Precision in Liquid Filling: How to Ensure Accuracy and No Contamination
Do you know what is the backbone of any modern and quality manufacturing? Precision. Precision in liquid filling is the core principle upon which quality, safety and efficacy of any manufacturing process depend. The minor errors of fill volume and sterility can result in product loss and compromise the consumer safety and cause non-compliance with the regulatory standards.
Ensuring accuracy and no contamination is not just limited to right machines. In fact, it is all about integration of advance technology and stringent process controls. The following guide Precision in liquid filling: how to ensure accuracy and no contamination is going to explain all your questions related to precision in liquid filling, so let’s begin!
1.Why is precision so important in liquid filling operations?
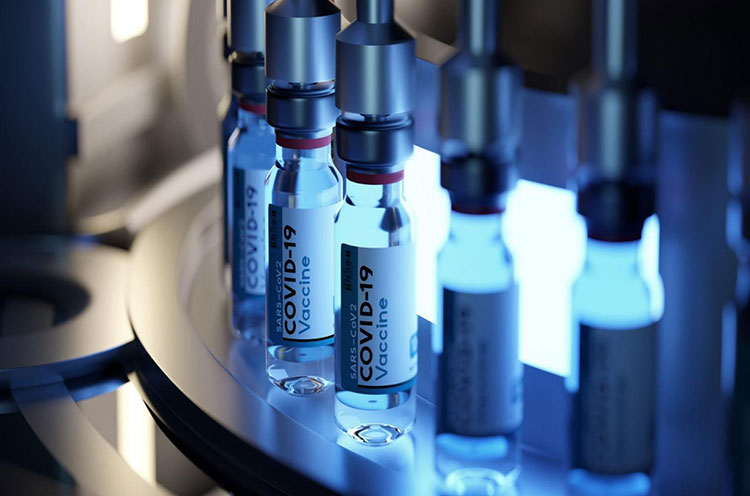
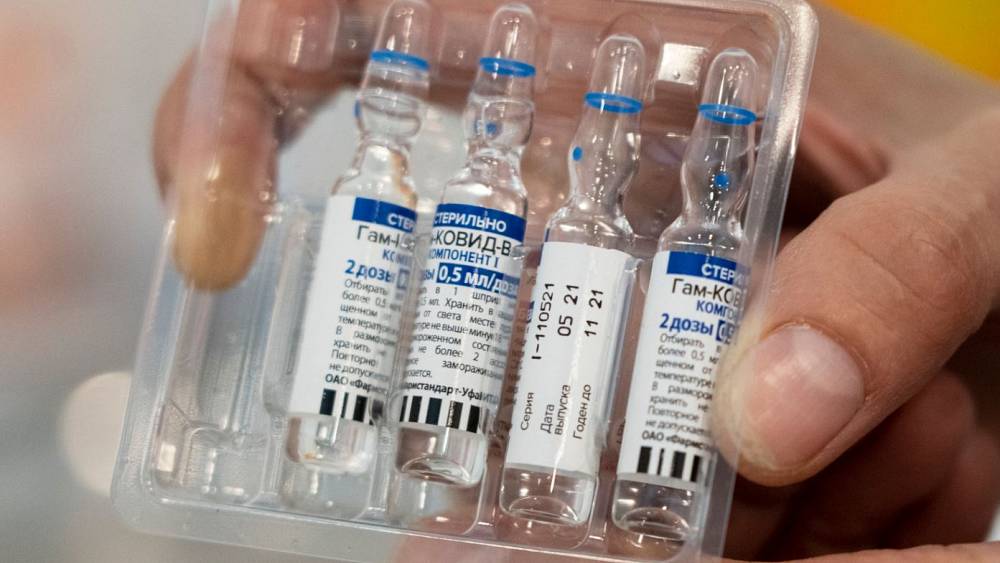
Injection vials filled with precision-picture courtesy: asset packaging
Foundation of quality and compliance:
Precision is an integral part of liquid filling because it has a major impact on the quality of product, its safety, cost effectiveness and regulatory compliance. An apparently minor variation in the liquid filling can have major and serious consequences, especially in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, cosmetics and food processing units.
Key factor in safety and efficacy of product:
Consider these two scenarios in pharmaceutical manufacturing, if a container is underfilled it cannot provide the required therapeutic effect and if it is over filled it will exceed the safe dosage limits and can be life threatening. Both of these conditions compromise the patient safety and product efficacy, only due to absence of precision in filling.
Product integrity and manufacturing efficiency:
Even in non-pharmaceutical cases, precision is equally important, because inconsistency in the fill levels will cause product wastage, packaging errors and dissatisfaction among the consumer market. Precision is not limited to a technical target which need to be achieved. It is actually the protocol which ensures that every single product leaving the production line is safe, and complies with standards.
GMP Compliance and process efficiency:
The uniformity across different batches during production is achieved through precision and accurate filling. It not only maintains the brand reputation but it also fulfills the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and FDA standards. The production becomes cost effective and overall efficient due to reduction in material loss and product downtime.
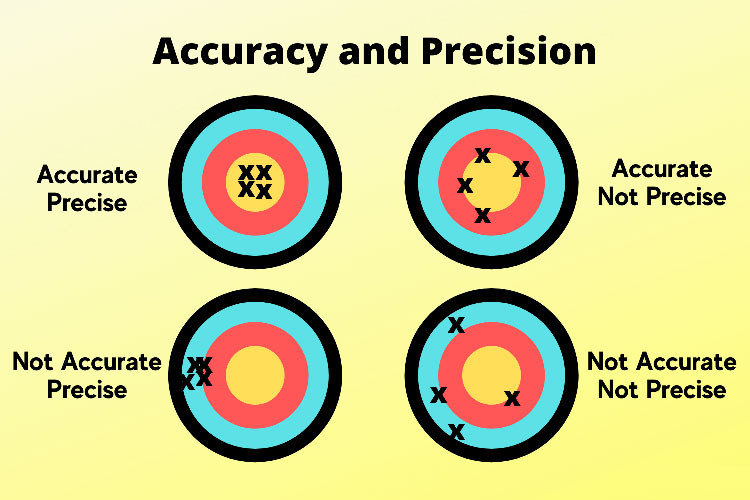
2.What Does “Precision” Really Mean in Liquid Filling?
every accurate dose is not necessarily precise-picture courtesy: science notes
The word “precision” means the extent of repeatability and consistency while achieving a specified point of measurement and output. When it comes to precision in liquid filling, it means that every single container is dispensed with same required volume of liquid, without showing any variation throughout the process, repeatedly and reliably. Precision is not a one-time thing and not limited to accuracy once a time.
Technical meaning of precision in filling operations:
In manufacturing terms, the ability of a filling system to perform with consistency in given controlled conditions in spite the presence of certain variable factors like product viscosity, temperature, humidity or speed of line. A liquid filling line is said to be precise if it provides a stable output within a defined range of tolerance and ensuring uniform weight and volume across every single batch.
Precision Vs Accuracy:
In order to fully understand precision, we need to understand the difference between precision and accuracy. These terms are actually often used interchangeably but both of them are not the same. Accuracy refers to how close filled volume of a liquid is to the required or target value. Whereas precision is the measure of consistency between those liquid fills.
In liquid filling precision and accuracy both are important. But precision is considered more crucial as it ensure the repeated performance of process and also maintains a uniform quality of the final product.
3.What Factors Can Lead to Inaccurate Liquid Filling?
The precision and accuracy in liquid filling are dependent upon a lot of key factors of the equipment and process parameters. A few very common causes are discussed below:
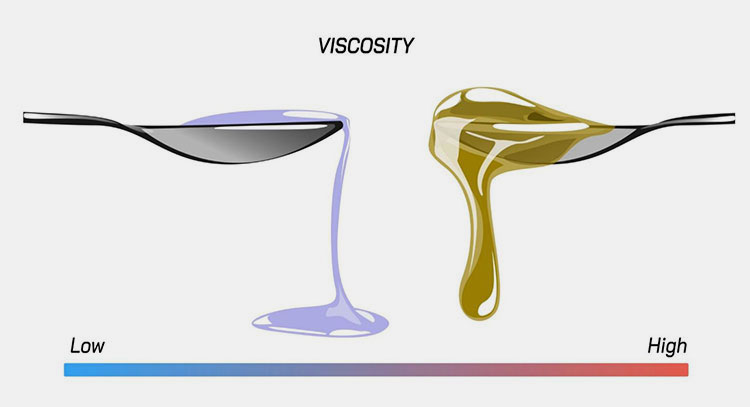
Product viscosity and temperature:
Different viscosity gradient-picture courtesy: industrial trading solutions
Change in viscosity of liquid due to fluctuations in the temperature cause a significant effect on the fill volume of the liquid. The liquid with high viscosity is thicker and have slow flowing speed while low viscous liquids are thinner and have a faster flow, this leads to under filling or over filling respectively. The compensation of viscosity differences and temperature control is an essential factor for precision in liquid filling.
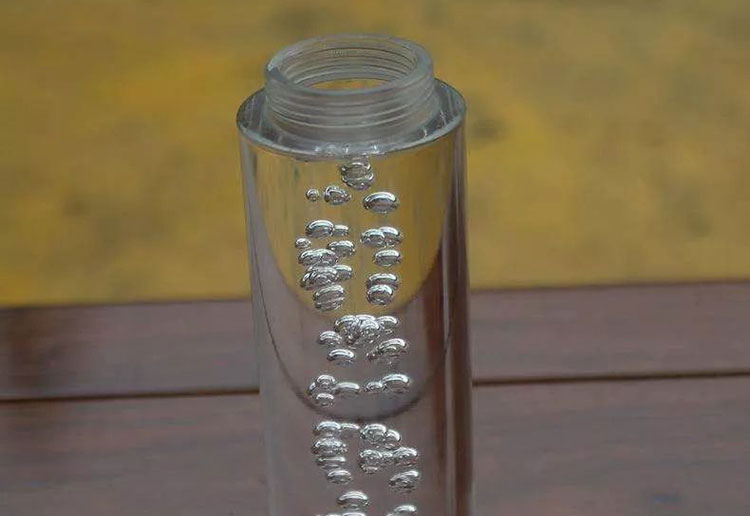
Air entrapment or foaming:
Air entrapment phenomenon-picture courtesy: zetarMold
If there are air bubbles or foaming in the production line it can significantly affect the perceived volume during the filling procedure. Thus, it becomes another factor for inconsistency in the product weight causing inaccurate dosing. There are anti foam devices and degassing systems which can be used to over come this factor in order to ensure accurate fills.
Improper machine calibration:
Picture courtesy: oden machinery
This is the most commonly occurring cause of inaccurate dosing. A filling machine without proper calibration will definitely cause a decrease in accuracy. The wear and tear in the machine parts like pumps, nozzles, and valves over time will cause drifting in the fill volumes. It is recommended to regularly calibrate and do preventive maintenance to preserve the precision in filling operations.
Mechanical wear and pump inconsistency:
The use of pumps at high speed and pressure can cause mechanical wear or seal leakage in the pumps. This leakage results in reduction of filling accuracy. There are peristaltic pumps or servo driven pumps which improves the control and repeatability of the process.
Container variation and misalignment:
The containers which could be bottles, vials, ampoules, filled injections, jars etc have different shapes, sizes and even stability. The misalignment of these containers on the conveyor belt can result in incorrect dispensing through the nozzle into these containers. The misalignment can cause inaccurate filling due to spillage. Container quality control and proper alignment systems are therefore necessary.
Operator errors and poor setup practices:
Operator error is possible even in the case of automatic machines because human error in initial setup, adjustment or even during cleaning can result in inconsistent fillings. The unclean nozzles, incorrect settings and improper handling of the equipment compromise the accuracy of the filling unit. Proper training and following SOPs can help minimizing this cause.
Inconsistent supply and flow rate:
Barometer to check air pressure-picture courtesy: stockcake
The inconsistent flow from the product feed tank or fluctuations in the supply pressure of the product can cause an impact on the amount to be dispensed per cycle. The use of pressure regulators or integration of steady feeding system can help ensuring smooth, predictable and accurate filling.
Summary:
In order to summarize the factors, we can say that inaccurate filling is a result of combination of mechanical, environmental and human factors. The regular monitoring of these variable factors and optimization of process parameters can ensure accurate, uniform and contamination free liquid filling operations.
4.How Can You Ensure Filling Accuracy?
Picture courtesy: taylor enterprise
Regular calibration:
The first step towards accuracy begins with regular apparatus calibration. The proper calibration of pumps, flow meters and weighing systems ensure that they are dispensing the required filled volume within the tolerance range. It is recommended to schedule equipment calibration after regular intervals of time or after every product changeover.
Stable process parameters:
There are certain variables like temperature, viscosity and pressure which are directly affecting the fill accuracy of the system. These factors cannot be fully avoided but we can adapt certain parameters like integration of temperature-controlled environment and by maintaining a constant stable liquid flow, we can ensure an accurate and precise liquid filling.
Automated feedback and control systems:
Now a days in modern automatic filling machines there are automated sensors and feedback systems which immediately detects and signals any major or minor deviation from the from the given values. There are advance systems like magnetic flow controllers, mass flow meters or servo driven filling mechanisms which are automatically adjusting the flow volumes through out the filling operation and thus maintaining the filling accuracy.
Optimization of filling equipment:
The basis of accurate filling start by choosing right filling technology. The choice of the equipment and technology should be according to flow properties of your liquid product. The minor details like as small as a filling nozzle holds an equal importance. The choice of anti drip or diving nozzles make the procedure splash free and minimize air entrapment. Hence, another step closer to precise filling.
Operator training and SOPs:
There should be clear SOPs (Standard Operating Procedure) for carrying out every operation from setting up of the equipment to the complete filling procedure. The GMP guidelines ensure there is no deviation from the SOPs and proper training is provided to operators so that they can identify any abnormality and fix it accordingly, without the disruption of whole procedure.
Equipment validation:
The regular equipment and process validation ensures that the filling accuracy remains consistent with time and changing environmental variables. There are statistical tools like process capability (Cp) or Cpk analysis which are used for measurement and maintenance of process performance within the acceptable limits.
Summary:
In a nutshell, the accuracy and precision in liquid filling is not just dependent upon advance machinery and tools. In fact, it is an art of calibration discipline, process stability and human precision. The manufacturers combine these factors to produce a consistent, compliant and high-quality product through out the operations.
5.How Can You Prevent Contamination in Liquid Filling?
Contamination free practices-picture courtesy: shutterstock
The prevention of contamination during liquid is equally important as precision in liquid filling. Both of these are integral part of the product’s safety, purity and compliance with regulatory standards. These are the following factors which can help preventing contamination during the filling procedure:
Controlled Environment:
The liquid filling in supposed to be take place in a cleanroom or controlled environmental spaces. The industries have controlled spaces with optimized temperature, humidity and proper air filtration using HEPA filters. It is ensured that the liquid filling room has a positive air pressure that prevents the any dust or micro-organisms from entering into the controlled environment.
In case of sterile and aseptic products, there is class 100, laminar air flow system is used, which is recommended by ISO 5. (International Organization of Standards)
Sterile Equipment:
After the environment, it is the equipment which needs to be maintained. Every single part of the equipment that comes in contact with the product is supposed to be made sterile, non-reactive, smooth and made from corrosion resistant material. Stainless steel is the best suited material for the equipment. Easy to clean designs with minimal cervices and sanitary fittings are best suited to eliminate microbes.
SIP And CIP Procedures:
Sterilization In Place (SIP) and Cleaning In Place (CIP) are essential for maintaining sterile environment in between the batches. CIP is done by using detergents or hot water for physical cleaning of the equipment and removing any residue before or after a batch. SIP is done using steam or chemical sterilant to destroy microorganisms from the equipment and environment.
Monitoring And Environmental Testing:
The regulatory guidelines for liquid filling recommend the implementation of microbiological monitoring programs, which keeps a check for contamination on the surrounding air, surfaces and personnels in contact with the equipment. There is microbiological equipment like:
- Settle plates, which check for the level of airborne contamination.
- Contact plates which detects the surface contamination.
- Active air samples are taken which gives a quantitative measure of microbial count present in the air surrounding the apparatus.
Filtration And Sterilization of The Product & Air Supply:
The product being filled is made sterile by filtering it properly through membrane filters of usually 0.2 µm in size. It makes the product free from any kind of contamination. Similarly, the compressed air being used in the liquid filling system is also sterilized before using by passing it through HEPA or hydrophobic filters. It prevents any microbial intrusion in the system.
Sealing And Handling:
Last but not the least. Contamination can occur even post filling operation. Therefore, it is important to make sure that the caps, seals and closures being used are properly sterilized and carefully handled in controlled conditions. The use of automatic closing and sealing systems minimize the cross contamination due to human contact and maintain the sterility of the final packaging.
6.How Do You Validate Precision and Sterility in Filling Operations?
Validated rubber stamp given to the process that qualify the validation
The validation in liquid filling for precision and sterility is done to make sure that both of these parameters are achieved consistently and repeatedly throughout the whole procedure and under real production conditions. It verifies the GMP requirements of the process, equipment and environment. Let’s find out how they are done:
Precision Validation:
The precision validation is done to verify the repeatability and reproducibility of the filling process. It ensures that every single container is being filled with the correct volume within the prescribed tolerance limits. These are the following key steps include in precision validation:
Filling equipment calibration:
It involves the verification of the weighing and volumetric systems of the equipment using traceable standards. The values of the equipment should be as similar as the reference standards. Any deviation is recorded and fix before using the equipment again.
Test runs and data collection:
Multiple filling cycles are conducted using an actual or simulated product. The fill weight and volume of these filling cycles are carefully recorded. It is done to point out any kind of inaccuracy or deviation from the prescribes values.
Statistical analysis:
The data collected after multiple test runs; the fill weight and volume of each container undergo statistical analysis to find out consistency of the process. Standard Deviation (SD) and Coefficient of Variation (CV%) are two main tools of statistical analysis.
Standard Deviation (SD):
It is the measure of difference in the individual fill values from the average (mean) value. Lower SD value means the process is highly precise and vice versa.
Coefficient of Variation (CV%):
It is the percentage expression of the standard deviation and it helps to compare the consistencies between the machines and different batches. The acceptable limits are ideally ±1% or even tighter. It also sometimes varies and depends upon the type of product being filled.
Control charts:
The control charts are made to establish the upper and lower limits of the liquid filling. It not only monitors the ongoing performance of the process but it also detects any deviations at early stage so they can be fixed right away without causing any major error with the process.
Sterility Validation:
Sterility validation -picture courtesy: NovaSterilis
Sterility is the paramount of the validation procedure in liquid filling, especially in the case of injectables and sterile products. The following steps explain how sterility validation is carried out in liquid filling:
Environmental monitoring and validation:
It is done to verify that all the surfaces in contact, surrounding air and operators meet with the ISO 5 or ISO 7 cleanliness levels. The HEPA filters efficiency, air pressure difference and particle count is monitored.
Sterilization validation:
Sterility test validation is performed for sterile products. It is to make sure that there is no micro-organism or microbial growth in the product. This can be done by using media techniques like direct incubation or membrane filtration.
Personnel qualification:
The operators in direct contact with the liquid filling process have to be properly trained, skilled and qualify the aseptic techniques. There should be a regular assessment of the operators involved about the maintenance of the sterile conditions and performance of aseptic techniques.
7.What validation steps (IQ, OQ, PQ) are required for filling machines?
Picture courtesy: MadgeTech
The validation in liquid filling machines play in important role in the qualification of the machine for GMP compliant production. It is done to ensure the consistency in performance, reliability and usage safety. The whole validation process comprises of three phases. Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ) and Performance Qualification (PQ).
This whole process is collectively termed as equipment qualification.
Installation Qualification (IQ):
Purpose:
The main purpose of installation qualification is to verify the proper installation of the machine according to its design, footprint, given specification and the manufacturer’s requirement.
These are the following steps included in installation qualification:
It begins with the cross checking of the equipment pack components against the packing list.
It is ensured that there are no damages in the equipment.
The installation of the electrical, mechanical and control systems is verified according to the approved design.
The other utilities which include power supply, compressed air and purified water etc. are verified against the required specifications.
The calibration certificates of the equipment are verified and it is ensured that the machine manual and drawings are authentic and up to date.
The equipment identification number, labels and nameplates are verified and matched with the documentation.
All these installation details are recorded in the IQ protocol file which is sent for formal approval before moving to the OQ.
Outcome:
After the successful completion of all the above steps, a documented assurance is achieved. This documented assurance shows that the filling machine qualifies the installation and is ready for use.
Operational Qualification (OQ):
Purpose:
The purpose of operational qualification deals with the required operation of the filling machine. It ensures that the filling machine is operating as prescribed and is in accordance with all the defined parameters and conditions. These are the following steps included:
All the functions of the machine starting from even the basics like nozzle movement, filling volume control, pump speed and sealing mechanisms are cross checked.
The functioning of alarms, sensor, interlocks and control panel is verified because the working of automatic machines greatly relies on these automated controls.
The critical operational parameters which include fill speed, pressure and temperature are established as per the requirement and their acceptable range is defined.
The simulation of worst-case scenario as well as normal operation conditions is carried out to ensure that the performance is consistent.
The results are documented and standard operating procedure (SOP) for production is set in place.
Outcome:
The operational qualification of the equipment gives a documented proof that the equipment is performing within the defined limits and responds right in normal and extreme conditions.
Performance Qualification (PQ):
Purpose:
It is done to make sure that the machine is consistently giving the desired output and there are accurate and contamination free fills during the actual real time production. These are the following steps included:
The sample runs are carried out on the machine with the actual product or any other representative medium, keeping the real production conditions.
In these sample runs, the fill weight and volume, rejection times and whole filling cycle time is monitored and carefully recorded.
The repeatability and precision across different batches is verified during performance qualification.
Incase of aseptic filling systems, media fill tests are performed which verify the sterility of the whole operation.
In carrying out all these steps, it is made sure that all the end results are in accordance with the pre-established acceptance criteria.
Outcome:
The performance qualification ultimately gives documented evidence of the machine performance which includes accurate, sterile and compliant fills in the real time filling operations.
8.What Are the Latest Innovations in Liquid Filling Technology?
Picture courtesy: the manufacturer
The following are the most significant innovations in the liquid filling technology which provide greater precision, zero contamination and flawless accuracy.
| Innovations | Characteristics |
| Servo Driven Filling System | They have replaced the traditional mechanical fillers. They offer greater control over fill speed, volume and nozzle movement. They ensure that there is minimal deviation from the target volume through micro-adjustment in real time.
Product spillage is reduced & accuracy is improved. |
| Peristaltic and Time Pressure Fillers | They are used by modern septic filling lines for sterile and sensitive liquids. The cross contamination is prevented as in these pumps, the liquid come in contact with the disposable tubing only and not with the machine parts. |
| Integration Of Robotics and Automation | They are the key component of high-speed automatic filling lines. They carry out all the container movement, capping and inspection which minimize contamination due to human contact. These vision-based systems have cameras and sensors that verify fill level and ensure is unit is met with quality criteria. |
| Smart Sensors and Iot (Internet of Things) Integration | They have brough digital transformation to the filling operations. They allow the manufacturers to monitor critical parameters like viscosity, temperature, pressure, fill volume remotely. They help in minimizing the downtime by the prediction of deviations before they even occur. |
| CIP & Single Use Technology | CIP ensure the automatic cleaning of the machine parts without the need to dismantle and save time and maintain sanitation.
Single use systems use pre sterilized disposable tubings, nozzles and bags that are relaced after every batch, thus minimizing the cross contamination. |
| Micro Dosing & Adaptive Control System | The ophthalmic and bio technology industries require the use of these systems as they have fill volume in micro liters usually. They make the dispensing ultra precise.
The combination with adaptive control systems, adjust the parameters on the basis of fluid properties, which ensure that the output is consistent even when there is change in temperature, pressure or viscosity. |
Conclusion:
This guide explains that precision in liquid filling is much more then just a technical achievement. The foundation of product quality, safety and regulatory compliance starts with precision in the filling. The achievement of true precision is a combination of calibrated equipment, validated processes and controlled environmental conditions. It won’t be wrong to say that future of liquid filling is depending upon the automation, robotics and digital intelligence. Therefore, precision and sterility go hand in hand and together they can transform the liquid filling from a regular basic step to a well-engineered process that is a definition of excellence, consistency and safety across every batch produced.
Don't forget to share this post!
Vial Filling Machine Related Posts
Vial Filling Machine Related Products
Vial Filling Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine