Dry Granulation Process Flow Chart
It might come as a surprise to you that not all pharmaceutical manufacturing process require extensive procedures of wetting, mixing and drying. Some materials and procedures are better left dry. This is where dry granulation process flow chart agrees. Dry granulation process neither rely on water or binders nor it requires absorption or evaporation.
Dry granulation process is best suited for moisture and water sensitive materials. Pressure is the secret weapon of dry granulation method which converts dry powder into granules. This process of dry granulation may seem simple at first but in the background there is a well devised flow of different steps to ensure precision, speed and stability.
Let’s dive into the following dry granulation process flow chart to understand each step involved!
1.What is dry granulation?
Dry granulation is a pharmaceutical process that is used to produce granules or granulates from dry powder or blend of powders. This process does not require addition of any liquid solution or heat rather it uses mechanical compression to compress the powder and change its physical properties and converting to granules.
The particle size, density and flow properties of the powder are influenced most through this process of dry granulation. This improves in the properties of the powder make it ready for compression into tablets or capsules. This process of dry granulation is mainly used for particles that are sensitive to moisture and heat as well. The granules produce through this method have very good flow properties.
2.What is the dry granulation process flow chart?
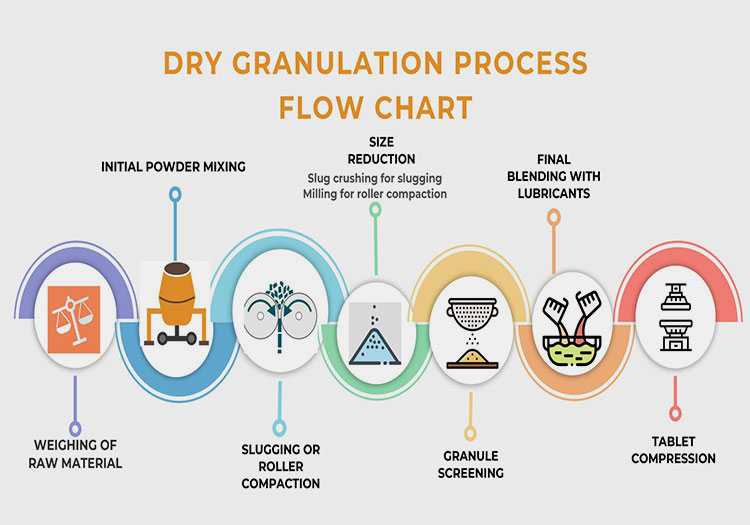
The visual representation of the steps involved in the dry granulation process which converts powder into granules leading to use in compression of tablets are shown in the following dry granulation process flow chart:
Understanding 7 points of dry granulation process flow chart:
Step 1: Weighing Of Raw Material:
As simple as it may looks like, but weighing of powders is a very critical step in the dry granulation process flow chart. The required amount of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and other excipients such as binders, lubricants and fillers is accurately measured to make sure the accurate dosing and consistency of the batch.
The product quality and accuracy of the formulation starts with the right weighing of the raw material. Weighing makes the basic foundation for the further process to continue. Any kind of error or inconsistency in weighing compromise the efficacy, safety and compliance of the final product.
Weighing process:
The weighing of the raw material is done by using calibrated electronic balances maintaining a controlled environment to avoid any cross contamination. The labeling and cross checking of the weighing material is ensured and recorded in batch manufacturing record. (BMR)
Step 2: Initial Powder Mixing API + Excipients:
Internal view of powder mixing picture courtesy: silverson
This step includes the uniform mixing of active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients without the addition of any liquid. This mixing of powders is done to make sure that the API is evenly distributed throughout the powder batch so that a uniform blend of powder is created for compaction.
Content uniformity which ensures that every tablet and capsule has the right amount of dose is achieved through the proper uniform mixing of the powders. The flow ability and compressibility of the powder is also improved through uniform mixing of powders because the excipients, binders and disintegrants are evenly dispersed in this process of mixing.
Mixing process:
This blending mixing process is carried out in special equipment to ensure the uniformity. The common types of blenders include:
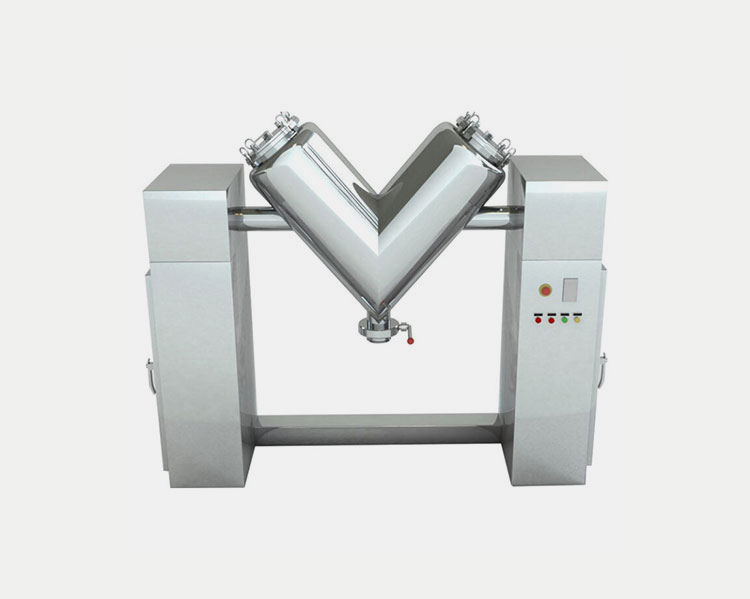
V-blender:
AIPAK V-series high efficiency mixer
The V-shaped design of this mixer provides a gentle tumbling action to ensure gentle mixing of powder. The gentle mixing is ideal for fragile powders that do not require high shear mixing. These V shaped mixer decrease the threat of powder degradation due to low intensity of blending and they produce free flowing powder. They are mostly used in low to medium size batches.
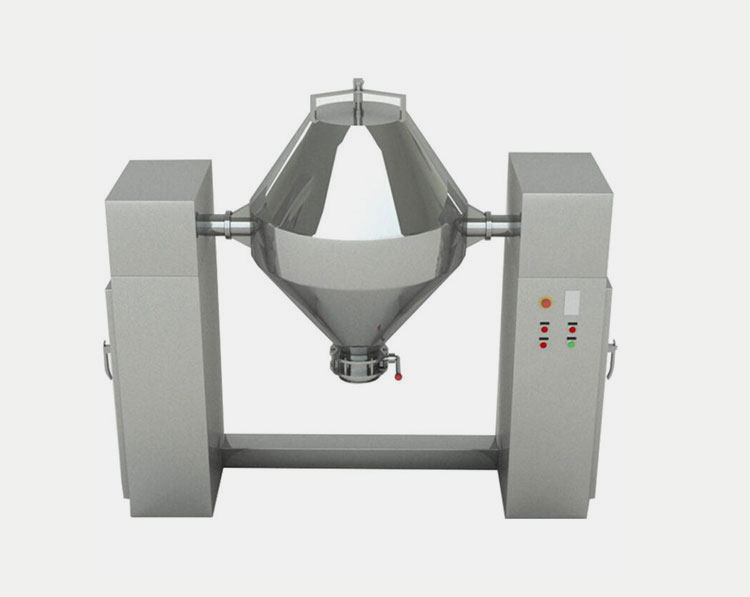
Double cone blender:
AIPAK double taper shaped mixer
This double cone blender has a very symmetrical body with structure resembling double cone. The mixing in this mixer is done under the influence of gravity by the rotation of double cone structure. A uniform mixing of the powder particles is achieved while maintaining a very minimal particle breakage.
They are very easy to clean which makes them GMP friendly and they are best suited for powder mixture with similar densities and large scale production.
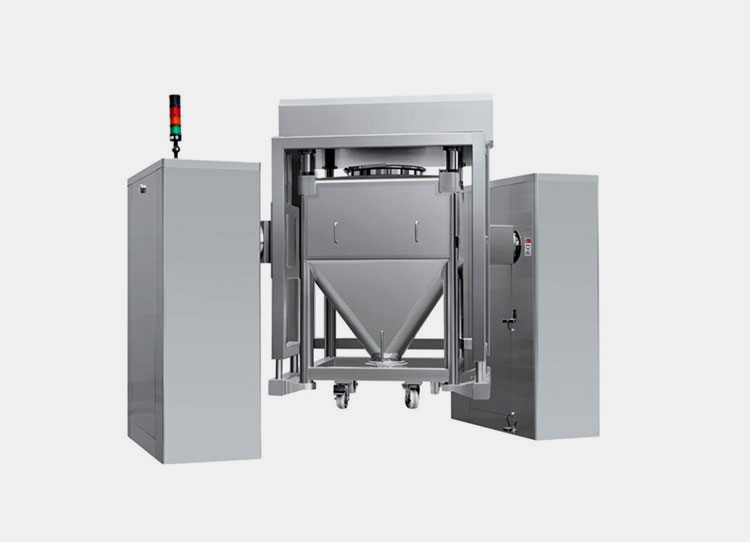
Bin Blender:
AIPAK high efficiency bin blender
They are also termed as IBC blenders (Interchangeable bulk containers). These mixers have interchangeable containers or bins for effective mixing of the powders. The interchangeable property avoids any kind of cross contamination among the powder particles. The mixing is done by the rotation of the bin maintaining its seal.
Sealing of the container reduces the exposure to dust during mixing and manual handling is reduced as well. These can be integrated into high speed production lines and large scale production. The potent APIs are best suited with IBC mixers.
Step 3: Slugging or Roller Compaction:
Powder slugs-picture courtesy: Getty images
Slugging and roller compaction are two different processes used for the compaction of powder to make it ready for further process of granulation.
Slugging:
The primary powder material after uniform mixing is compressed in machines to form slugs. Slugs are basically large size tablets or they may resemble a brick. The pressing machine subjects the powder to high pressure which causes the particles to bond together in a slug. This process of compaction of powder using pressure is called slugging.
The manufacturing companies usually do slugging through a conventional tablet press or a heavy duty rotary press for the compaction of powder into slugs. The usual size of slugs is 25mm diameter and 10-15mm thick. Slugging is better suited for powder material with poor flow properties. Slugging is inexpensive and does not require very highly trained staff or equipment. Slugs are broker down through milling.
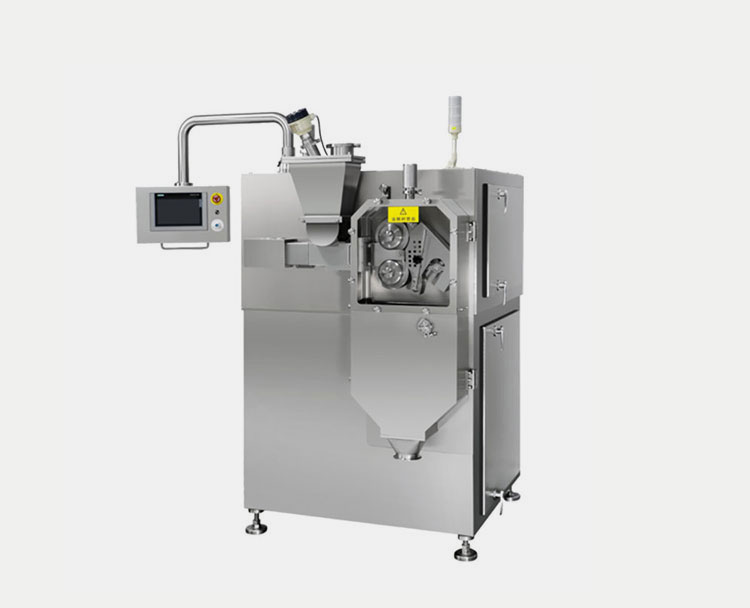
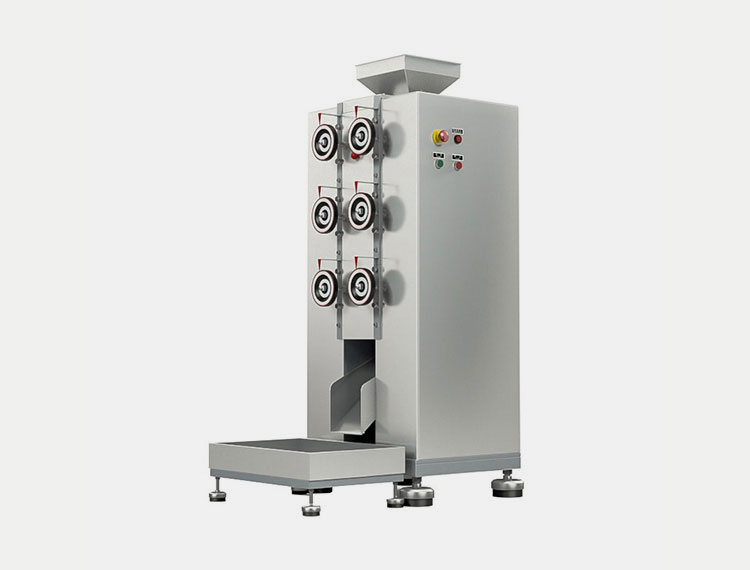
Roller compactor:
AIPAK LG series roller compactor
Roller compacor is an advanced and gentle alternative to slugging. It is done by using roller compactor machine. The powder is squeezed through two oppositely rotating rollers to be compressed in a form of a sheet or ribbon sheet. These compressed sheets are brittle which are easily broken into flakes. This further process of converting the compressed sheets or flakes is done through milling.
The roller compaction is best suited for large scale production and these machines can be integrated into continuous manufacturing lines. The roller compaction process is better validated in the pharmaceutical industry which makes it a better choice. Also, roller compaction produces granules of uniform size with very little powder dust.
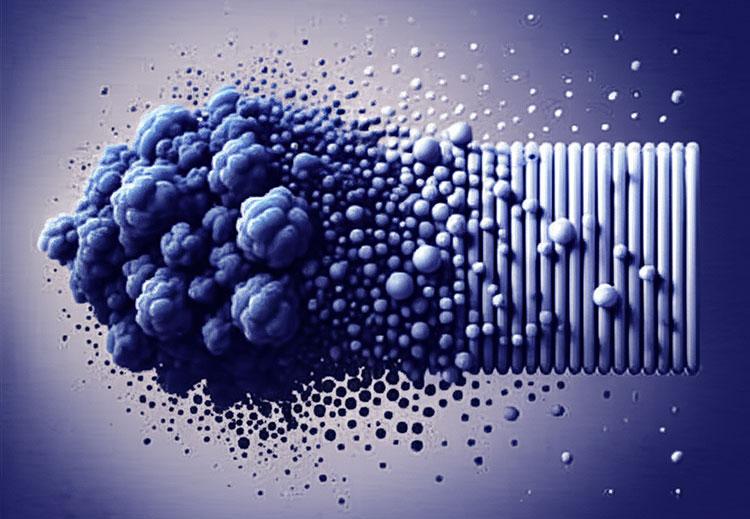
Step 4: Size Reduction:
Beautifully captured process of size reduction
Size reduction is the process where these large slugs or compacted ribbons are broken down into smaller granular particles using a dry granulator or milling. Size reduction is done to convert these compacted masses of powder into granules of required size. The flow properties, compressibility and uniformity of the granules are improves after size reduction. This makes the granules suitable for compressing to tablets or capsules. Following are the two processes used for size reduction:
Slug crushing for slugging:
Reduced size granules-picture courtesy: economy ball mill
Slug crushing is the immediate steps after the powder slugs are formed. The slugs are either broken down manually or mechanically by the using of a crusher or coarse mill. This size reduction converts those huge slugs are converted to manageable and useable granular particles.
The particles produced here can further undergo to finer milling or directly to screening. The hammer mills, crusher mills or oscillating granules are usually used for this purpose. The granular particles produced here are not final product, they still need further processing to achieve the required uniform size granules.
Milling for roller compaction:
AIPAK roller mill crusher
The compacted powder through roller compaction is crushed through roller mill crusher. Milling is also done following the slug crushing process to breakdown those particles into a finer and smaller particle size. The compacted ribbon particles are passed through the milling machine, from the hoppers into the squeezing rollers, where they are further reduced to the required particle size.
There are advanced roller mills which allow you to get different size of granule particles just by adjusting the distance of two rollers. The particles which remain oversized are recycled or pass again through the mill to attain the desired granule size. The purpose of this milling for size reduction is to narrow down the particle size distribution for good flow properties uniformity.
While size reduction is important, it is required to make sure that there is uniform size distribution so that the dosage uniformity is achieved. There are some sensitive powder materials which can be destroyed with over milling therefore precautions should be taken.
Step 5: Granule Screening:
Screening different size of granules-picture courtesy: j.engelsmann
Screening is the process in which the granule particles are separated on the basis of their particle size. Screening is done after the size reduction through milling or crushing. Screening is done to make sure that only the desired size of granular particle is obtained and moved forward for final process of blending or compression to the tablets or capsules.
Screening process:
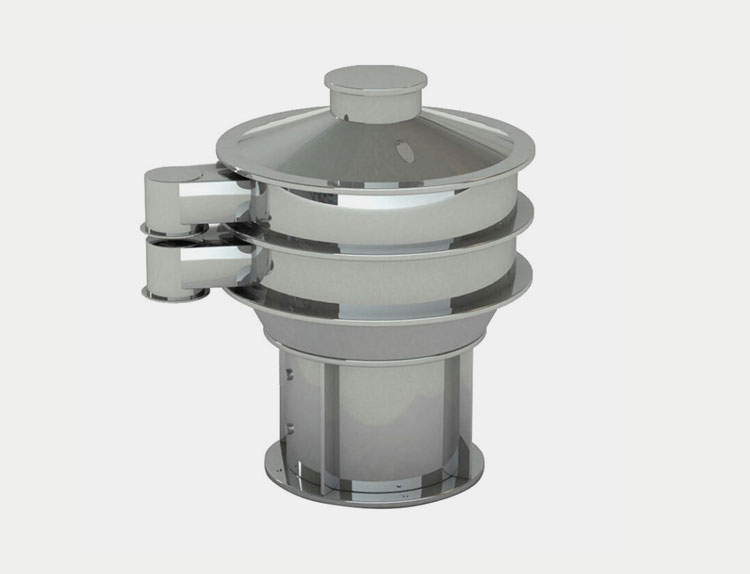
AIPAK high efficient screening machine
The granules are made to pass through a sieve or mesh or a specific desired size. The sieve or mesh screen has vibratory sifters, centrifugal sifters or rotatory screeners for oscillating the granules through the sieve. The sieve or mesh is of a specific size and it allows only the granules of that specific desired size to pass through it and move to next step.
The sieve or mesh screens come in different sizes. The commonly used size for tablets or capsules filling is 12-30 mesh which is about 500-1700 microns. Screening is important because it not only cancel out the larger than required particles but the very small particles are also removed which can cause poor flow property of the granules and cause capping during tablet compression.
The uniformity in granular size can have a major impact on the hardness and dissolution rate of the tablet. Screening is important to achieve the quality control standards and regulatory compliance during production.
Step 6: Final Blending With Lubricants:
Blending of powder
The final blending of powders is the last step before the compression of granules into tablets or filling of capsules. This is the stage where additives like lubricants, disintegrants and glidants are added to the granulated mixture. These additives enhance the quality of tablet.
Blending process:
First the granules are added into a blending container, which can be a V type blender, double cone blender or bin blender. The lubricants are added afterwards. The blending is done very gently to avoid any over lubrication of the granules.
This process of blending is carried out a slow speed and last about 2-5 minutes usually to ensure that the lubricants are distributed evenly throughout the granular mixture. The gentle blending also makes sure that it does not have any further effect on the tablet hardness.
The commonly used lubricants are:
| Magnesium steatrate:
It is the most commonly used lubricant. It gives high effect with a small quantity. It prevents the sticking of tablet and reduces friction among the granules. |

Picture courtesy: shutterstock |
| Talc:
It is a naturally occurring lubricant. It improves the flow property of granules. It acts as a glidants by decreasing the interparticle friction among granules. The capping and lamination defects of tablet are controlled by addition of talc. |

Talc lumps-Picture courtesy: anglo pacific minerals |
| Stearic acid:
Stearic acid is basically a kind of fatty acid, which acts as both a binder and a lubricant. It is used in formulations which are compatible with the fatty components. It not only lubricates but helps in the compression of tablet. It helps in formulation of cohesive granules and slow release dosage forms. |

Picture courtesy: ingredi |
| Sodium stearyl fumarate:
It is used in formulations which are sensitive to disintegration. It is water soluble hence preferred in high solubility formulations. The risk of slow drug dissolution is reduced by its addition. It maintains a fast disintegration of the tablet while keeping the tablet strength. |

Granular form of sodium stearyl fumarate |
The addition and blending of these lubricants is a very critical step. The over blending of the granules can cause poor hardness of the tablet and slowdown tablet disintegration. The under blending can cause sticking of tablet or inconsistent ejection during the tableting procedure. Hence, it is very important to keep a balance in every step performed.
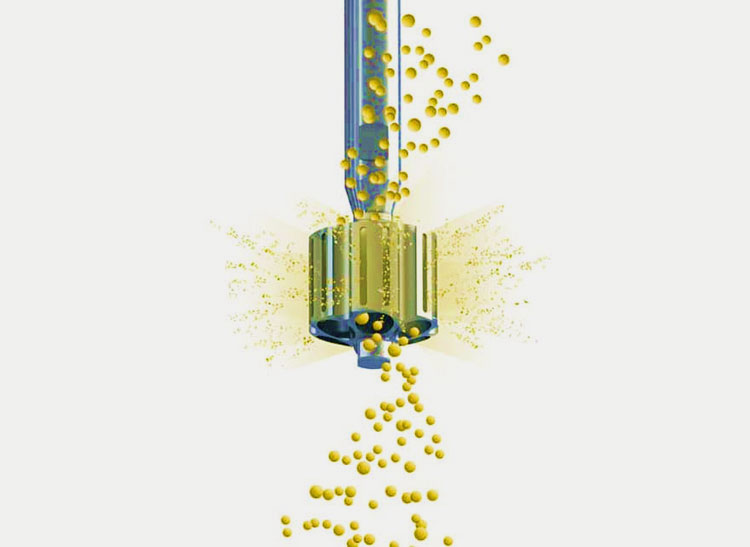
Step 7: Tablet Compression
Fine powder particles-picture courtesy: amixon
This is the stage where granules are ready to be compressed into final product. The finely blended and weighed granules after going through the process size reduction; screening and final blending are finally obtained in the desired properties and ready to be compressed into the tablets.
Compression process:
AIPAK tablet press machine
The compression of granules is done in tablet pressing machine. The granules are fed into the machine through the feeding hopper. The granular particles are flown down to a rotary press or single punch tablet press. The granules are compressed into tablet form under the high pressure exerted through two upper and lower punches of the machine.
The compressed tablets are ejected through the die cavity and collected from there. There are some main factors like compression force, pre compression and dwell time of the tablet which are controlled very critically to achieve a high quality tablet.
This final step marks the completion of dry granulation process flow chart and now at this stage the dry granulation process shows that the granule particles are ready to be compressed into tablets or filling in capsules or any other dosage form production.
3.Significance of dry granulation process flow chart process
Picture courtesy: elite exports
The dry granulation process has a major role in not only pharmaceutical manufacturing but many other manufacturing units. There are formulations which are moisture sensitive and cannot tolerate even a little amount of moisture which are only formed through dry granulation process. Dry granulation process flow chart provides high quality powder and granules by improving the flow properties, compressibility and uniformity of the powders which are essential for further processing of high quality.
The keys significances of dry granulation process flow chart are given below:
Ideal for moisture and heat sensitive formulations:
Moisture controlled dry powder
The moisture sensitive APIs and other ingredients can overcome the fear of hydrolysis or degradation in dry granulation process. There is no kind of solvent used throughout the dry granulation process flow chart, hence, no need of the drying step and exposing the products to heat.
The risk of chemical instability is also reduced which maintains the shelf life of chemically sensitive products. This process is also best suited with hygroscopic powders and granules which can absorbs moisture during wet granulation.
Enhanced powder flow and compressibility:
Improved compressibility through granulation
Dry granulation helps in converting the powders with poor flow properties into large and dense granules. This leads to enhanced flow property of the granules in tablet dies and easy processing. The granules with good flow properties have reduced segregation which improves the content uniformity. The granules formed through dry granulation produce stronger tablets due to enhanced compressibility.
Simple but energy efficient:
Picture courtesy: shutterstock
Dry granulation process is fast and effective. It has limited operation units but gives quality product at the end. Less operation time leads to a fast processing which not only reduce the mechanical force but reduce the operational cost as well. There is no consumption of thermal energy hence promoting a lean production and ideal for time sensitive cycles.
Scalable with industrial production:
Dry granulation on a larger scale-picture courtesy: Cambrian food
Dry granulation process flow can be easily integrated into large scale production. The roller compaction technique is best suited for large scale manufacturing. The automation friendly machines used in dry granulation process flow chart make it compatible with the advanced pharmaceutical technology. Dry granulation process is flexible enough to be customized for batch to batch performance and requirements.
Minimum material loss:
Different products of dry granulation process flow chart-picture courtesy: pacmoore
The major part of operations in the dry granulation is carried out in a closed system which reduce the cross contamination of the products and handling errors are reduced as well. This also ensures that a very minimum or no product is loss during the handling or transfer of the products.
The wet mixtures offer stick around the equipment which cause product wastage, dry handling means there are no chances of product sticking on the equipment and there is no crust formation on the equipment. All these factors lead to a better batch yield and minimized waste.
Complies with GMP and regulatory:
Picture courtesy: ERIKs
The less complicated and fewer operating units lead to a better control of the process. The absence of moisture minimizes the risk of microbial growth in the product. A brief procedure makes it easier for documentation control and steps validation. It fulfills the FDA and GMP requirements. The traceability is enhanced in less complicated procedures. The documentation is also simplified for audits and inspections.
Conclusion:
Now that you are well familiar with the dry granulation process flow chart, you can understand why it is a vital technique in the pharmaceutical and other manufacturing units. There are a lot of ingredients used in manufacturing which are moisture sensitive, dry granulation process flow chart provides a well suited environment for such products. This dry granulation process flow chart has well controlled and calculated steps which gives high quality consistent granules with uniform size. Irrespective of the method used in the dry granulation process flow chart, i.e., slugging or roller compaction, this process increase the production efficiency while keeping the product integrity intact. To know more about the process and the equipment used in this dry granulation process flow chart visit us at our AIPAK website.
Don't forget to share this post!
Granulator Machine Related Posts
Granulator Machine Related Products
Granulator Machine Related Videos
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 6426 8586
Want the best price & newest pharmaceutical machinery buying guide,tips and trends sent straightly to your box?Sign up for AIPAK’s monthly newsletter,we’re free for your consultation and Offer you the most suitable solutions!
The Buyer's Guide
- Capsule Filling Buyer's Guide
- Blister Packaging Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Counting Buyer's Guide
- Tube Filling Buyer's Guide
- Cartoning Buyer's Guide
- Gummy Making Buyer's Guide
- CO2 Extraction Buyer's Guide
- Empty Capsules Buyer's Guide
- Suppository Filling Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Coating Buyer's Guide
- Tablet Press Buyer's Guide
- Softgel Encapsulation Buyer's Guide
Most Popular
- 7 Importance Of Pharmaceutical Packaging In Different Applications You Must Know
- 6 Advantages You Must Know About Tablet Counting Machine
- 8 Advantages of Blister Packaging You Must Know
- 6 Critical Applications of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- 6 Stations You must Know to Improve the Filling Quality of Automatic Capsule Filling Machine