material moisture absorption.
Optimize Material Particle Size and Distribution
Material Particle Size-Sourced:ftmmachinery
The particle size and distribution of materials also affect punch sticking. If the particle size is uneven and there is too much fine powder, during tablet pressing, the fine powder may fill the gap between the punch and the die hole, increasing the risk of sticking.
To address this, materials should be crushed and screened to achieve a more uniform particle size distribution. Multi-stage sieving equipment can be used, such as first using a coarse sieve to remove larger particles and then using a fine sieve (e.g., 80-100 mesh) to select materials with the appropriate particle size range, thus reducing the proportion of fine powders.
Additionally, flow aids like micro-silica can be added to improve material flow and prevent fine powders from clumping together. A typical addition amount is 0.1%-0.5%.
Adjust Material Formulation
Adjust Material Formulation-Sourced:eskagglobal
Certain ingredient interactions within materials may lead to punch sticking. For example, in some composite tablets, chemical reactions or physical adsorption may occur between the active ingredients and excipients. If the active ingredient is a sticky extract, mixing it with certain excipients may enhance the stickiness.
In such cases, it may be worth considering changing the excipient or adjusting the ratio of active ingredient to excipient. For instance, replacing starch dextrin with microcrystalline cellulose can be a good solution, as microcrystalline cellulose has good compressibility and flowability, and is less likely to cause punch sticking.
Alternatively, increasing the proportion of hydrophobic excipients, such as magnesium stearate, can help. Magnesium stearate forms a hydrophobic layer on the particle surface, reducing the likelihood of sticking. Typically, the addition range for magnesium stearate is 0.3% - 1%.
Optimizing Tablet Pressing Equipment and Process Parameters
Clean and Maintain Punches and Dies
Clean and Maintain Punches And Dies-Sourced:fluidpack
During the tablet pressing process, residual material may remain on the surface of the punches and dies. If not cleaned in time, the accumulated material can increase the likelihood of punch sticking. For example, after continuous tablet pressing, some sticky ingredients may adhere to the punch, and during the next pressing cycle, they can transfer to the surface of the new tablet.
Therefore, it is important to regularly clean the punches and dies. Appropriate cleaning agents, such as specialized die cleaners, can be used. A soft cloth or brush should be used to gently wipe the surfaces of the punches and dies, removing any residual material. Additionally, the surfaces should be checked for damage, such as scratches or dents, which can make it easier for material to stick. Damaged punches or dies should be promptly replaced or repaired.
Adjust Tablet Pressing Pressure and Speed
Adjust Tablet Pressing Pressure and Speed-Sourced:avetechnologies
When the pressing pressure is too high, the material may become overly compacted, causing the material to spill over the edge of the die hole and stick to the punch.Similarly, if the tablet pressing speed is too fast, the material will not have enough time to evenly distribute in the die hole, which can also result in sticking.
Optimization through testing can be conducted to find the best pressure and speed settings. Typically, start with lower pressure and speed and gradually increase, observing the tablet quality to find the optimal range that ensures tablet hardness and appearance while avoiding punch sticking. For tablet pressing speed, adjustments can be made based on material properties and equipment performance.
Control Tablet Temperature
Control Tablet Temperature-Sourced:romaco
During the pressing process, the temperature of the tablets may rise due to friction and other factors. If the temperature becomes too high, the material’s viscosity may increase, leading to punch sticking. For example, some thermoplastic materials become more viscous as the temperature rises.
Temperature control measures can be taken to address this. On one hand, a cooling system, such as air cooling or water cooling, can be installed on the tablet press to cool the tablets during the process. On the other hand, optimizing the pressing process to reduce unnecessary friction, such as appropriately lubricating the punches and die holes, can help minimize the heat generated by friction.
9.What ElseYou Should Pay Attention To In Tablet Pressing Work Besides Pressure?
What else you should pay attention to in tablet pressing work besides pressure? There are the important factors for you to make the reliable tablet pressing work.
Powder Properties
Powder Properties-Sourced:azom
Powder properties concerned a lot on tablet pressing work. You should improve powder flow, make even particle size, reduce powder moisture and make granule for the improvement of your powder products. Your powder properties concern a lot on your pressed tablet quality.
Punch and Die Design
Punch And Die Design-Sourced:licdn
The design of your punch and die also make great impact for your tablet pressing work. The depth of cup and length of punch, land ,die design are all parts of punch and die design. The size and relative design can all affect the tablet completeness and tablet products and ejection.
Machine Settings and Operation
Machine settings and operation contained the compression speed, pre-compression, feeder speed, overload set points, cam tracks, autoregulation, feeder seals and dust extraction and so on. The suitable parameter setting and operation of the above parts are the prove of your high qualified tablet products.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental Conditions-Sourced:senieer
The manufacturing environment can also make great impact for your tablet pressing work. You should make the great control of humidity, temperature and dust for the sensitive particle type. Environmental conditions affect your tablet pressing technique.
Quality Control
Quality Control-Sourced:medium
You should also pay attention to the quality control of your tablet pressing process. The strict monitoring for your quality of tablet products help monitor the tablet weight, hardness, friability and so on which is the prove for your products.
Conclusion
How does uneven pressure affect your tablet? Here are the comprehensive guide about pressure on your tablet manufacturing process. After reading, you may know much about this parts. Do you have any problem or question about uneven pressure on tablets? If you do, feel free to contact AIPAK now.
Don't forget to share this post!
Tablet Press Machine Related Posts
Tablet Press Machine Related Products
Tablet Press Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 156 0710 8630
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine