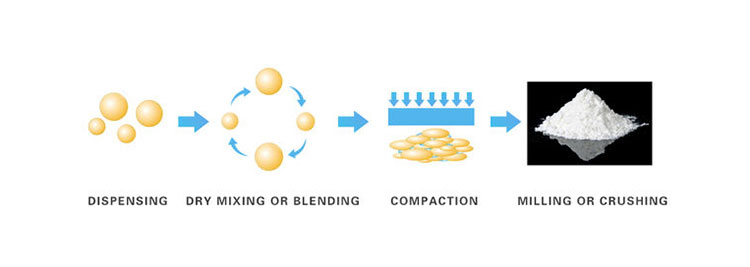
Wet Granulation VS Dry Granulation
Granulation is a commonly used term in the pharmaceutical industry that refers to the formation of grains or granules ranging in size from 0.2-0.4mm.
The granulation process plays a vital role in the production of solid dosage form both capsules and tablets. It is the procedure in which particles are enlarged and granules are produced. Granulation modifies the powder into dust-free granules.
Compression of tablets is achieved by granulation. It also enhances the packing of dry granules and creates a coating for drugs for their sustained release. There are two main types of granulation: wet and dry granulation.
To know more about the major differences between wet and dry granulation. Keep reading this informative review.
Table of Contents
I.What is Wet Granulation Vs Dry Granulation?

Wet Granulation
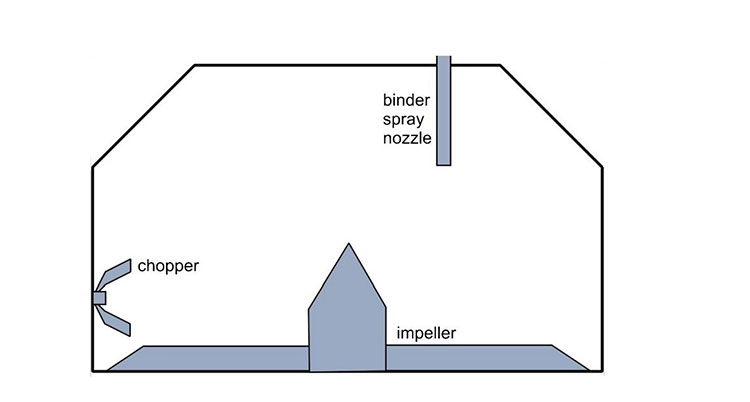
Wet granulation as the name depicts requires liquid during processing, a binder or solvent for facilitating the agglomeration process that usually works by adhesion of the powder particles due to the wet solvent. Wet drying is the most common technique used for granulation or agglomeration despite its long and time-consuming process but yields better results.

Dry Granulation
Dry granulation uses slugs and roll compactors for compacting the powder and converting it into granules also known as an agglomeration of the powdered drug. Dry granulation is done without the involvement of any liquid for the formation of granules. This technique is mostly used for the granulation of moisture-sensitive and heat-sensitive materials.
The type of granulation one needs for a certain product, whether tablet or capsule formation needs detailed knowledge and know-how of the drug, the types of excipients required, and release properties of the drug.
II.Difference Between Wet Granulation and Dry Granulation
CLASSIFICATION

Wet Granulation
Wet granulation which is the most commonly used granulation process is achieved by various methods. These include
- High shear granulation
- Low shear granulation
- More advanced techniques involve
- Reverse wet granulation
- Steam Granulation
- Moist activated dry granulation
- Thermal adhesion granulation
- Melt granulation
- Freeze granulation

Dry Granulation
Two main techniques or types of dry granulation are
- Roller compaction
- Slugging
The very new or innovative technique introduced for dry granulation is Pneumatic Dry Granulation (PDG).
COMPONENTS

Wet Granulation
Whereas wet granulation requires refined powder, an aqueous medium as granulating fluid, and a sieve.
Granulating fluid
A volatile and non-toxic fluid that acts as amassing agent for powder particles. The volatile nature of powder is must make it easier to dry the final dosage.
Sieve
To make granules of the wet mass (powder and granulating) it is passed through a sieve.
The main components involved in dry granulation are finely powdered compounds, rollers, or compactors for tablet compressing.

Dry Granulation
For dry granulation of fine powders, there are two main components
Tablet press
Heavy-duty Tablet presses are used to make large tablets. As there is no solvent involved in making tablets through tablet press, the uniformity of tablets may get affected.
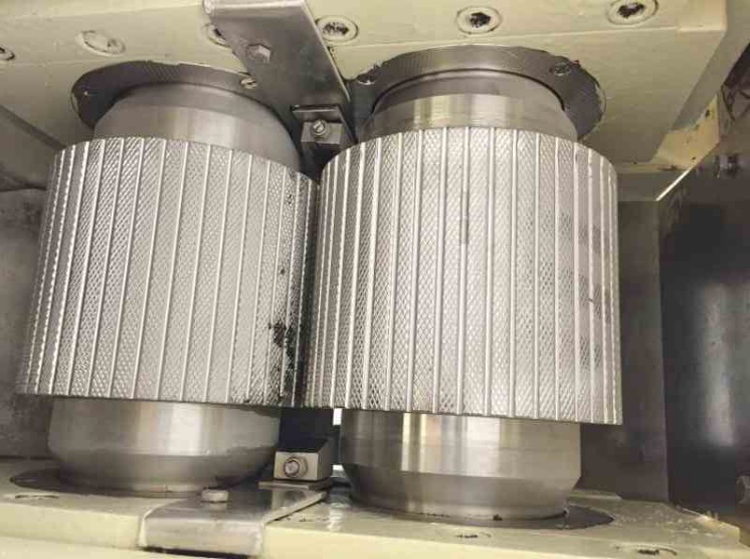
Roll Compactors
Two rollers compress or compact the powder to make continuous sheets. These sheets are more uniform than tablets as there are two rollers through which powder is consistently processed.
PROS

Wet Granulation
Wet granulation involves granulating liquid also known as a solvent which is mixed with the fine powder. This volatile solvent is later evaporated by drying techniques.
The major advantages of wet granulation are as follows:
Better flow properties: More spherical granules are produced having better flow properties hence suits best for various dissolution rates.
Easy compression: Enhancing the flow, compression ability, and cohesiveness of the powder wet granulation makes the compression of powder into tablets a very smooth process.
Suitable for high-dose pharmaceuticals:wet granulation provides the solution for high-dose pharmaceuticals that are insensitive to heat and moisture.
Reduced Dust levels:In wet granulation, there is minimum to no dust produced during the process as compared to the dry methods.
Uniform density granules: through wet granulation equally dense granules are formed thus providing a more uniform method of granulation.
Easier tablet coating: Wet granulation is best. suited for coated tablets.

Dry Granulation
Less Equipment: As the process does not involve any liquid solvent and subsequent drying it needs less equipment and space for the machinery.
Moisture sensitive Dosage: Eliminating the use of any solvent or liquid it’s the best fit for moisture-sensitive drugs or the dosage that changes its properties after coming in contact with aqueous media.
Best for heat liable compounds: As there is no liquid involved excluding the need for excessive drying, dry granulation is best for heat liable compounds and materials.
Sustenance of drug morphology: There is no change in the drug morphology by dry granulation.
Faster disintegration: This process is known for making tablets that are readily disintegrating due to the dry binder which has less binding or adhesive properties.
Scalable:Dry granulation is highly scalable and can be used at the production level straightforwardly.
CONS

Wet Granulation
- Wet granulation is a lengthy and costly process.
- This process requires extensive time, energy, and labor to dry the wet granules.
- An extensive validation process is required for granulation endpoint and granules mixing time.
- This process highly depends upon the degree of sterility and cleanliness of mixers. Extensive cleaning is required for blenders, ovens.
- Lack of uniform temperature through drying trays.
- High possibility of product degradation due to humidity and heat exposure.
- Wet granulation is complicated with low-density and hydrophobic substances.
- Difficult to recover material from trays.

Dry Granulation
- The high tendency of tablet softening or breaking with dry granulation than tablets manufactured from wet granulated powders.
- High tendency uneven and color distribution.
GRANULES FORMATION

Wet Granulation
- Granules formed by wet granulation are roughly textured.
- They do not glide smoothly.
- They are less denser.
- They do not run easier into dies.
- They are more prone to break during compression because of porosity.

Dry Granulation
- Granules formed by dry granulation have a smooth texture.
- They glid efficiently.
- Their density is compact.
- They can flow into dies instantly.
- They give strong compact with minor lesser friability.
KEY STEPS

Wet Granulation
The major steps of wet granulation are discussed below for you to have an idea of the process
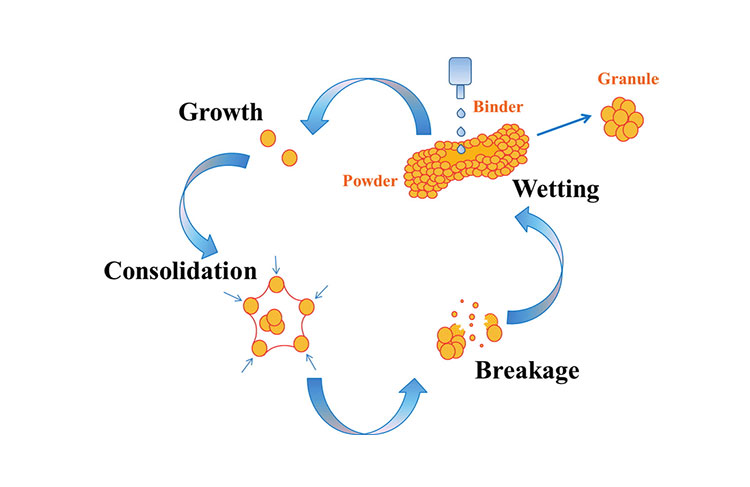
Wetting and nucleation
The very first step in granulation which is of prime importance is wetting and nucleation. It refers to the primary wetting of the powder by the granulating fluid to make nuclei. Spray rate and fluid distribution greatly impact this process.
Coalescence
Also referred to as ball growth involves the formation of granules. The less wetted particles and larger nuclei come closer to make granules. This process is the conversion of two smaller granules making a bigger granule.
Consolidation
In this step, the granules from the previous step are consolidated by forces generated by the agitation bed to make the granules into a compact shape. The higher the agitation the higher the consolidation of granules takes place. The physical properties of granules such as tensile strength, compactness/hardness, and dissolution are controlled by this step.
Breakage
Breakage or attrition is the final step in wet granulation where the granules start breaking into fragments that ultimately result in binding of these fragments to other granules making a layer over the lasting granule.

Dry Granulation
The important steps of dry granulation are discussed here for your ease:
Weighing Formulation Components
The first step is to take out appropriate amounts of desired constituents including the API and excipient. These components should be in fine powder form for further processing.
Mixing
The next step is to mix the components in a mixer to make a uniform mixture. After mixing some amount of lubricant is added to increase the flow of powder while slugging and prevention of sticking powder on the equipment.
Compression of Powder Mixture
This process involves the compression of mixed powder into tablets. This step is also referred to as slugging or precompression as the pressure applied here is much lesser than the final compression step. The tablets usually of 10-15mm thickness are termed as slugs. Here compaction can be attained via two methods i.e. slugging or roller compaction.
Milling and Sieving
After making slugs, these slugs are broken down by a specially designed hammer mill or specific milling apparatus into smaller pieces. After breaking they are passed through a sieve to get uniform-sized granules leaving the odds.
Addition of Lubricant and Disintegrant
After choosing the right-sized granules the other part of lubricant is added along with the excipients such as disintegrant and mixed ultimately.
Final Compression to form tablets
The last step is to make tablets via compression. This is achieved by tablet press either single or rotary using suitable dies and punches. The coating can be done if desired for the dosage form later on.
RECENT ADVANCEMENTS
Granulation procedures have been modified and upgraded with the advent of technology.

Wet Granulation
Wet granulation technology has been impacted by the recent advances in the technology sector. Many innovations have been made to generate pharmaceutical formulations. Various advanced wet granulation techniques are as follows:
Steam Granulation
In this advanced technique of wet granulation, the granulating liquid is replaced with a water stream to be used as a binder. Steam acts efficiently and diffuses readily into the powder as it is transparent gas providing a high diffusion rate as compared to a liquid.
A hot thin film is produced over the powder which evaporates easily and readily without much energy required. This technique allows uniform distribution, granules with large surface area, and less processing time.
Moisture activated dry granulation (MADG)
This is an enhancement of the classical wet granulation technique which utilizes much less water for agglomeration. The two main steps are an agglomeration of powder and moisture absorption. The agglomeration occurs when the granulating fluid activates the binder, after the agglomeration a material that can absorb moisture is added to remove excess moisture. Usually, silicon dioxide or microsatellite cellulose is used. This step generates a relatively dry granule mixture as compared to the usual wet granulation procedure.
The main advantage of MADG is faster release, no lump formation better flow, and compression.
Thermal Adhesion Granulation (TAG)
This technique is patent of Wei-Ming Pharmaceutical Company (Taiwan). This technique utilizes water and solvent both as granulation liquid. Besides heat is utilized to facilitate the process. in a closed system, the dosage and excipient are mixed and heated to 30-130°C to agglomerate the powder eliminating the need for drying as there is very little addition of liquid is done which is used up during the agglomeration. After agglomeration desired sized granules are obtained by cooling and passing through a sieve ultimately.
High tensile strength granules with good flow properties are obtained by this simple and convenient technique.
Melt Granulation
This technique makes use of meltable binders for agglomeration. These binders have relatively low melting temperatures i.e. 50-90oC. the next step is the cooling of agglomerated powder followed by solidification of the molten binder. Binders having a low melting point can be used that melt during the process having the drug or dosage which enables to get a variety of granules with different properties.
Melt granulation offers the best alternative wet granulation technique for water-sensitive materials. It also improves the poor physical properties of the therapeutic.
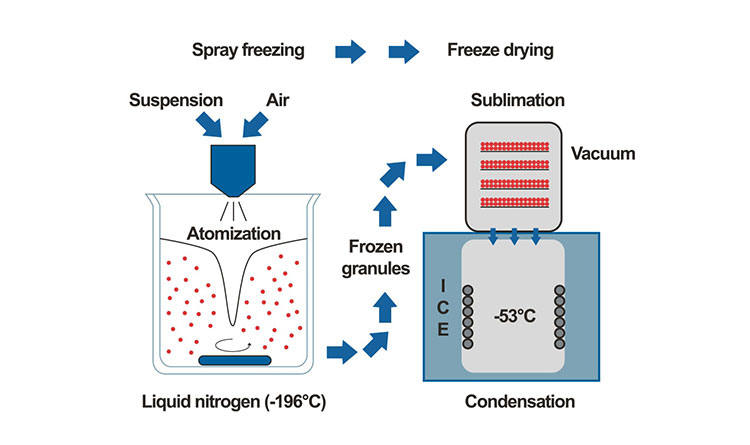
Freeze Granulation
As the name suggests this technique is based on spraying powder particles in the form of a suspension into the liquid nitrogen to freeze the droplets and then subsequent drying of these droplets. The drops are converted into granules by the sublimation process eliminating any segregation effects. The advantage that makes this technique extraordinary is that the homogeneity and structure of the particles or granules are retained.
Foam Granulation
This technique is analogous to spray granulation except the binder is added as foam instead of poring or spraying liquid on the powder. Dow chemical company owns this technique and first introduced this technology in 2003. It reduces the varying and irregular distribution of binder that affects the tablet compactness and drug disintegration or release.

Dry Granulation
For dry granulation, a highly robust method such as pneumatic dry granulation has been reported.
Pneumatic Dry Granulation
In this type of dry granulation, roller compaction is combined with an exclusive air classification system which generates granules having high flow and compression abilities.
In the very first step, mild compaction force is applied via a roller compactor to generate a mixture of granules and adequately fine particles. The next step is to extract the smaller or undesired granules from the right-sized granules inside a pneumatic system which is a gas stream. The right-sized granules then enter the fractioning chamber to form tablets.
The smaller extracted granules are then processed in a cyclone-like device or returned to a compactor where reprocessing of the smaller granules is done to achieve the desired size. Then these right-sized granules can enter the chamber for compression to form tablets.
Advantages
PDG hold many advantages over simple roller compaction used for dry granulation
- Low cost
- Less material wastage
- A closed unit enables less exposure to dust
- High flowability even with low roller compaction
III.Which is Widely Used Techniques -Wet Granulation Vs Dry Granulation?
Wet and dry granulation holds their specific pros and cons. Wet granulation is considered best and widely used despite its complex procedure and more equipment required as it does not affect or destroy the active components of the drug while there is a danger of such destruction while dry granulation makes tablets.
The qualities like uniform mixing, efficient binding while using less quantity of binder, scalability, and less wastage of drug during compression make it more attractive.
At places, dry granulation, on the other hand, has an edge over wet granulation for the drugs or compounds that are heat sensitive and moisture sensitive. As there is no involvement of solvent or liquid binders in dry granulation it saves the drug from moisture exposure and thus intensive drying through heating.
IV.Which one is More Cost-Economical- Wet Granulation VS Dry Granulation?
As we have discussed how wet and dry granulation processes work and the specific techniques involved, it is evident that there is more advancement made in techniques for wet granulation.
Wet granulation besides being more complex is still mostly desired because of its advantages while dry granulation has lost its popularity compared to wet granulation.
With all the advantages and multistep complex processes in the technology for wet granulation, comes the cost of it. Wet granulation is much costly as compared to dry granulation owing to the heavy machinery and more equipment requirement. Wet granulation also requires more cleaning cycles of the equipment also makes it more expensive.
Conclusion
Dry granulation and wet granulation are two important techniques for granulation. Though dry compaction is getting obsolete but still used by major pharmaceutical companies. while wet granulation and its advanced techniques are bringing more promising solutions. We hope this blog has answered your major queries regarding types of granulation and their specific uses.
Don't forget to share this post!
Granulator Machine Related Posts
Granulator Machine Related Products
Granulator Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine