What Is the Difference Between Drug and Medicine?
Taking a drug in hopes to get better health and restoring normal physiological activities would perhaps be making you sicker. Do you know why? This is because, drugs are not meant to cure you, but temporarily subside the symptoms. On the contrary, if you take medicines, it is ensuring good health and is entirely meant to treat the symptoms. So, taking the right medicine can completely cure your bodily functions.
Many of you think drugs and medicine are the same but in reality, they’re not! Surprised?
In the article’ What is Difference between Drug and Medicine’, we are going to discuss important perspectives associated with two entities. By the end of the blog, we assure you’ll be able to distinguish the major differences between them.
1.What Are Drugs and Medicines?
To answer this question you must be aware that the words drug and medicine are used synchronously today, however, they do not fall meaningfully the same in an entire way.
According to FDA a Drug can be explained as a substance entitled to cure diseases and prevent ailments, used to identify and diagnose types of disorders, and whose intake is for therapeutic, recreational, and spiritual benefits. These drugs are listed in pharmacopeias and their specific purpose of use, mechanism of action, adverse effects, and dosages are all known. However, the drug doesn't need to be always of benefit to its consumer.
The drug can be of potential interest to mitigate illnesses or can be of substantial harm if used illegally or in a negative role. They have the ability to cause psychological dependence when taken in doses beyond the limit or when tolerance develops, thus causing harm. A drug’s formulation solely consists of an active pharmaceutical ingredient which is called the drug.
Whereas Medicine, can be also understood similarly they treat your health problems and relieve the symptoms to cure certain diseases or infections, but here the difference arises that All drugs are not medicines, but all medicines are drugs. That means a medicine can be denoted to have positive health effects without causing any noticeable potential harm unless intentionally taken for abuse. A medicine is formulated in such a way that it contains not only the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) but also the excipients.
2.What Is The Difference Between A Drug And A Medicine?
We’ve seen by now the definitions of what a drug and medicine is. To further understand and clear any confusions, we will outline the differences that makes both of them unique.
Below are the headings representing some important and clear-cut variances amongst the drug and medicine. Let’s read to find out.
DEFINITION
DRUG
The word “Drug” is derived from the French origin Drogue meaning “Dry herb” . It denotes that earliest drugs were evolved from plant sources. Drugs have the ability to change body’s physiological and psychological states.
A Drug is pharmacological entity which is intended specifically for the treatment, prevention or diagnosis of any illness producing a physiological effect (either negative it positive) on the living body. It contains usually the active pharmaceutical ingredient which is known to be strong and potent.
All drugs cannot be called medicines.
MEDICINE
The word “Medicine” is rooted in Latin Medicus which means “Physician”. As a physician takes care of the patient’s health condition by treating and diagnosing the illness, the same is applied to understanding the term Medication or Medicine.
Medicine is a therapeutic substance taken for its action to cure and treat diseases. It contains active ingredients of pharmaceutical nature and some other excipients which aid to carry the medication and act as supportive ingredients.
All medicines can be said as drugs.
HISTORY
DRUG
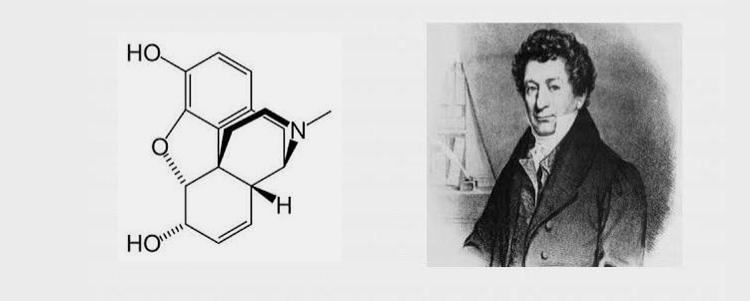
The first invention of the drug was done by Frederick Serturner , as he extracted morphine from opium in 1804. Mostly drugs were prepared using plant extracts and sources. The first synthetic drug was chloral hydrate , discovered in 1869.
MEDICINE
Medicines were invented by ancient Greeks and Hippocrates is popularly known as “Father of Medicine”. One of the oldest discovered medicine is known to be “Cannabis Sativa” which was introduced in 2700 BCE. However Medicine was anciently brought up by Egyptians, the first physician was Imhotep.
SOURCES
DRUG
The originating form of the drug can be attributed to various sources such as the most essential and common one being plants. The rest of the sources are also vital such as animals, microorganisms, minerals and artificial or synthetically prepared drugs.
Once the source is decided, it is further processed for preparation and then it’s evaluation for safety and efficacy.
MEDICINE
Similar to drugs, medicine also finds its sources from natural and some synthetic origination. They can be formulated from plants, animals, microbes, biosynthesis etc.
Once formulated and analyzed for research purposes, they are made available for consumer use.
PREPARATION
DRUG
Formulation of a drug is an extensive process which undergoes several pharmaceutical steps starting from the collection of raw material or active pharmaceutical ingredient(s), the decision of an appropriate dosage form and the measurement of doses, incorporation of any additional ingredient, carrying out it’s preparation and then being subjected to clinical research and trials. The preparation can be carried out either on small scale extemporaneously for eg some emergency IV reconstitution drugs or on large scale by industrial manufacturing.
MEDICINE
Medicines are prepared by using natural sources of ingredients or are synthesized in laboratories. They can also be made simply by extemporaneous mixing of two or more pharmaceutical substances. Preparation of medicine also undergoes research and evaluation steps before final administration.
Likewise, drugs and medicines can also be manufactured in pharmaceutical industries for large-scale batch production.
SITE OF ACTION
DRUG
A site of action refers to the specific area where the drug will reach and show its effect. It can be categorized as tissue compartment, cellular compartment, and molecular target binding area. The drug may show its action depending upon the route of administration and its intended purpose of use.
MEDICINE
The site of action where the medicine will reach after being ingested, to produce its effect either systemically or locally depends on where the treatment is required and also according to the medicine’s pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties.
DOSAGE
DRUG
The dosage of a drug signifies the amount or quantity by weight, volume, or by number taken by the patient as directed by the doctor. There are many considerations to focus on while designing a dosage for a specific patient. It depends upon their age, sex, weight, physiological functions, and lifestyle. It must be ensured that as the drug is in it’s potent form the prescribed value of dosage does not exceed.
MEDICINE
Similar to drug dosage application, it is necessary for all medicines to be taken under directed doses as per your physician or pharmacist's instructs. To understand dosage, it is the simple intake of a certain amount of medicine at a certain time and specific frequency.
THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS
DRUG
Therapeutic effects of a drug are said to be achieved when the desired action of the active ingredient results in a favorable positive response in the patient. Although the drug doesn’t always possess favorable outcomes. It also has some idiosyncratic effects which are of unknown cause and which may affect variedly to different patients.
For eg: NSAID Ibuprofen is known to reduce inflammatory conditions and reduce pain and also treat feverish states. This is the therapeutic effect of the drug. It should also be remembered that for therapeutic effects to be achieved, the drug must reach a certain level in plasma and be absorbed by the body without hindrance.
MEDICINE
A medicinal therapeutic action is found when its chemical molecules reach the target binding site and show their wanted response, after fulfilling pharmacokinetic parameters, such as reaching the required plasma concentration level.
Similar to drugs, the medicine also might have the potential for getting a negative response if the proper way of administration and its instructions are not followed.
For eg: When an antibiotic is prescribed it is said to be taken in certain doses for a mentioned period of time according to dosing intervals. If followed properly the desired action is achieved, and that is said to be the therapeutic effect.
TYPES
DRUG
The drugs are categorized according to their intended action into different groups such as Those that affect our psychological states:
| Anti-Depressants They retard the action of the central nervous system, affecting your ability to concentrate and be conscious of your surroundings. Small doses of depressants can give the feeling of calmness while large doses can severely affect and cause unconsciousness and even death. |
 |
| Hallucinogens They affect a person’s sense of reality and make them assume things that are not true, like you might hear, taste, feel or see things differently. |
 |
| Stimulants They stimulate the body’s function of the central nervous system and make you feel more energetic and alert. However large doses might cause anxiety, seizures and panic. |
 |
| Analgesic More commonly known as painkillers, they’re effective to relieve pain and are taken in acute and chronic conditions. Some of these analgesic medicines are only given upon prescription. |
 |
| Inhalants
These substances are inhaled through nose or mouth to give quick action of drug as they immediately get released in the body. |
 |
| Opioids Opioid drugs are also known as narcotics, they’re strictly prescription based and give their users feeling of wellbeing. |
 |
| Prescription Drugs These drugs are supposed to be given by the pharmacist or chemist only upon a doctor’s advise. Most prescription drugs have the potential to be misused as patients often do not understand or neglect the instructions to be followed by using these drugs. |
 |
MEDICINES
Medicines come in different types of preparations such as liquid dosage form, tablet dosage form, capsule dosage form, topical medications, suppositories, drops, inhalers, injections, and implants.
| Liquid : This form contains dissolved molecules of active form of drug substance to make it patient complaint to be easily taken. Liquid medications are also referred to as syrups and suspension. |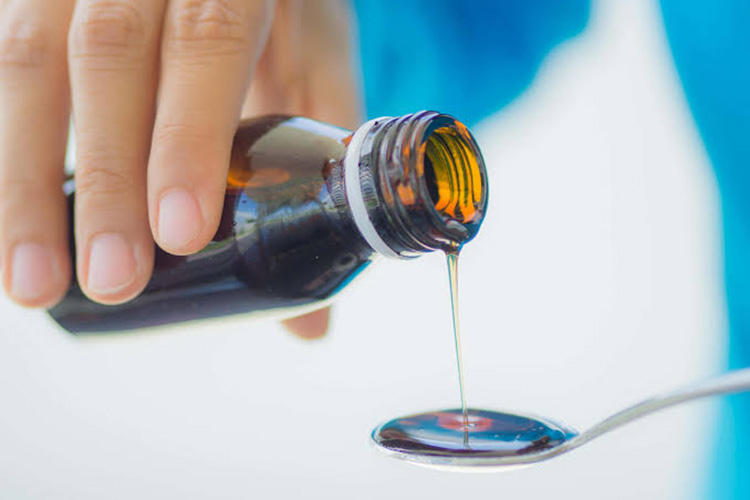  |
| Tablet: A tablet is a solid dosage form of medicine, usually a powdered form of drug compressed to given shapes such as round or oval, etc. |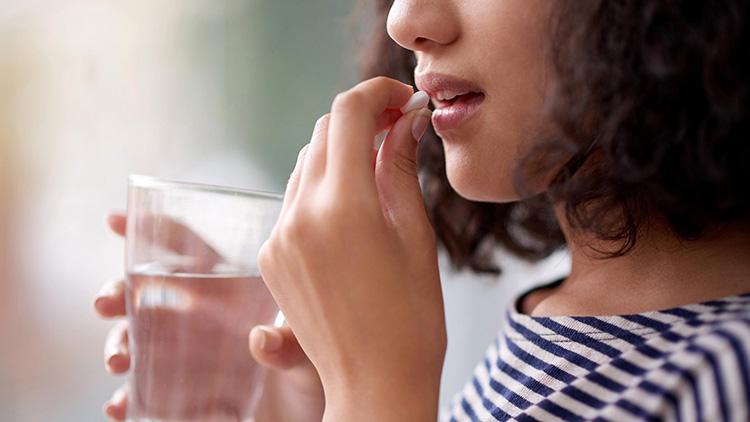  |
| Capsules: This is another solid form of drug that is contained in a powder or liquid state inside the shell of the capsule. It is designed to be delivered inside the body and release its content when gradually dissolved in the stomach. |  |
| Topical medications: These type of medicines are formulated into semi-liquid state like creams, lotions, and ointments that are intended to be rubbed or applied directly onto the affected surface of the skin. |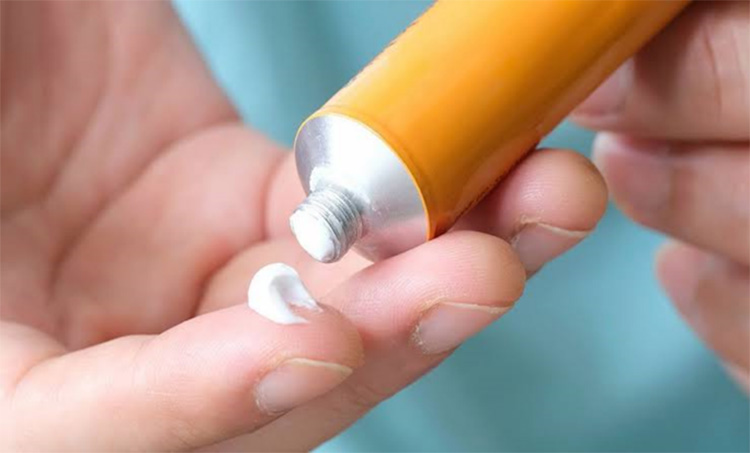  |
| Suppositories: These are a special type of dosage form that is not to be taken by mouth, instead it is for rectal route only. Suppositories contain medicated substance along with excipients in a bullet shape solid form to be inserted into the rectum. |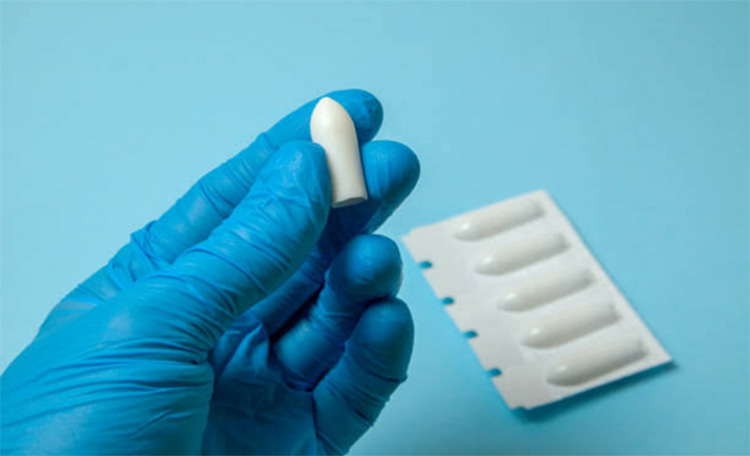  |
| Drops: are a fluid form of medication intended to be inserted locally where the action of a drug substance is required for eg: in the eyes, ears, and nose . | 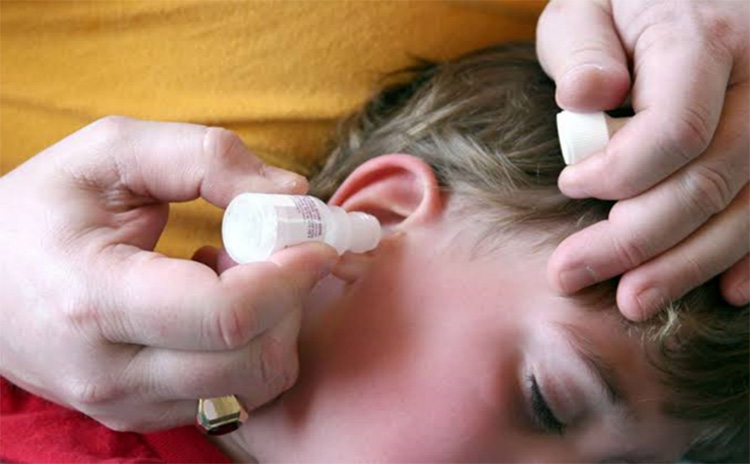 |
| Inhalers: release the medicated substance with pressure directly into the lungs, they’re used by sniffing through nose or mouth. | 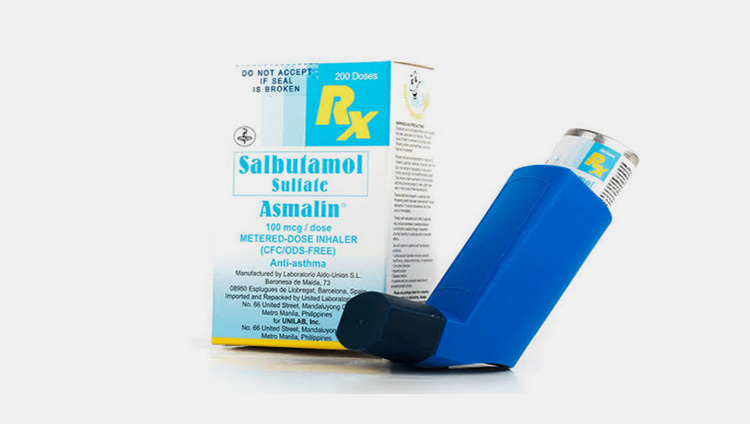 |
| Injections: are liquid medicine available in different types such as Intravenous, Intramuscular, Intrathecal, Subcutaneous etc. They provide quick onset of action once inserted into the desired area. |  |
| Implants: This form of medicine is to be absorbed into the skin wherever it is placed. |  |
SIDE EFFECTS
DRUG
Drugs not only possess favorable outcomes, you just read above. So the unwanted results that diminish a person’s health and which might affect the patient’s physiological condition is said to be a drug’s side effect that is not intended.
It should be natural to remember that as all drugs are chemical molecules altering the physical states of the body, they might necessarily show some extra and unwanted effects too.
For eg: most drugs have common side effects such as nausea and vomiting.
MEDICINE
A side effect is actually an unwanted symptom of the medicine that may be expected or unexpected, causing discomfort and some other type of sickness than the former pathological condition of the patient.
It is noticeable that any type of medication whether it is an OTC or a prescription medicine has the ability to cause side effects.
For eg: Allergic reactions in response to penicillin antibiotic is commonly known.
ADDICTION
DRUG
When you get addicted to a drug that means your brain asks for more of it to fulfill its reward feeling. Addiction is a brain disease that makes you excited and eager to keep taking a certain drug . It is not necessary that these drugs are for potential misuse, it can be any drug like sleeping pills, anti-depressants , caffeine, etc.
MEDICINE
Addiction to medicines means that your brain will ask for more quantity of that medication and your body will become physically dependent on it. The bad thing about being addicted is even though you might feel your health deteriorating because of overuse of any medication, you still won’t be able to give up. For eg: Smoking nicotine.
Strangely some painkiller medicines also have the potential to make you addicted. It is not confined to medicines like opioid or narcotics etc, any medicine that is taken more than prescribed in uncontrollable frequencies have a chance to make one addicted.
ANTIDOTES
DRUG
When a drug becomes poison or causes toxicity in a patient, of course when the value of the dose exceeds in the body such that it causes severe harm “Antidotes” is required. Antidotes work by counteracting the effects produced by the drug either by preventing the absorption of toxic chemicals further in the body, by neutralizing its action, or by converting the toxic metabolite into a less harmful one.
The common antidotes for a few drugs are for eg: N-Acetylcysteine for Acetaminophen poisoning, Atropine for organophosphate poisoning, etc.
MEDICINE
Likewise, drugs and antidotes for medications are also present in pharmacopeias and toxicological laboratories that aid against the deleterious effects of poisoning. Antidotes for medicines work similarly to antidotes for drugs. There are different types of antidotes given for different types of medication poisoning. For eg: Various forms of anti-venoms are present in different types of animal and insect bites.
3.How Are The Drug And Medicine Related Clinical Trials Carried Out?
Once the drugs and medicines are formulated and prepared they undergo different, vigorous testing and research steps to finalize their efficacy and safety by the Food and Drug Authority. The clinical trials conducted for drugs and medications consist of the following stages:
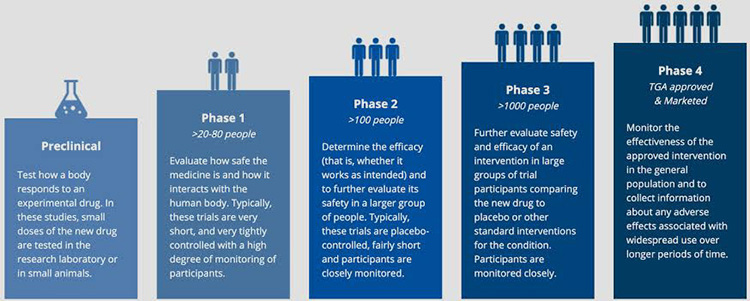
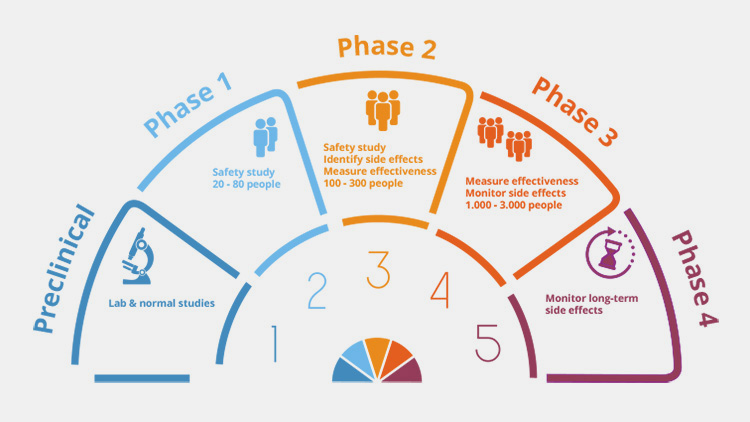
| First Stage: Pre-Clinical Trials :
In this stage the initial safety parameters of a drug are evaluated and analysed. The safe and effective concentration of dosage that will be required to be taken is found and the possible side effects are considered. Usually in this stage, medicines are tested on animals at laboratory scale such as on rats, mices, rabbits, pigs etc. These studies take upto several years. |
| Second Stage: Clinical Trials Phase I
In phase II trials, a small group of people are selected randomly to experience the effects of that particular drug through pharmacokinetic parameters. Dosage quantity for this new drug is analysed by administration to few healthy volunteers or sometimes terminally ill patients like those of AIDS and cancer. This study is evaluated and monitored closely for any dangerous side effects. It takes about several months to complete and drugs usually pass this trial phase. |
| Third Stage: Clinical Trials Phase II:
Phase II studies are conducted upon a group of people that are chosen randomly for analysing the effect of standard drug or placebo (harmless substance). These trials are carried out to research if the drug works properly for some disease and what concentration of dose would be effective at what frequency to show efficacy of the drug. Greater knowledge about side effects of the drug is achieved in this study and so the participants are closely monitored. |
| Fourth Stage : Clinical Trials Phase III:
Phase III studies are usually randomised and blinded (subject or the physician and sometimes both are unaware of the treatment used) , carried out upon thousands of people. Participants need to be strictly monitored. These trials provide furthermore information about the drug’s safety profile which can be inserted in a leaflet after marketing. After this phase the manufacturers can submit an application of drug approval to FDA and so it takes several years to complete this trial phase. |
| Fifth Stage: Post Clinical Trials Phase IV:
After the approval from FDA, the drug is marketed and then studied amongst the population for seeing any adverse effects of the . Frequent monitoring and evaluation is performed over longer period of time to assess any possibility of error in drug’s performance. |
4.Are All Medicine Drugs?
Yes. All medicines can be without any doubt, called as drugs. But fascinatingly, NOT ALL DRUGS ARE MEDICINES. However, here lies an exception too. According to a famous medical scientist and physician, Paracelsus, “What is there that is not poison? All things are poison and nothing is without poison. Solely the dose determines that a thing is not a poison,”. To elaborate and explain this , recall what we mentioned above drugs can cause toxic effects if their dose value exceeds.
It is also said that the medicine can be anything that brings your body relief and healing, which can help to regulate your normal physiological processes without any harm. For eg: Eight glasses of water per day can keep you fit and healthy, so it is a medicine. , A good sleep of an average of six to seven hours is medicine for a normal adult. Whereas drugs are confined to controlling your body and mind by chemical molecules interfering to regulate your normal health condition. For eg: If you’re a diabetic patient you’ll need anti-diabetic drugs to bring your sugar levels under control.
Contrary to the general assumption that both drugs and medicines are the same, the saying is not 100 percent true. The chemical substance that can affect the normal functioning of a human is known as a drug whereas the substance that is used to treat any physiological illness is known as medicine. Still, somehow, both terms are used interchangeably.
5.Are Drugs Available As OVER-THE-COUNTER (OTC) Form As Medicines?
You might’ve often heard of the terms, OTC drugs, OTC medications, and OTC products. But do you know what they actually mean? OTC or Over-the-counter form of drugs are those that are available at the pharmacy which can be purchased by any consumers without the need of a prescription or doctor’s advise. Moreover such drugs must be strictly compliant to it’s safety parameters as instructions on the label given must be clear enough for the patient to understand it’s use.
Drugs that are available Over-the-counter do more than just provide you relief from any sort of pain and allergy. They can also be used to prevent and cure diseases like for eg: treatment of migraine can be done by some drugs like Aspirin, Acetaminophen, Ibuprofen, Naproxen, etc, curing a vaginal infection by use of antifungal ointment and anti-itching soap, etc. Some commonly taken forms of OTC drugs are vitamins and mineral supplements, herbs, anti-histamines, NSAIDs, cough and cold medicines, anti-diarrheal medicines, nasal sprays, antibiotic ointments, lotions, and creams for topical infections, etc.
Conclusion
After reading the blog, what is the difference between drug and medicine; you might capable enough to reject the normal belief that drug or medicine is the same. We have proven this through the enlightenment of various kinds of literature and reports. If you still have queries to ask; we would suggest contacting our experts just by sending a short message. We’re here to help, Please contact us Now.
Don't forget to share this post!
Capsule Filling Machine Related Posts
Capsule Filling Machine Related Products
Capsule Filling Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586

Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
Tell us your material or budget,we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours