High-Shear Mixers Vs. Low-Shear Mixers: Which Meets Your Application?
Mixing holds a vital role various manufacturing operations and industries. It is equally important in the production of liquid products as well as many solid manufacturing. There are different equipment with different potentials and intensity of mixing. High shear mixers and low shear mixers are those two applications with different intensities of industrial mixing.
Just imagine you are mixing oil with a liquid and on the other hand same oil and liquid are mixed using a high speed blender, that’s how you can classify low shear and high shear mixing. The world of pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals, and cosmetics does not only rely on the speed of the mixers, in fact it is the product integrity, precision and performance that matters.
Let’s go through the following blog to learn the science behind high shear and low shear mixers so you can decide which meets your application standards.
1.What is a high shear mixer and a low shear mixer?
High shear mixers and low share mixers are the two types of mixing equipment used in pharmaceutical, food, cosmetic, chemical and many other manufacturing industries. They are basically doing the same work, the difference lies in the “shear” of both of them. Shear is the amount of mechanical force exerted by the mixing equipment onto the material which are being mixed.
High Shear Mixer:
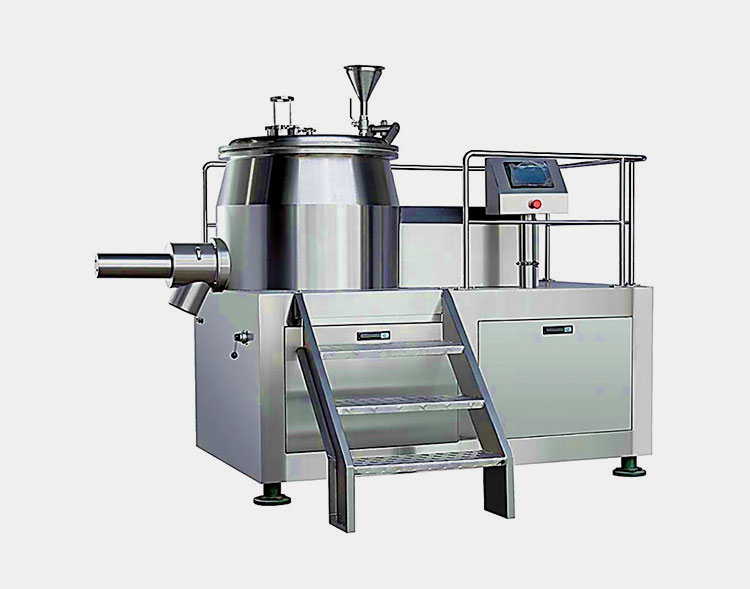

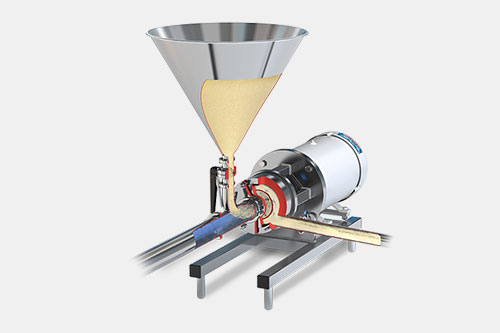
AIPAK high shear mixer
High shear mixers utilize immense energy to break down the particles rapidly, emulsify liquids and mix the immiscible substances to create a homogenous product. It is also known as high shear reactors or high shear homogenizers. These high shear mixers operates at high rotor tip speed and shear rates which make them stronger than the standard industrial mixers.
These high shear mixers have a very high mixing speed, with minimum 2500RPM. It has a rotor stator mechanism which creates very strong turbulence in the mixture and cause particle size reduction.
Low Shear Mixer:
Portable low shear mixer-picture courtesy: ebara HG
Low shear mixing as the name suggest use a very small shear on the particles undergoing mixing. These machines applies a gentle mixing blending action on the delicate particles. The miscible substances which are easily mixed under the influence of turbulence and flow are mixed using the low shear mixers. These mixers provide very gentle agitation with very less shear.
They carry out the mixing operation at a low and gentle RPM. The mixing is carried out through paddles, blades or tumbling motion. These mixers are best suited for mixing of delicate powders and sensitive biological.
2.High shear mixer vs. low shear mixer which meets your application?
A high shear mixer (left) vs low shear mixer (right)-picture courtesy: admix
High shear and low shear mixers are most widely used equipment across various operating systems even they are integrated into continuous processes like wastewater treatment, fuel energy production and mining of minerals etc. Both of them have their own unique characteristics, uses and applications. Following points will give you a better picture about which meets your application:
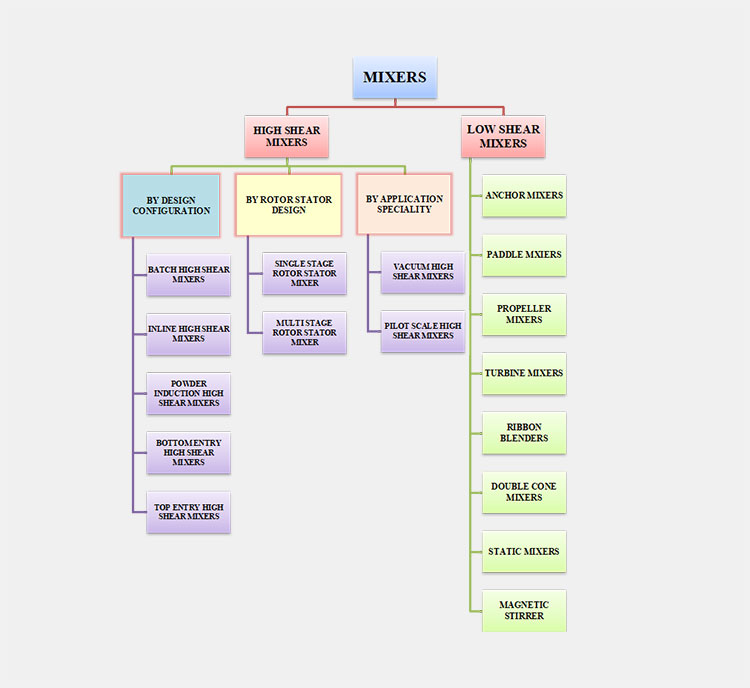
Types:
These are the following types in which we further classify high shear mixer and low shear mixer:
| HGH SHEAR MIXER | |
| BY DESIGN CONFIGURATION | |
| Types | Features |
| In line high shear mixer
Inline mixer –picture courtesy: ross mixer |
These inline high shear mixers are integrated into continuous processing lines with a continuous mixing operation. These mixers have a sealed chamber provided with inlet and outlet ports. A powerful pump is attached to circulate the product for mixing through the mixer. A high concentrated shear zone is created which cause dispersion and material homogenization. These mixers are ideal for emulsions, suspension and viscous products. |
| Batch high shear mixer
Batch high shear mixer-picture courtesy: tetra pak |
These batch high shear mixers are used with fixed large volume substances. The whole mixing procedure is carried out in a single tank which is more suitable with high viscous compounds and materials that require prolonged mixing. They offer a high efficiency with adhesives, chemical processing, food production and chemical manufacturing. |
| Powder induction high shear mixers
Picture courtesy: silversons |
Powder induction high shear mixers are used where powder-liquid processing is required. These mixers ensure uniform dispersion of powders into liquids without any clumping or making dust. The powder induction mixers create a vacuum or suction force in this high speed liquid stream. This vacuum leads to rapid pull of dry powder into the liquid stream. This way the powder is instantly wet and dispersed with minimized dust. |
| Bottom entry high shear mixers
Picture courtesy: silversons |
Bottom high shear mixers are integrated at the bottom of the mixing tanks. They have a rotor stator system which draws the ingredients towards bottom of the tank for intense mixing. They have a slow moving scrapper unit which ensures the gentle and uniform distribution of the ingredients. These bottom entry high shear mixers are best suited with viscous and high solid formulations. |
| Top entry high shear mixers
Picture courtesy: silversons |
Top entry high shear mixers have a motor and a mixing shaft which is mounted vertically downward from top of the mixing tank which is further driving a rotor stator system which is submerged in the liquid. The strong shear force pulls the material downward from surface and break agglomerates if there are any. They can be integrated with open tanks or closed tanks. |
| By Rotor-Stator Design | |
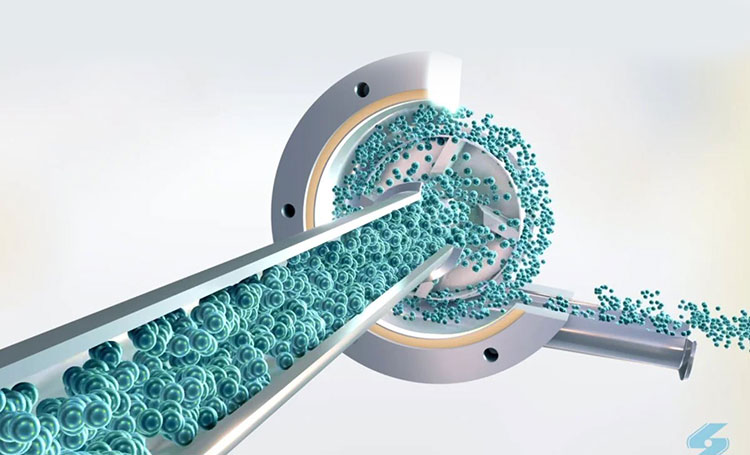
| Single-Stage Rotor-Stator Mixers
Rotor stator mixer-Picture courtesy: direct industry |
They are called rotor stator mixer because they have a rotor which spins inside a stator, which is stationary. The rotor spins at a very high tip speed which creates an ultra-high shear zone. These mixers have the ability to reduce the particle size to sub-micron levels. They are best suited with nano technology, polymer emulsification, pigment dispersion and homogenization of the substances. They can be used in line or batch processes. |
| Multi-Stage Rotor-Stator Mixers
Picture courtesy: Myers mixers |
These multi stage rotor stator mixers have multiple rotor stator systems arranged on a same shaft in series. This multiple rotor stator systems allow the material being mixed to pass through several high shear zones in a single run. This multi stage mixing results in uniform dispersion of the particles, fine emulsion and consistent results. This design is ideal for emulsions, suspensions and creams. |
| By Application Specialty | |
| Vacuum High Shear Mixers
Picture courtesy: ross mixers |
As the name suggests, these vacuum high shear mixers work by creating a vacuum in the mixer system. These mixers have a rotor stator system with a sealed vacuum capable vessel system. These mixer systems operate under reduced pressure to create a vacuum and remove all the air particles entrapped during high speed mixing. These vacuums high shear mixers efficiently produce air free suspensions and emulsions. |
| Pilot-Scale or Lab-Scale High Shear Mixers
|
These lab scale high shear mixers are mainly developed for R&D purposes at lab scale or pilot testing. These mixers are made to completely mimic the full large scale performance. They have a rotor stator assembly to achieve dispersion along with particle size reduction and emulsification of small lab scale batches. The rotor stator assembly exerts a milling action on these particles as well resulting in particle size reduction. |
The next following table classifies different types of low shear mixer:
| LOW SHEAR MIXER | |
| Types | Features |
| Ribbon mixer
Picture courtesy: sudenga industries |
The ribbon mixer is a very commonly known type of low shear mixers. They provide a gentle but thorough blending and mixing of the powders and granules. They have a U-shape trough with helical ribbons like blades which rotate for the mixing of ingredients. They are easy to clean and best suited for sensitive, cohesive and free flowing particles. They can be used for a batch mixing or in a semi continuous operation. |
| Double cone mixers/ V-blenders
Picture courtesy: ross mixers |
The tumble mixer is like a diffusion mixer. In this mixer the mixing is carried out in a hollow drum which rotates around its axis. The vessels are partially filled and rotated which cause the blending of particles inside. These mixers require an optimum speed for the proper mixing. The V shaped mixer, double cone mixer are basically types of tumble mixers. They are best suited for free flowing particles. |
| Paddle mixer
Picture courtesy: cemsan |
They are horizontal mixers with paddles like blades in them. They provide a good medium agitation to both wet and dry mixtures. They can be integrated with cooling or heating jackets for the temperature control as required. They are ideal for the pastes, solids, materials with thick consistencies and high viscous materials. |
| Propeller mixers
Picture courtesy: ace processes |
These propeller mixers have a three blade or a four blade propeller which is mounted on a vertical shaft. These mixers are ideal for less viscous liquids and mainly used for liquid-liquid type of mixing. They are low shear but still they produce a strong circulation in the mixture. The axial flow they create effectively pull the material from the top to the bottom. In this way these mixers effectively homogenize the solution mixture. |
| Anchor mixers
Picture courtesy: anchor mixer |
The mixer or agitator used in these mixers is shaped like an anchor. These anchor shaped agitator effectively sweeps the wall of the container ensuring there are no dead ends left. These mixers are sometimes integrated with scrappers on it so that there is no material buildup. These anchor mixers are best suited with semi solid and viscous materials. Therefore, they are commonly used with creams, gel and thick suspensions manufacturing. |
| Turbine mixers
Picture courtesy: direct industry |
Turbine mixers use impellers or blades attached to a vertical shaft. These impellers can be flat for radial flow. These impellers can also be pitched at an angle which promotes both, axial and radial flow. The shear level and mixing pattern of these turbine mixers is affected by the shape and angle of it blades. These mixers are ideal for solid liquid suspension mixtures. These turbine mixers are often used in waste water and chemical industries. |
| Static mixers
Picture courtesy: Wikipedia |
Static mixers have no moving parts and are a motionless mixing device itself. These mixers rely on internal stationary elements which can be helical, baffle like or grid shape. When the fluid is passed through this mixer it splits into multiple streams as it hits the first mixing element. These mixers exert a forced flow mechanism on the fluid to merge miscible and immiscible ingredients into a uniform mixture. They provide an effective mixing to constant stream of gases and liquids. |
| Magnetic stirrer
|
The mixing takes place under the influence of magnetic field created inside the mixing vessel. This mixer comprises of a magnetic stirrer which is a small magnetic device placed in the vessel containing the liquid. This vessel is placed over a magnetic plate. The magnetic stirrer inside the vessel rotates under the influence of the magnetic place when powered on. These mixers create minimal shear, and used for lab scale small volumes of liquid. |
Applications
High shear mixer:
High shear mixers are widely used in various industries due to their efficient mixing, emulsifying, dispersing and granulate material abilities. Following are few common applications of high shear mixers:
Pharmaceutical industry:
Particle size reduction through inline high shear mixer-picture courtesy: Ross mixers
In the pharmaceutical industry, the high shear mixers are used in wet granulation procedures. They are well integrated with high production lines. They are used in particle size reduction which is a very important procedure in every other pharmaceutical preparation. The production of emulsions, suspensions, syrups, creams, ointments and gels cannot be complete without high shear mixers.
Chemical industry:
Two immiscible liquids-picture courtesy: istock
The production of paints, inks and coatings require high shear mixers because they contain many immiscible liquids and particles. The high shear mixers blends the ionic and non-ionic particles into a clear opaque solution. In paints and coatings these mixers uniformly disperse the pigments, fillers and stabilizers which enhance their quality, gloss and consistency.
Food and beverages industry:
Mixing required in ice-cream making-picture courtesy: behanace
The production of different sauces, dressings and mayonnaise is completed through high shear mixer which gives them a smooth texture with no phase separation and stable emulsion. There are dairy products in which uniform distribution of flavors is done through high shear mixers. The rapid dissolution of sugar, thickeners, vitamins and flavors beverages is done through high shear mixers on large scale.
Cosmetics and personal care:
Oil in water emulsion serum
The production of creams and lotions which are emulsions require high shear mixing for a homogenous final product. There are many cosmetic products which are oil in water emulsion or water in oil, there texture, shelf life and spread ability is maintained through high shear mixers. The homogenization of surfactants, actives and fragrances in cosmetic products is possible through high shear mixing.
Low shear mixer:
Pharmaceutical industry:
Fine powder particles
The low shear mixers in pharmaceutical industry are required for efficient blending of powders for tablets and capsules. They carry out the blending and mixing of sensitive APIs with excipients without damaging or over shearing. In granulation they maintain the coating integrity and there is no broken coatings. The moisture sensitive and low dose formulations are best suited with low shear mixers.
Chemical industry:
Powder pigments for paints
They are used in homogenization of the pesticides formulations and fertilizer powder, they do not cause any dust during the process due to low shear. In paints and polymer processing, the additives and fragile fillers are mixed through low shear mixing which keeps them safe and prevent any kind of structural changes or agglomeration.
Food and beverages:
The dry powder spices made through low shear mixing
In food industry, the blending of dry ingredients like sugar, salt, flour, fibers is carried out through low shear mixing. These mixers not only preserve their texture but they prevent any dusting or layering due to their low shear. There are tea and herbal mixes prepared through low shear mixers, without any damage to the sensitive leaf structure and aromatic properties.
Cosmetic and personal care:
Translucent powder made through low shear mixer
The production of baby powders and cosmetic foundations requires low shear mixing during their production. The low shear mixers maintains the texture and fragrance of these powder particles and still give them a uniform blend of color and fragrance. These mixers ensure the uniform distribution of ingredients in soap powders and detergents.
Uses and performance differences
High shear mixer will make sure that there is micro level dispersion with high speed process but the low shear mixers offers consistency in the product while protecting the sensitive ingredients.
The following table will give you a comparison of uses and performance differences of high shear mixer and low shear mixer:
| Feature | High shear mixer | Low shear mixer |
| Mixing intensity | Very high | Low to medium |
| Resulting product | It is a fine dispersion, emulsified liquid or granulated particles. | There are uniform powder blends forms through it. |
| Time required | Short mixing time, fast and effective. | The process cycle time is longer. |
| Homogeneity | High level of homogenization, especially in case of emulsions. | The powders obtained at the end are well blended and mixed but may require extra time and repeated cycles for complete homogenization. |
| Type of motion | Rotor-stator and intense flow is mostly applied. | Paddle, tumble and gentle motions are applies. |
| Best suited with | Emulsions and granulation, especially wet granulation. | Powder blends and mixing of fragile items. |
| Heat generation | Significant heat is generated in the process. | Minimal heat generation which make them suitable with temperature sensitive products. |
High shear mixer :Advantages vs Disadvantages
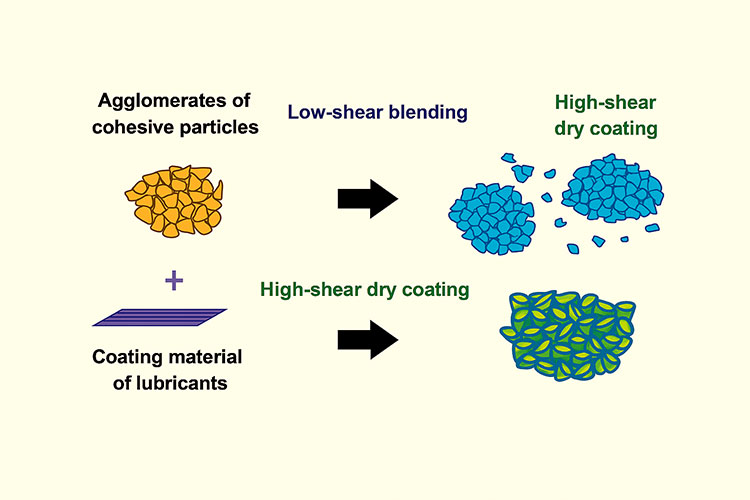
Coating of cohesive powders through low shear mixing vs high shear mixing
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It provides efficient mixing of the particles. | This fast mixing of particles come at a price of high energy consumption. |
| Effective particle size reduction is achieved. | Heat is generated during the procedure which can damage thermo labile substances. |
| In wet granulation, high shear mixing provides uniform distribution of the binder. | There is a constant threat of damage to the sensitive APIs or biological in high shear mixing. |
| It can handle multiple phases like solids, liquids, slurries, paste and also handle complicated and immiscible particles. | It requires more frequent cleaning of the machine parts and replacement as it is high maintenance. |
| High shear mixing provides a homogenous mixture and excellent emulsification. | There is a risk of over processing like incase of granulation, there could be a risk of over granulation. |
Low shear mixer: Advantages vs Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Low shear mixing offers a gentle mixing which maintains and preserve the integrity of the particles involved. | The low shear mixing is comparatively a slower process which leads to longer batch times. |
| Energy consumption is lower. | The low shear mixing is not really effective in particle size reduction or emulsification of the particles. |
| It is ideal for sensitive and thermo labile ingredients. | There is a risk of segregation or layering of the particles with poor flow properties. |
| It is cost effective and easy operation with less complicated steps. | It may not be suitable for complex solutions and mixtures and offer limited functions. |
Material Suitability/Compatibility
It is very important point to identify the compatibility of the materials to use with high shear mixers and low shear mixers. It is crucial so that we can ensure the efficient mixing of the materials without causing any damage to the properties of the particles involves and there is no unwanted reactions.
Let’s find out the in the following details:
Compatibility of high shear mixers:
Mixing of complex liquid phases through high shear mixers
Cohesive powders:
The high shear mixers are best suited with the cohesive powders and granules. They effectively break down the agglomerates and does not allow sticking.
Viscous materials:
The high shear mixers exert a larger energy onto the ingredients which makes mixing of the sticky or viscous materials easier.
Different kinds of creams, emulsions and suspensions mixed using high shear mixers
Immiscible liquid phases:
High shear mixers are ideal for emulsions and suspensions. They are usually comprised of immiscible liquid phases, with oil in water or water oil and sometime even more complicated like oil in water in oil. These kind of liquid phases are homogenized through high shear mixers.
The solid particles in the suspensions are uniformly suspended and homogenized through high shear mixers.
Heat resistant materials:
Picture courtesy: istock
In high shear mixing some amount of heat is generated during to process due to high energy utilization. It is to ensure that we are using heat resistant particles with high shear mixing so that there is no kind of damage to the structure and properties of the ingredients.
Shear tolerance:
The APIs and excipients used in high shear mixing should be resistant to the shear applied. It is ensure that the materials used can tolerate the mechanical stress without any negative effect on their properties.
Non-compatible:
Other than these compatibilities, the fragile, thermo labile or shear sensitive materials are not at all compatible with the high shear mixers as they can degrade. The materials with tendency of polymorphic changes are also not compatible with high shear mixers.
Compatibility of low shear mixers:
Free flowing powders and granules:
Finely mixed powder
The free flowing particles are best suited with the low shear mixers. These mixers provide a gentle blending without any damage to the powder properties. The free flowing powders are well mixed and homogenized with low shear mixing.
Shear sensitive ingredients:
Tea powders made through low shear mixing-picture courtesy: ramina akperova
Most of the APIs used in the pharmaceutical manufacturing are shear sensitive. Even apart from pharmaceuticals, there are ingredients and biological which are shear sensitive. The low shear mixers ensure the integrity of sensitive crystals and prevent any kind of degradation of the particles.
Materials prone to static charge:
Delicate powder and granules
There are some fine powders, micronized APIs and materials like silica, magnesium stearate or talc which have the tendency to develop electro static charge when subjected to high speed motion and collision. The low shear mixing is gentle so there is no such disturbance among the particles. Minimum static charge between the particles leads to less dust formation and reduce powder fly off during operations.
Non-compatible:
The sticky and cohesive powders are not well compatible with the low shear mixers and they may not blend properly. Dense slurries and viscous materials are also not recommended with low shear mixers.
Automation and control
Automatic procedure require less man power-picture courtesy: optiPro ERP
High shear mixers are preferred in high performance operations such as pharmaceutical and chemical processing operations. It is because in these operations, repeatability and strict process control holds a very critical value. On the other hand low shear mixers are preferred in comparatively simple procedures where precision control is less critical.
The following table gives a comparison of automation and control among the high shear and low shear mixers:
| Features | High shear mixer | Low shear mixer |
| Automation level | They are advanced, programmable and fully automatic mixers. | They have a basic to moderate level of automation. |
| Control system | They are integrated with PLCs and HMI software which monitor, control and automate the whole process. | They have timer based systems which control the batch duration.
The control systems are manual or sometimes basic programmable for blending speed and rotations. |
| Speed and torque control | These mixers have completely adjustable speed options.
The impeller and chopper speeds are adjustable along with the spray rate of binder. |
The low shear mixers have a fixed or limited range of speed variation. |
| PAT integration | Process analytical technology (PAT) are inline sensors which are integrated in the high shear mixers.
These sensors monitor the torque, moisture content, and particle size and also detect the end point especially in wet granulation. |
PAT is very rare in low shear mixers and usually not supported in these mixers. |
| Data logging compliance | These mixers have software which support them for complete data logging and complies with regulatory standards of pharmaceuticals. | In low shear mixers there has to be a manual logging of data. |
| Repeatability | They have high batch memory available, through which these machines remember the multiple product recipes which helps in consistency across different batches. | Low shear mixers have a low to medium ability to keep track of the recipe for repeatability.
This too depends upon the system being used. |
Wet granulation:
Wet granulation is a process of mixing and combining the powder particles using a liquid binder to form granules. These small dense agglomerates are made to improve the flow properties, compressibility and uniformity of the powders which is further required in procedures like tablet compression.
The outcome and extent of wet granulation efficiency depends upon the type of mixer used. Here is details of high shear mixer and low shear mixer in wet granulation:
High shear mixer: gold standard for wet granulation.
A close-up view of high shear mixing inside the mixer
Wet granulation is best suited with high shear mixers. High shear mixers produce dense and uniform size granules while maintaining a narrow particle size distribution. These mixers offer a fast processing time, usually 5-10minutes. This high speed quality make them suitable for moisture sensitive APIs because of short exposure time to moisture.
The binder mixing, granules growth and shear force exerted all these factors are very precisely controlled in high shear mixers. The consideration with high shear mixer is might be required in case of heat sensitive ingredients. These mixers can produce heat during operation which is not suited with thermo labile products.
Low shear mixer: gentle but limited use for wet granulation.
Wet granulation through Fluid bed granulator mixer
Low shear mixing is a traditional method of granule production. The powder is mixed gently or tumbled with the addition of liquid binders to form granules. This gentle mixing in these mixers protects the sensitive APIs and other excipients. There is no risk of mechanical shear stress on delicate particles and no over distribution of the binder.
This is a slow processing and may require longer drying time of the granules. The granules produced are also less uniform and loosely bound or porous. Low shear mixers for wet granulation are better suited at a small scale or for R&D batch. Low shear fluidized bed granulation system is mostly used for this purpose.
Energy efficiency
Picture courtesy: zenith energy
Let’s go through this comparison table to see the energy efficiency and environmental impacts of high shear mixer vs low shear mixer:
| High shear mixer | Low shear mixer |
| High shear mixers have intense rotor stator system which require high energy consumption. | Low shear mixers have gentle tumbling and slow motions due to which they have low energy consumption. |
| This is a fast process so they have less processing and operating time. | These mixers have longer operations and processing time due to slow mixing process. |
| The energy consumed per minute is higher, but due to fast processing, these mixers are efficient with time sensitive procedures. | The energy consumed per minute may be lower, but due to the slow process the overall time required for operation is extended and more energy is consumed. |
| These mixers generate enough heat that sometimes cooling systems are required, which also increase the energy costs. | There is a very minimal heat generation in low shear mixers which are negligible and have no effect on energy cost. |
| There is a significant increase in the energy consumption and cost at large scale production. | The lower shear mixers are cost effective and efficient with large batches. |
Conclusion:
We can summarize our topic with the fact that when it comes to mixing and choosing the mixers, one size doesn’t fill all. The choice of a high shear mixer and a low shear mixer can make or break your process. Both of these mixers have their own pros and cons. It’s not a competition of better or worse, in fact the choice between a high shear mixer vs a low shear mixer totally depends upon your formulation, flow and future needs. High shear mixers are work horses when high speed is required along with precision. On the other hand low shear mixers become the equipment of choice due to their gentle processing and energy efficiency. For more interesting details and right place to find the mixers visit our AIPAK website.
Don't forget to share this post!
Bin Mixer Related Posts
Bin Mixer Related Products
Bin Mixer Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586

Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine